Genetics Study Guide Answers What are different forms of a
advertisement
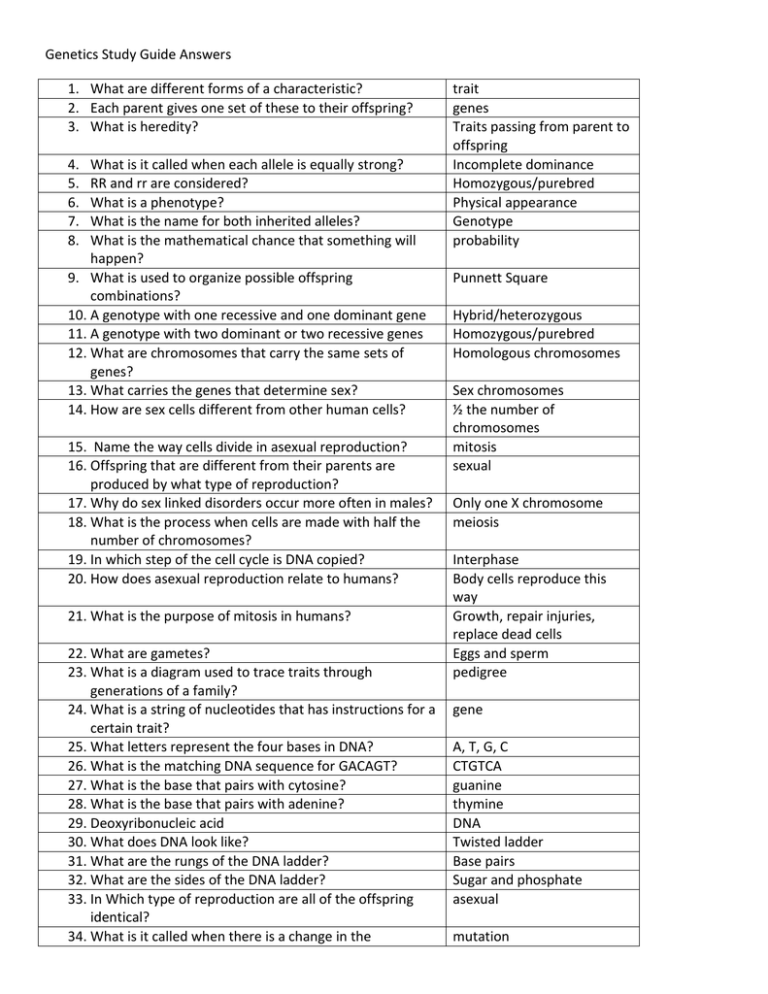
Genetics Study Guide Answers 1. What are different forms of a characteristic? 2. Each parent gives one set of these to their offspring? 3. What is heredity? 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is it called when each allele is equally strong? RR and rr are considered? What is a phenotype? What is the name for both inherited alleles? What is the mathematical chance that something will happen? 9. What is used to organize possible offspring combinations? 10. A genotype with one recessive and one dominant gene 11. A genotype with two dominant or two recessive genes 12. What are chromosomes that carry the same sets of genes? 13. What carries the genes that determine sex? 14. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 15. Name the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 16. Offspring that are different from their parents are produced by what type of reproduction? 17. Why do sex linked disorders occur more often in males? 18. What is the process when cells are made with half the number of chromosomes? 19. In which step of the cell cycle is DNA copied? 20. How does asexual reproduction relate to humans? 21. What is the purpose of mitosis in humans? 22. What are gametes? 23. What is a diagram used to trace traits through generations of a family? 24. What is a string of nucleotides that has instructions for a certain trait? 25. What letters represent the four bases in DNA? 26. What is the matching DNA sequence for GACAGT? 27. What is the base that pairs with cytosine? 28. What is the base that pairs with adenine? 29. Deoxyribonucleic acid 30. What does DNA look like? 31. What are the rungs of the DNA ladder? 32. What are the sides of the DNA ladder? 33. In Which type of reproduction are all of the offspring identical? 34. What is it called when there is a change in the trait genes Traits passing from parent to offspring Incomplete dominance Homozygous/purebred Physical appearance Genotype probability Punnett Square Hybrid/heterozygous Homozygous/purebred Homologous chromosomes Sex chromosomes ½ the number of chromosomes mitosis sexual Only one X chromosome meiosis Interphase Body cells reproduce this way Growth, repair injuries, replace dead cells Eggs and sperm pedigree gene A, T, G, C CTGTCA guanine thymine DNA Twisted ladder Base pairs Sugar and phosphate asexual mutation nucleotide base sequence of DNA? nucleotide 35. What is a subunit of DNA that consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and a base? 36. In rabbits, the allele for black fur (B) is dominant over the allele for white fur(b). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for offspring. 1. BB - Black 2. Bb - Black 3. bb- white B b B BB Bb b Bb bb 37. Show the Punnett Square for two heterozygous rabbits. a. What percentage of the offspring will be black? 75% b. What percentage of the offspring will be white? 25% 38. Show a Punnett Square for a pure breeding black rabbit and a white rabbit. a. What percentage of the offspring will be black? 100% B B b Bb Bb b Bb Bb b. What percentage of the offspring will be white? 0% 39. What makes the process of mitosis different than the process of meiosis? Explain. Mitosis is a type of asexual reproduction where you get two identical cells after cell division with a full set of chromosomes in each cell. Meiosis is the way that eggs and sperm are made. In the end you have 4 new cells with a ½ set of chromosomes.