Second Grade Science Pacing Guide
advertisement

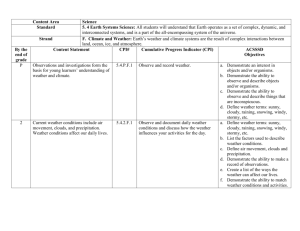
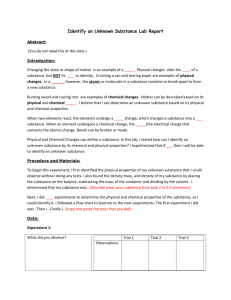
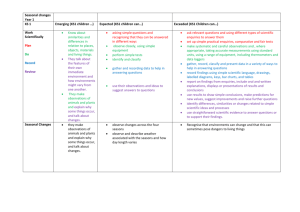
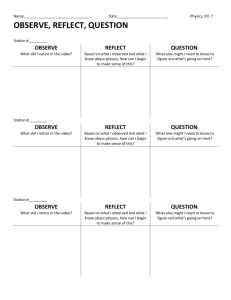
Second Grade Science Pacing Guide First 9 weeks Red: change made during 2010 standards Blue: Resource that you can use from VDOE Green: where an I-STEM unit is in place to support that SOL strand 2.1 The student will demonstrate an c) observations are repeated f) time is measured using the i) data are analyzed, understanding of scientific reasoning, to ensure accuracy; proper tools; and unexpected or logic and the nature of unusual quantitative science by planning and conducting d) two or more characteristics g) conditions that influence a data are recognized; investigations in which or properties are used to change are identified and classify items; inferences are made; j) conclusions are a) observations and predictions are made drawn and questions are formed; e) length, volume, mass, and h) data are collected and temperature are measured in recorded, and bar graphs are k) observations and b) observation is differentiated from metric units and standard constructed using data are personal interpretation; English units using the numbered axes; communicated proper tools; Unit Observing and Classifying Life Cycles of Animals *Students were introduced to living and non-living in K.6 *Students learned about the basic needs and life processes of animals in K.7 SOL by number and letter 2.1 2.4 a 2.5 a 2.7 a- monarch butterfly migration, significance of the seasons on animal life cycles Enhanced Scope and Sequence connection Observe & Classify Looking at Life Cycles (painted lady caterpillars and ‘house’ supplied to 2nd grade teachers) *2nd Grade Integrated Animals Unit Suggested Topics: *Unit Introduction *Topic 1- "What Makes Something Alive?" *Topic 4- "What is a Life Skills l) simple physical models are designed and constructed to clarify explanations and show relationships.; and m) current applications are used to reinforce science concepts. Essential Observe, Compare, contrast, describe, predict, classify, Vocabulary Change, Classify, Life cycle, egg, adult, tadpole, caterpillar, larva, pupa, frog, butterfly, living, nonliving, water, food, space, shelter, system, white-tailed deer, mealworm, metamorphosis, mature, mantis, yearlings, fawn, buck, doe, lifespan, organisms, dependent Cycle?" Weather (ongoing) -Discuss transition from summer to fall and changes that occur - See specific vocabulary for this 9 weeks regarding weather Unit Habitats I STEM unit: Wiggling Worms 2.1 2.6 SOL by number and letter 2.5 2.8 c Backyard Weather Collecting Weather Data Making Weather Instruments Enhanced Scope and Sequence connection There’s No Place Like Home *2nd Grade Integrated Animals Unit Suggested Topics: *Topic 3 "What is a Habitat?" *Topic 5- "What is a Food Chain?" Observe, record, compare, describe, construct chart, Skills Temperature, wind, precipitation, rain, sunny, cloudy, thermometer, hurricanes, thunderstorms, frost, fog, flood Essential Observe, compare and contrast different ways animals use plants as homes/shelters, describe, construct and interpret models of different habitats, construct and interpret a chart illustrating plant foods consumed by different animals (food web) Vocabulary Oxygen, food, water, home, shelter (cover), habitat, forest, stream, system, dependent, living, non-living, fossils Second Grade Science Pacing Guide Second 9 weeks 2.1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific reasoning, logic and the nature of science by planning and conducting investigations in which a) observations and predictions are made and questions are formed; b) observation is differentiated from personal interpretation; Unit Animal & Plants adaptations c) observations are repeated to ensure accuracy; f) time is measured using the proper tools; d) two or more characteristics or properties are used to classify items; g) conditions that influence a change are identified and inferences are made; e) length, volume, mass, and temperature are measured in metric units and standard English units using the proper tools; h) data are collected and recorded, and bar graphs are constructed using numbered axes; SOL by number and letter 2.7 a Enhanced Scope and Sequence connection What Changes When the Seasons Change? i) data are analyzed, and unexpected or unusual quantitative data are recognized; j) conclusions are drawn k) observations and data are communicated Skills 2.1 Let’s Find the Mass m) current applications are used to reinforce science concepts. Essential Vocabulary Observe, compare, construct model, identify, evaluate Migration, hibernation, camouflage, dormancy, behavior Observe, record, Matter, volume, mass, *2nd Grade Integrated Animals Unit Suggested Topics: *Topic 6- "How Do Animals Adapt to Survive?" Matter – measuring mass & volume l) simple physical models are designed and constructed to clarify explanations and show relationships.; and 2.3 b Matter - Solid, Liquid, and Gas 