Regents Review
advertisement

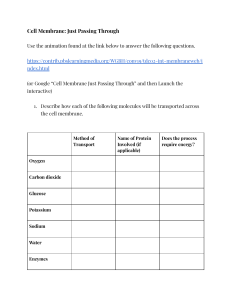
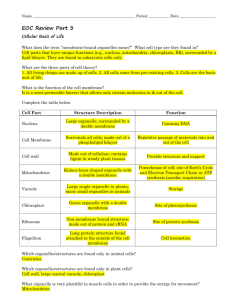
Good Things to Remember… Living Environment 2010-2011 1. Scientific Method: a. Experimental Design: hypothesis, independent variable, dependent variable, control, variables, graph (axes) 2. Cells: a. Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic (your cells are eukaryotic, Pro= bacteria-not much organelles inside cell) b. Plant vs. Animal i. Shape ii. Organelles c. Organelles-know function, shape i. Ribosome ii. Mitochondria iii. Nucleus iv. Vacuole v. Chloroplast vi. Cell membrane/plasma membrane d. Diffusion Through a Membrane Lab i. Onion cells-salt water shrink, regular water-swell ii. Small molecule can diffuse (glucose, iodine, water, oxygen, carbon dioxide) 3. Cell Respiration and Photosynthesis a. CR: i. Mitochondria ii. Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP (energy) iii. Takes place in all cells b. Photo: i. Chloroplast ii. Carbon dioxide + water (sunlight/energy)= glucose + oxygen iii. Only in plant cells 4. Enzymes a. Catalyst that speed up chemical reaction. b. Temp/pH/concentration will have an affect c. Lock and Key Method 5. Body System: Respiratory, Circulatory, Digestive, Nervous, Endocrine, Muscular, Skeletal, Excretory- work together to maintain homeostasis!! a. General Function b. Diagram c. Disease/Disorder 6. Genetics! a. Mitosis vs. Meiosis b. Sexual vs. Asexual reproduction c. Diagrams d. Structure of DNA and RNA e. Transcription/Translation/Replication-nucleus then ribosomes f. Universal Genetic Code Chart (they will give it to you but you need to know how to use it!) to code for amino acids g. Genetic Engineering h. Recombinant DNA i. Restriction enzymes (cut DNA) j. Electrophoresis 7. Evolution a. Natural Selection b. Evolutionary Trees-diagrams and how to read them c. Evidence of Evolution- comparative anatomy, DNA, embryology, vestigial structures d. Beaks of Finches Lab!! 8. Ecology: a. Autotroph vs. hetertroph b. Biodiversity c. Food chains/food web/energy pyramids d. Producers/consumers-herbivores, carnivores, decomposers, etc. e. Succession f. Symbiotic Relationships-mutualism, commensalism, parasitism g. Human Ecology i. Greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide-b/c of cars, deforestation ii. Pollution- causes acid rain iii. Invasive species iv. Renewable vs. nonrenewable resources 9. Lab Techniques: a. Microscopes b. Diffusion Through a Membrane c. Beaks of Finches d. Chromatography e. Electrophoresis f. Metric conversation g. Reading a graduated cylinder