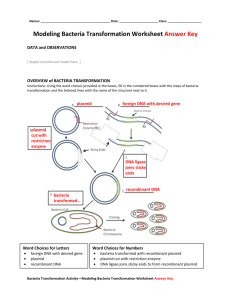
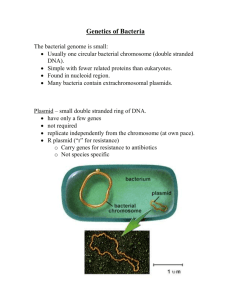
Prokaryote Labels
advertisement
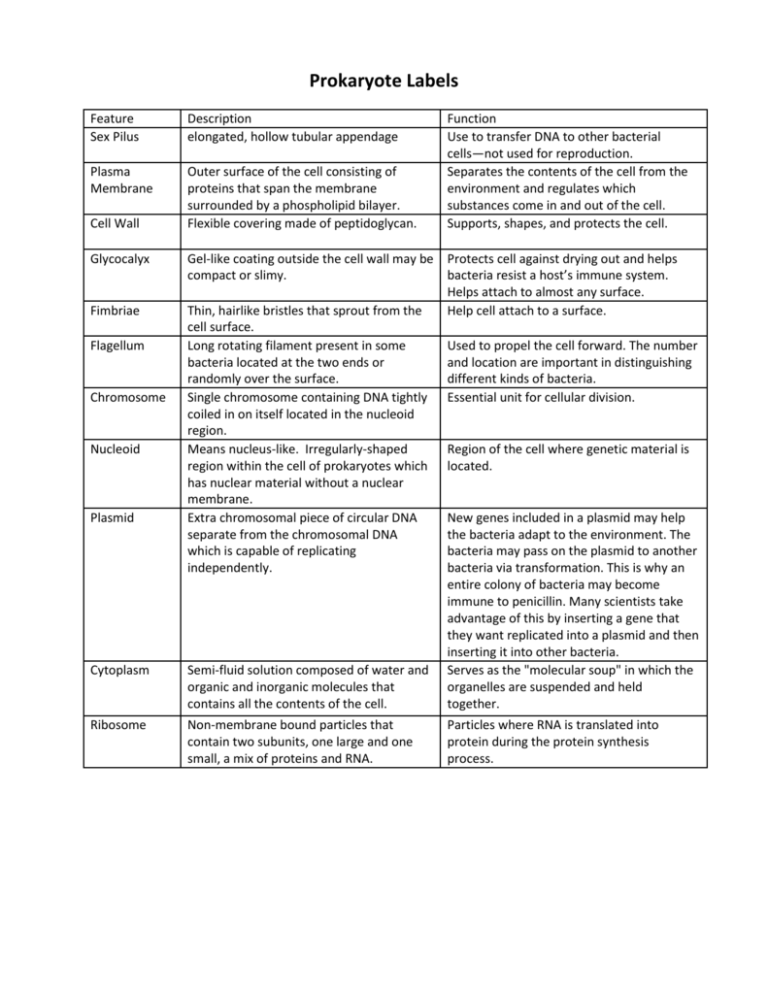
Prokaryote Labels Feature Sex Pilus Description elongated, hollow tubular appendage Plasma Membrane Outer surface of the cell consisting of proteins that span the membrane surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer. Flexible covering made of peptidoglycan. Cell Wall Glycocalyx Fimbriae Flagellum Chromosome Nucleoid Plasmid Cytoplasm Ribosome Function Use to transfer DNA to other bacterial cells—not used for reproduction. Separates the contents of the cell from the environment and regulates which substances come in and out of the cell. Supports, shapes, and protects the cell. Gel-like coating outside the cell wall may be Protects cell against drying out and helps compact or slimy. bacteria resist a host’s immune system. Helps attach to almost any surface. Thin, hairlike bristles that sprout from the Help cell attach to a surface. cell surface. Long rotating filament present in some Used to propel the cell forward. The number bacteria located at the two ends or and location are important in distinguishing randomly over the surface. different kinds of bacteria. Single chromosome containing DNA tightly Essential unit for cellular division. coiled in on itself located in the nucleoid region. Means nucleus-like. Irregularly-shaped Region of the cell where genetic material is region within the cell of prokaryotes which located. has nuclear material without a nuclear membrane. Extra chromosomal piece of circular DNA New genes included in a plasmid may help separate from the chromosomal DNA the bacteria adapt to the environment. The which is capable of replicating bacteria may pass on the plasmid to another independently. bacteria via transformation. This is why an entire colony of bacteria may become immune to penicillin. Many scientists take advantage of this by inserting a gene that they want replicated into a plasmid and then inserting it into other bacteria. Semi-fluid solution composed of water and Serves as the "molecular soup" in which the organic and inorganic molecules that organelles are suspended and held contains all the contents of the cell. together. Non-membrane bound particles that contain two subunits, one large and one small, a mix of proteins and RNA. Particles where RNA is translated into protein during the protein synthesis process.