Covalent Bond
advertisement

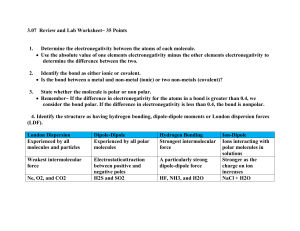
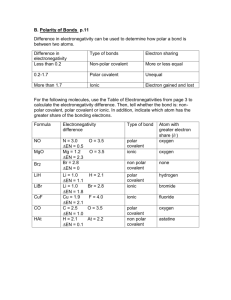
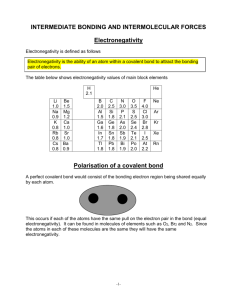
Covalent Bond - Chemical bonding involving non-metals only. - Chemical bond formed by the sharing of at least a pair of electrons between two atoms to obtain an octet. - The degree of sharing depends on the value of electronegativity for each atom. The bigger the value of electronegativity, the greater the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons. - Electronegativity increases as you go across and up the Periodic Table. - A pure covalent bond results when you have equal sharing of electrons. The electronegativity values are the same for each atom, i.e. diatomic molecules. - A polar covalent bond results when you have unequal sharing of electrons. - You can use the bonding continuum to indicate the degree of polarity. Type of Bond 100% covalent Difference in Electronegativity 0 Slightly Very Polar 100% polar polar Ionic covalent Ionic covalent covalent 0.5 0.6 1.6 1.7 - If the electronegativity difference is = to or > 1.6, then the bond is ionic or has ionic properties. - If the electronegativity difference is < 1.6, then the bond has some degree of covalent properties. To Do: - Show the formation of covalent bonds in the following combinations. Indicate if the bonds formed are pure or polar covalent, as well include the appropriate dipoles. Cl and Cl Br and Br Ne and Ne N and N H and O P and P H and F Cl and O B and N C and O F and F I and I O and O H and Cl S and S N and N H and Ne H and N B and Cl Si and Cl