Life_Science_Study_Guide
advertisement

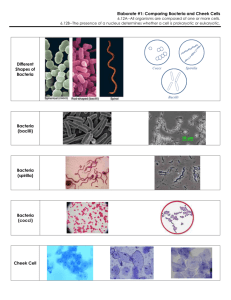
Life Science Test Study Guide 1. What is a cell? Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. 2. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? Give examples of each. Unicellular – made up of one cell Examples: Bacteria, Amoebas, Paramecium Multicellular- made up of many cells Examples: Humans, Plants, Animals 3. Describe a prokaryotic cell. They do not have a nucleus, and their DNA is scattered randomly throughout the cell. They don’t contain as many organelles as eukaryotic cells. They contain cytoplasm, a cell membrane, and ribosomes. They are less complicated and smaller that eukaryotes. All Bacteria and Achaea are prokaryotes. 4. Describe a eukaryotic cell. They have a nucleus where DNA of the cell is stored. They have many organelles that work together to help the cell function. Eukaryotic cells are much more complex than prokaryotic cells. They can be just one cell or can make up more complex multicellular organisms. All plants, animals, humans, fungi, and protists are composed of eukaryotic cells. 5. Give examples of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes: Bacteria, Archaea Eukaryotes: Animals, Fungi, Protists, Plants, Humans 6. An organism lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles would be called what? Prokaryote 7. What is the broadest classification in taxonomy? Domain 8. Name all 3 Domains and characteristics of each. Eukarya: have a nucleus (eukaryotic), most are multicellular, can be autotropic or heterotrophic Archaea: don’t have a nucleus (prokaryotic), live in extreme habitats, reproduce asexually, unicellular Bacteria: don’t have a nucleus (prokaryotic), can be found anywhere, reproduce asexually, unicellular 9. Name all 6 kingdoms. Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya, Protista, Animalia, Fungi, and Plantae 10. Define abiotic and biotic factors? Abiotic-nonliving things Biotic- living things 11. Give 5 examples of abiotic factors. Give 5 examples of biotic factors. Biotic: Trees, Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists Abiotic: Air, Temperature, Water, Sunlight, Soil, Rocks 12. What is the difference between a heterotroph and an autotroph? Give examples of each. Autotroph: organisms that make their own food or producers Examples: Algea, Plants, Trees, Shrubs Heterotroph: organisms that feed off of or consume other things for energy Examples: Humans, Animals, Most Bacteria, and Fungi 13. What is the primary source of energy in an ecosystem? Sunlight 14. What is the formula for speed? S = D/T 15. What is the purpose of gravity in our solar system? Governs the motion of all objects in our solar system.