Cell2_Test_Key
advertisement

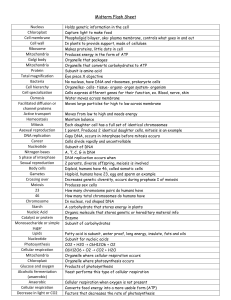
LIFE AND THE CELL UNIT TEST 2007 – PART 2 Part 1 – Energy and the Cell C6H1206 + ???? >>>>>>>>> 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy 1. What chemical process does the above formula represent? A) Decomposition B) Aerobic or Cellular Respiration C) Photosynthesis D) Carbonation (carbon dioxide production) 2. What is the other reactant (indicated by question marks above) needed for the reaction in order to get energy out of glucose (C6H12O6)? A) Water B) Carbon dioxide C) Oxygen D) ATP 3. Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis are both ways that organisms obtain: A) Oxygen B) Water C) Protein D) Energy 4. What process is happening in the cow? A. Decomposition B. Photosynthesis C. Nitrification D. Cellular Respiration 5. Which is not needed by the tree for photosynthesis? A. Chlorophyll B. Water C. Oxygen D. Carbon dioxide 6. We breathe oxygen A. To keep our brain neurons alert and active. B. For cellular respiration. C. For fermentation. D. To make the hemoglobin in our blood cells. 7. Which of these processes is not a characteristic of all life? A) Having cells B) Cellular Respiration C) Reproduction D) Sensing and reacting to the environment PART 2 CELL ORGANELLES 8. What cell part contains the genetic information (DNA) and is the control center for the entire cell? A) Chloroplast B) Nucleus C) Ribosome D) Mitochondrion 9. The outer boundary of all cells which controls movement of materials in and out of cell is the: A) Cell Wall B) Cytoplasm C) Endoplasmic Reticulum D) Cell Membrane 10. Which of the following organelles are only found in plant cells? A) Cell membrane and cell wall B) Cell wall and chloroplast C) Chloroplast and cell membrane D) Cell wall and mitochondria 11. Which cell part contains chlorophyll, the chemical that converts sunlight energy into the chemical energy of glucose? A) Mitochondrion B) ATP C) Ribosome D) Chloroplast 12. Which cell part requires a lot of oxygen because of the energy releasing process that occurs there? A) Chloroplast B) Nucleus C) Ribosome D) Mitochondrion 13. Plants do not need skeletons because plant cells have a A) chloroplast B) cell wall C) cell membrane D) mitochondrion PART 3 CHEMICALS OF LIFE 14. What organic chemical is used by animals to store energy? This is also the chemical that cell membranes are made of. A) water B) lipid C) protein D) carbohydrate 15. Which of the following is an organic chemical? A) H2O B) C12H22011 C) NH3 D) NaCl 16. What is the chemical that contains the genetic material which acts as the blueprint for the cell? It has a chemical code which assembles proteins to make our cells. A) ATP B) protein C) lipid D) DNA PART 4 17. In the example below, which statement would be most correct? (“W” represents a molecule of water.) W W W W Outside of the Cell W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W W Inside of the Cell W W W W W W W W W W W W A) Water will move out of the cell by osmosis. B) Water will move out of the cell by passive transport. C) Water will move into the cell by osmosis. D) Water will move into the cell only with an input of energy. 18. Which best describes the effect of adding salt water to plants? A) Salt will enter the cells through the cell membrane. Once in the cells the salt will cause the mitochondria to malfunction, killing the plant. B) The salt water is an acid and will kill the cells. C) The greater water concentration now in the cell will cause water to diffuse out of the cells, thus killing the cell. D) The greater water concentration now outside the cell will cause water to diffuse into the cells, thus causing them to burst. 19. Which best describes the process of mitosis? A) In mitosis, cells divide in half. B) In mitosis, chromosomes containing DNA copy and separate, forming 2 cells. C) In mitosis, the mitochondria line up and split. Then a new cell membrane forms, creating 2 new cells. D) In mitosis, cells grow and reproduce when the chloroplasts line up and separate. 20. Bacteria are prokaryotes because A) They are simple cells with no cell membrane. B) They have very few cell parts and no DNA. C) They have ribosomes and chromosomes. D) They are simple cells with a cell membrane and no nucleus. 21. Which of the following are eukaryotic cells? A. bacteria and fungi B. bacteria and protists C. bacteria and plants D. protists and animals 22. Mitosis is a part of A. growth and reproduction. B. osmosis and diffusion. C. photosynthesis and respiration. D. decomposition and nitrification. PART 5 BCR Choice: Select one of the three Why are aerobic respiration and photosynthesis considered opposite? In answering the question: Make it clear that you know what both processes are. State clearly their role in organisms obtaining energy. Indicate clearly why the two processes are opposite to one another. Cite the reactants (what is needed) and products (what is produced) in each process to support your answer. Use your best science vocabulary. (Limit: 11 lines on your paper) Exemplary Answer: Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are opposite ways that organisms obtain energy. In photosynthesis organisms trap sunlight with chlorophyll and covert it to chemical energy in glucose molecules. They use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose and produce oxygen as waste. Respiration is the opposite chemical process; in this process organisms break the glucose apart to release this stored energy. Respiration breaks the glucose down into carbon dioxide and water, the same chemicals that photosynthesis started with. Respiration begins with glucose and oxygen, what photosynthesis ended with. They are thus opposite reactions, photosynthesis using energy to make glucose, respiration breaking the glucose up to release the energy. # 2 – Compare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. In answering the question: Explain the difference between the 2 cell types. Explain how they have a different level of complexity. Give examples of organisms having each cell type. Exemplary Answer: Prokaryotic cells were probably the first cells, and they are much simpler than eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. Their DNA floats around loose in the cell. These cells have few cell parts and are much smaller than “regular” cells. Bacteria are the organisms with prokaryotic cells, and they are all simple, unicellular organisms. Protists, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. These have a nucleus containing the DNA and usually many more cell parts. # 3 – Explain why DNA is the key to life. In answering the question: Explain what DNA is. Show how its characteristics relate to the characteristics of life. (In other words, why does what DNA can do make the characteristics of life possible?) Exemplary Answer: DNA is the key to life because it makes life possible. Growth and reproduction are the key activities that are unique to life, and DNA makes them possible. The DNA molecule can duplicate itself, and this allows the duplication of the cell that we see in mitosis. Organisms can thus grow by adding new cells and reproduce by creating a new cell to begin a new life. DNA has the code for building proteins, the building blocks of life. Thus the very creation of a cell depends totally on DNA. It can duplicate itself and then has the code to build a new cell around it.