Sci Template5.4.F
advertisement
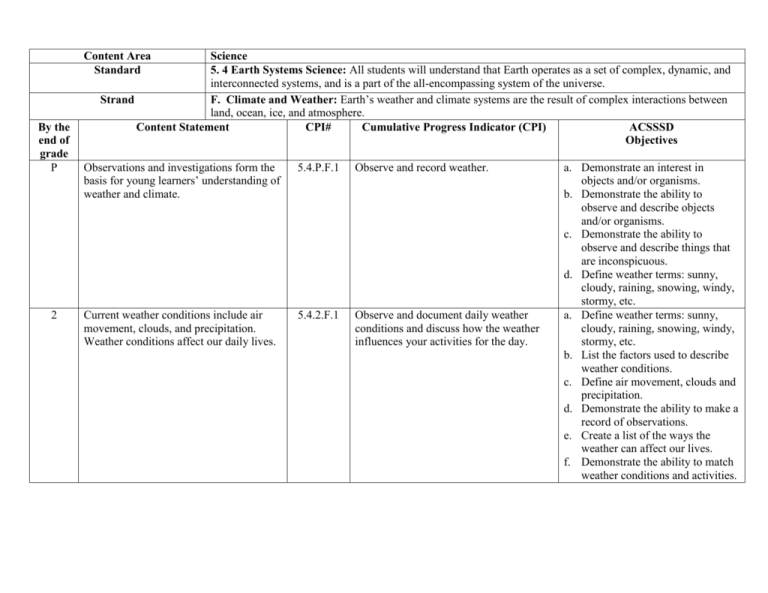
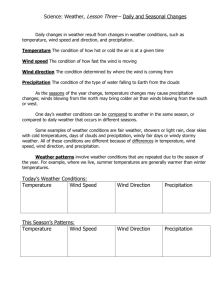
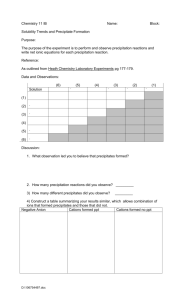
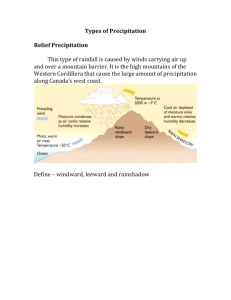
Content Area Standard By the end of grade P 2 Science 5. 4 Earth Systems Science: All students will understand that Earth operates as a set of complex, dynamic, and interconnected systems, and is a part of the all-encompassing system of the universe. F. Climate and Weather: Earth’s weather and climate systems are the result of complex interactions between Strand land, ocean, ice, and atmosphere. Content Statement CPI# Cumulative Progress Indicator (CPI) ACSSSD Objectives Observations and investigations form the basis for young learners’ understanding of weather and climate. 5.4.P.F.1 Observe and record weather. Current weather conditions include air movement, clouds, and precipitation. Weather conditions affect our daily lives. 5.4.2.F.1 Observe and document daily weather conditions and discuss how the weather influences your activities for the day. a. Demonstrate an interest in objects and/or organisms. b. Demonstrate the ability to observe and describe objects and/or organisms. c. Demonstrate the ability to observe and describe things that are inconspicuous. d. Define weather terms: sunny, cloudy, raining, snowing, windy, stormy, etc. a. Define weather terms: sunny, cloudy, raining, snowing, windy, stormy, etc. b. List the factors used to describe weather conditions. c. Define air movement, clouds and precipitation. d. Demonstrate the ability to make a record of observations. e. Create a list of the ways the weather can affect our lives. f. Demonstrate the ability to match weather conditions and activities. 4 Weather changes that occur from day to day and across the seasons can be measured and documented using basic instruments such as a thermometer, wind vane, anemometer, and rain gauge. 5.4.4.F.1 6 Climate is the result of long-term patterns of temperature and precipitation. 5.4.6.F.2 Identify patterns in data collected from basic weather instruments. a. Define weather, day, season and measure. b. Identify ways to take and record measurements. c. Demonstrate the ability to take and record measurements. d. Demonstrate the ability to identify patterns in data. e. Demonstrate the ability to use one basic weather instrument to record data. f. Create a record of data collected using one basic weather instrument. Create climatographs for various locations a. Define weather, climate, around Earth and categorize the climate temperature, precipitation and based on the yearly patterns of climatograph. temperature and precipitation. b. Demonstrate an understanding of the difference between weather and climate. c. Demonstrate the ability to create a bar graph. d. Demonstrate the ability to create a line graph. e. Demonstrate the ability to measure and record temperature. f. Demonstrate the ability to measure and record precipitation. g. Identify the factors that combine and affect an areas climate. h. Identify the Earth’s major climate categories. i. List the characteristics of each major climate. 8 Climate is influenced locally and globally by atmospheric interactions with landmasses and bodies of water. 5.4.8.F.2 12 Climate is determined by energy transfer from the Sun at and near Earth’s surface. This energy transfer is influenced by dynamic processes, such as cloud cover and Earth’s rotation, as well as static conditions, such as proximity to mountain ranges and the ocean. Human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, also affect the global climate. 5.4.12.F.2 Explain the mechanisms that cause varying daily temperature ranges in a coastal community and in a community located in the interior of the country. a. Identify the factors that influence daily temperature. b. Identify the factors that influence climate. c. List the conditions and features that make a community “coastal”. d. List the conditions and features that make a community “interior”. e. Demonstrate the ability to identify environmental features (oceans, mountains) in a picture or on a map. Explain how the climate in regions a. Define climate, region, weather throughout the world is affected by and energy transfer. seasonal weather patterns, as well as other b. Identify the Earth’s regions. factors, such as the addition of greenhouse c. Identify the Earth’s major climate gases to the atmosphere and proximity to categories. mountain ranges and to the ocean. d. List the characteristics of each major climate. e. Identify the factors that combine to affect an areas climate. f. Identify the dynamic processes that influence energy transfer. g. Explain how “greenhouse gases” are formed. h. Explain how “greenhouse gases” affect the global climate.