Year 11 Biology Revision - Microbes
advertisement

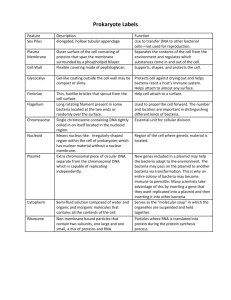
Year 11 Biology Revision These tasks are designed for you to test yourself and see if you can do each of the objectives for this topic. These objectives are listed on page 48-49 in your yellow workbooks. Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Culture bacteria and fungi following correct procedures, including the safe disposal of plates. Put these steps in the correct order to explain how to culture a colony of bacteria: 1. As quickly as possible wipe the cotton bud over the surface of the agar 2. Place the agar plate at room temperature for 2 or 3 days 3. Wipe a sterile cotton bud over the surface your shoe 4. Lift the lid of a sterile agar plate 5. Replace the lid on the agar plate, tape it on and turn the plate upside down State the one safe way to safely dispose of the plate once it is finished with. Objective: Plot and interpret a bacterial growth curve Task 1: Plot a line graph of bacteria numbers vs time. Time (mins) 0 20 40 60 80 100 No. of bacteria (x1000) 20 40 80 160 320 640 120 140 160 180 200 1280 2560 2540 2500 2460 Task 2: Bacteria can double their numbers every 20 minutes or so. Give 2 possible reasons why the number of bacteria starts to decrease after 140 minutes? Objective: Task 1: Draw and label a typical fungus using the terms hyphae, sporangium and spores Draw a diagram of a fungus. Put these labels correctly onto your diagram: hyphae, sporangium, spores Circle the conditions that are required for a fungus to grow: Plenty of light Food Agar Insects to carry spores Moisture Warmth Dirt Dryness Carbon dioxide Antiseptic Task 2: Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Objective: Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Task 3: Draw and label a typical virus and draw a diagram of the main stages of it’s replication cycle Draw a diagram of a virus. Put these labels correctly onto your diagram: protein sheath, nuclear material Explain how a virus replicates using a labelled diagram Draw and label a typical bacterium. Draw a diagram of a bacterium. Put these labels correctly onto your diagram: flagellum, capsule, cell membrane, nuclear material Match the part with it’s function: Part Function Flagellum controls the functions of the cell Capsule Helps the bacteria move around Cell membrane Protects the bacteria from toxins Nuclear material Controls the movements of substances in and out of the bacteria Compare and contrast feeding, reproduction and size of typical bacteria, fungi and viruses Describe extra-cellular digestion Explain the meaning of “extra-cellular digestion”. Which group(s) of microbes reproduce this way? Define the term “saprophyte” Task 4: Use a diagram to explain what binary fission is. Objective: Name some harmful and useful micro-organisms Task 1: Complete the table: Organism Helpful example Bacteria Harmful example Fungi Viruses Task 2: Define the term “pathogen” Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Task 3: Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic respiration Complete the equation for aerobic respiration: Glucose + oxygen Complete the equation for anaerobic respiration: Glucose Give an example of where each of these could occur. Objective: Task 1: Describe ways of reducing the spread of disease Disease can be spread by contact, droplet infection (eg sneezes and coughs), body fluids (blood, semen, saliva etc) or vectors (eg insects, rats, cockroaches etc). For each of these ways, describe what could be done to prevent this spread occurring. Match the chemical with it’s use: Chemical Used for Disinfectant killing bacteria inside the body Antiseptic killing bacteria on the body Antibiotic killing bacteria on surfaces Task 2: Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Describe how micro-organisms are used in food production Yoghurt is a food that contains a bacterial culture. Explain why the bacteria are necessary to produce yoghurt. Beer is made using yeast, which is a type of fungus. Name the process carried out by the yeast cells that produces alcohol and carbon dioxide gas. Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Describe the structure of DNA Sketch the shape of a DNA molecule. What sort of chemical do the letters A, T, C, G represent? (you do not need to give their specific names.) Objective: Task 1: Describe the relationship between chromosomes, DNA, genes and alleles True or false: DNA is a long molecule which makes up our genetic information An allele is a pair of chromosomes A gene is a section of chromosome that codes for a particular trait (characteristic) A chromosome is a long length of DNA consisting of many genes. Objective: Task 1: Describe sexual reproduction in terms of gamete production (halving of chromosome number), fertilisation (regaining the full chromosome number), and zygote formation Complete the diagram: Ovaries Meiosis eggs 46 chromosomes ? chromosomes Fertilisation zygote ? chromosomes Testes Meiosis sperm ? chromosomes ? chromosomes Objective: Task 1: Describe the function of X and Y chromosomes Describe the gender of people with the following chromosomes a) XX b) XY Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Distinguish between meiosis and mitosis List 3 differences between meiosis and mitosis Give an example of a place in he body where each would occur Objective: Task 1: Define the following terms: gamete, gene, zygote, chromosome, mitosis, meiosis Match the term with it’s definition Term Definition Gamete Cell division which produces identical cells to the parent cell Gene A section of DNA that codes for a particular trait Zygote A fertilised egg cell Chromosome One form of a gene Mitosis A sex cell (egg or sperm) Meiosis Cell division process that halves the chromosome number Allele A long molecule that contains genetic information DNA A long piece of DNA that consists of many genes found in the nucleus of cells Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Understand the importance of meiosis for producing variation in offspring Why is it important to have variation in a species During which stage of meiosis does the variation occur? Objective: Define the following terms: genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, allele, dominant, recessive, punnet square, pedigree chart, pure breeding Task 1: Term Genotype Phenotype Definition Two different alleles An allele which is expressed if it is present Objective: Task 1: Objective: Task 1: Task 2: Homozygous Heterozygous Allele Dominant Recessive Punnet Square Pedigree Chart Pure breeding A possible combination of alleles One form of a gene An allele which is expressed if there is no other to mask it The physical traits shown by an organism A way to work out possible genotypes of offspring Two identical alleles A diagram which shows the characteristics of a number of generations Organisms which always produce the same characteristic through generations Construct monohybrid crosses (punnet squares) to show the expected phenotype and genotype ratios in the offspring If a homozygous recessive black winged fruit fly breeds with a heterozygous grey winged fruit fly: a) what proportion of their offspring will have black wings? b) What proportion of their offspring will be homozygous dominant? Explain examples of the contemporary application of genetics such as selective breeding of plants and animals, cloning and genetic modification Select one application of genetics you studied and describe how it could benefit humans Select another application of genetics you studied and describe any potential problems that may be caused by this technology.