2.1 2.3 a, c Are all Containers Created Equal? (suggest water play with cups/containers of different volume) The Water Cycle Disappearing Water measure volume, measure mass, Backyard Weather Collecting Weather Data Making Weather Instruments Observe, record, compare, describe, construct chart, evaluate Classify, describe, compare, contrast, examine, identify, design I-STEM unit: Keep it cool Weather (ongoing) Discuss transition from fall to winter and the changes that occur 2.1 2.6 Second Grade Science Pacing Guide Third 9 weeks weight, kilogram, gram, pound, liter, milliliter, ounce, cup, gallon, metric, standard English units Solid, liquid, gas, ice, steam, water, matter, Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, melting, freezing, physical change, phase Temperature, wind, precipitation, ice (sleet & hail), snow, sunny, cloudy, thermometer, blizzards 2.1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific reasoning, logic and the nature of science by planning and conducting investigations in which a) observations and predictions are made and questions are formed; b) observation is differentiated from personal interpretation; Unit Magnets **moved from end of year** c) observations are repeated to ensure accuracy; f) time is measured using the proper tools; d) two or more characteristics or properties are used to classify items; g) conditions that influence a change are identified and inferences are made; e) length, volume, mass, and temperature are measured in metric units and standard English units using the proper tools; h) data are collected and recorded, and bar graphs are constructed using numbered axes; SOL by number and letter Enhanced Scope and Sequence connection k) observations and data are communicated Skills l) simple physical models are designed and constructed to clarify explanations and show relationships.; and m) current applications are used to reinforce science concepts. Essential Magnetic Fishing North and South Poles Which Way is North? Magnetic Barbershop Observe, record, compare, describe, construct chart, Use a magnetic compass, predict, conduct, identify, classify 2.1 2.6 Backyard Weather Collecting Weather Data Making Weather Instruments Observe, record, compare, contrast, describe, construct chart I-STEM Unit: Magnificent Magnetic Race Cars Transition from winter to spring and changes that occur j) conclusions are drawn 2.1 2.2 Students are introduced to attract and repel in K. 3 Weather i) data are analyzed, and unexpected or unusual quantitative data are recognized; Vocabulary Compass, direction North, South, attract, repel, poles, magnetic, nonmagnetic, iron, nickel, metal, natural magnet (lodestone or magnetite), artificial magnets, magnetism Temperature, wind, precipitation, rain, ice (sleet & hail), snow, sunny, cloudy, thermometer, rain gauge, weather vane, tornadoes, thunderstorms, drought, flood Second Grade Science Pacing Guide Fourth 9 weeks 2.1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific reasoning, logic and the nature of science by planning and conducting investigations in which a) observations and predictions are made and questions are formed; b) observation is differentiated from personal interpretation; Unit Weathering, Plants & Erosion Plants c) observations are repeated to ensure accuracy; f) time is measured using the proper tools; d) two or more characteristics or properties are used to classify items; g) conditions that influence a change are identified and inferences are made; e) length, volume, mass, and temperature are measured in metric units and standard English units using the proper tools; h) data are collected and recorded, and bar graphs are constructed using numbered axes; SOL by number and letter 2.1 2.7 a,b 2.8 d 2.1 2.4 b 2.5 a 2.7a 2.8 a,b Enhanced Scope and Sequence connection none We Need Plants! 2.4 b – none – suggest fast grow plants. Examine seeds, flowers & fruits i) data are analyzed, and unexpected or unusual quantitative data are recognized; j) conclusions are drawn k) observations and data are communicated Skills l) simple physical models are designed and constructed to clarify explanations and show relationships.; and m) current applications are used to reinforce science concepts. Essential Model, compare, contrast, construct, interpret Observe, Compare, contrast, describe, predict, classify, list, construct models, construct charts, identify, interpret Vocabulary Weathering, rocks, soil, erosion, roots, surface Flower, fruit, seed, stem, pollen, roots, leaves, blossom, soil Dependent, growth, change, seasons, product, fiber, cotton, I-STEM unit: Plant Cycle Project Weather Transition from spring to summer and the changes that occur 2.1 2.6 Backyard Weather Collecting Weather Data Making Weather Instruments Observe, record, compare, describe, construct chart, oil, spices, lumber, rubber, medicines, and paper, oxygen, food, peanuts, soybeans, apples, evergreens Temperature, wind, precipitation, rain, sunny, cloudy, thermometer, rain gauge, weather vane, tornadoes, thunderstorms, drought, flood