photo_resp_replic_cancer_vocab
advertisement

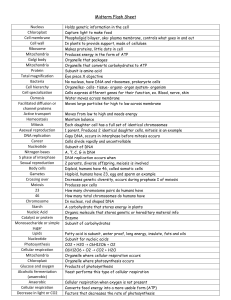
Suggested Method for Vocabulary Mastery Word Definition Picture Vocabulary Autotroph – organisms that creates organic carbon (food) Heterotroph – organism that gets energy from organic carbon ( Food chain – transfer of energy between organisms. Beginning with producers and ending with decomposers. Trophic levels – organisms at energy levels within an ecosystem Photosynthesis – carbon dioxide plus water with sunlight yields sugar and oxygen Xylem – plant tissue that moves water from roots to leaves Phloem – moves sugar and other compounds throughout the plant (both ways) Stomata – small openings in underside of leaves. CO2 in water vapor and O2 out Guard cell – opens and closes the stomata Chlorophyll – pigment in the chloroplast. Absorbs radiation. Reflects green Pigments – compounds that absorb visible light Chloroplast – organelle in the cell of plants where photosynthesis happens ROYGBIV – colors of the visible light spectrum Respiration – glucose plus oxygen yields carbon dioxide plus water plus ATP Cytoplasm Mitochondria – organelle in cell that breaks down pyruvate into CO2 water and ATP, Glycolysis – breakdown of glucose by an enzyme in cytoplasm Fermentation – making energy without using oxygen ATP – adenosine triphosphate, energy currency Cell Division – cell divides into two daughter cells Cell Cycle – lifecycle of a cell Interphase – cells grows readies for division. DNA replication Prophase – centrioles move to opposite sides Metaphase – chromosomes line up with spindle fibers attached Anaphase – chromosomes separate, spindle fibers shorten Telophase - furrow develops and cells begin to divide. Nuclear envelope reforms Cytokinesis – organelles reproduce, cell is divided DNA replication - copying DNA Nucleotide - nitrogen base, phosphate group, sugar Codon – 3 nucleotides, codes for an amino acid that make protein. Base pairing – A:T and C:G Chromosome – structure in nucleus that hold DNA Chromatid – one half of the chromosome Virus – DNA that infects other cells, Bacteriophage – virus that affects bacteria Lytic – virus that injects DNA and reproduces immediately Lysogenic – virus DNA becomes part of host cell Cancer – mutated cells, reproduce abnormally and fast Mutations – changes in DNA that damage the cell Tumor – abnormal growth Radiation – using radiation to kill cells Chemotherapy – treatment with pharmaceuticals Surgery – Key Concepts Photosynthesis Changes in CO2 and O2 in leaves In the dark plants do respiration In the light plants do photosynthesis Pigments and Visible light spectrum Many pigments allow plants to absorb more of the visible light spectrum Light dependent, light independent Respiration Fermentation – less efficient, anaerobic