Ch 8-11 Review
advertisement

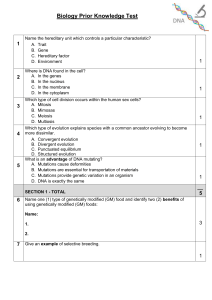
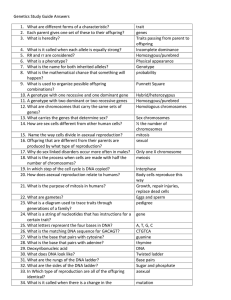
1. Describe the structure of DNA. Be sure to include what forms the skeleton and how are the strands held together? 2. Compare and contrast chromosomes, chromatids, genes, and alleles. 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. 4. Describe the process of asexual reproduction in eukaryotic cells. (DNA replication and mitosis) 5. Compare and contrast animal and plant cell asexual reproduction. (mitosis) 6. Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis. 7. Without genetic testing how could you determine if an organism is homozygous or heterozygous for a specific trait (ie hair color)? 8. Describe three ways that genetic variability is increased. 9. Two fruitflies are bred. One is true breeding for red eyes and one is true breeding for white eyes. Red eyes are dominant. What will the genotype and phenotype of the offspring be? 10. If two of the offspring of the above match are crossbred what will the genotype and phenotype of their offspring be? 11. In the above examples how would the genotypes and phenotypes be different if red eye color was partially dominant producing pink eyes when heterozygous? 12. In the example above (#9) the red-eyed fruitfly has straight wings and the whiteeyed fruitfly has wrinkled wings. Straight wings are dominant. What would the genotype and phenotype of the offspring be? 13. What characteristics can make genetic disorders more likely to be passed from one generation to the next? (at least 3) 14. Describe the process of DNA replication. What is meant by semiconservative replication? How are continuous synthesis and discontinuous synthesis involved in the process? 15. How common are mistakes in replication? What safeguards are in place to prevent mistakes? What types of mistakes are relatively common? 16. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 17. Describe the process of transcription. 18. Describe the process of translation. 19. What are codons and how do they function in protein synthesis? 20. Describe the ways by which gene expression may be regulated.