Pretest
advertisement

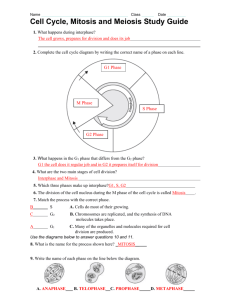
Name: _____________________________ Matching: Pretest Score: _____/61 Posttest Score: _____/61 Ch 10+ Pretest: Cell Growth and Division 1. _____ Having the normal number of A. anaphase chromosomes, 2n. 46 for humans B. autosome 2. _____ When homologous chromosomes have C. binary fission replicated and paired up, this forms D. chromatid 3. _____ Stage where the centromere splits and E. chromatin sister chromosomes move to opposite F. chromosome sides of a cell G. crossing over 4. _____ Stage outside of cell cycle for cells that H. cytokinesis do not divide, e.g. nerve cells. I. diploid 5. _____ Exchange of DNA from one chromosome J. DNA to its homolog, usually occurs during K. G0 phase prophase I of meiosis L. G1 and G2 phases 6. _____ Final stage of cell division, chromosomes M. haploid are separated and nucleus reforms N. homologous chromosome 7. _____ Cell division where gametes form, O. interphase daughter cells are haploid P. M phase 8. _____ A “regular” chromosome, does not Q. meiosis determine gender, come in pairs R. metaphase 9. _____ Chemical that is the basis of all life, S. mitosis contains instructions for cell functions T. prophase 10. _____ Pairs of chromosomes that have the same U. S phase genes and same shape V. sex chromosome 11. _____ A time in the cell cycle when the cell is W. telophase functioning normally, i.e. nothing X. tetrad special is happening 12. _____ A single copy of a chromosome, 2 of them are joined at the centromere together during cell division 13. _____ Cell division where identical cells are made, daughter cells are diploid 14. _____ The stage of cell division where the contents of the cytoplasm are divided 15. _____ The time in the cell cycle where DNA is replicated in preparation for dividing 16. _____ Stage of cell division where chromosomes line up in the center of the cell 17. _____ A complete set of genetic material; copies itself during cell division; humans have 46 of them, DNA is “wound up.” 18. _____ Stage of cell division where the nucleus breaks down, and chromosomes become visible 19. _____ Process of cell division for prokaryotes 20. _____ X or Y chromosome, two of them together determine gender 21. _____ Stages in the cell cycle, not usually considered cell division. The cell is growing and performing specialized functions 22. _____ Half the number of chromosomes, 23 for humans; products of meiosis contain this number 23. _____ Form of DNA that is “unwound” long, thin strands. 24. _____ Stage in the cell cycle where the cell divides; really two separate events, mitosis and cytokinesis 25. – 30. Draw the cell cycle with correct relative sizes of each stage. Label each stage and include G0 and interphase. Draw a cell in each stage of the cell cycle. Use 2n = 6 (diploid number of 6) 31. Interphase: 32. Prophase: 33. Metaphase: 34. Anaphase: 35. Telophase: Label each of the following stages of Meiosis and identify each as haploid or diploid 36. ___________________ 37. ___________________ 38. ___________________ 39. ___________________ 40. ___________________ 41. ___________________ 42. ___________________ 43. ___________________ Short answer: 44. - 47. Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis by naming at least 2 similarities and 2 differences between the two processes. 48. – 51. Compare and contrast cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryoes by naming at least 2 similarities and 2 differences between the two processes. 52. – 57. DNA takes many forms during the cell cycle. Explain/describe these forms and give an example of when in the cell cycle they can be found. Chromatin: Chromatid: Chromosome: 58. – 61. Differentiate (tell the difference) between sexual and asexual reproduction. Explain whether each of the following is associated with sexual or asexual reproduction: mitosis, meiosis, binary fission. Original images: http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/n100/2k4ch9meiosisnotes.html