Organic Chemistry Notes
advertisement

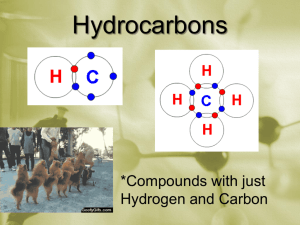
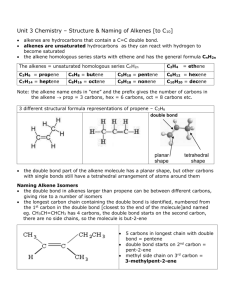
Organic Chemistry Notes Organic Chemistry; Chemistry of Carbon Compounds Carbon: o (almost) always forms 4 bonds; we will not consider exceptions. o can achieve many different geometries and structures Hydrocarbons: o Compounds containing only H and C o Flammable o Can be saturated or unsaturated: o Saturated: No double bonds “Saturated w/ Hydrogen” Solid at Room Temperature o Unsaturated: some dbl./trpl. Bonds less Hydrogen Liquid at Room Temperature Classes of Hydrocarbons: Naming Hydrocarbons 1 carbon: 2 carbons: 3 carbons: 4 carbons: 5 carbons: MethylEthylPropylButylPenta- 6 carbons: 7 carbons: 8 carbons: 9 carbons: 10 carbons HexaHeptaOctaNonaDeca- Alkanes o Single C-C bonds o Can be straight chain, branched chain or cyclic CnH2n+2 o Alkenes o Double C-C bonds o Can be straight chain, branched chain or cyclic o Unsaturated; “Kinks”not free to rotate around double bond o Fewer Hydrogens CnH2n o Cyclic (“Aromatic”) Compounds o Ring Structures o Sometimes Includes Dbl, Triple Bond o Multicyclic Hydrocarbons o Many important biochemical compounds; nucleic acids (DNA), hormones, medicines, amino acids (proteins), etc. For help drawing skeletal formulas, follow this link.