NOTES THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF
advertisement

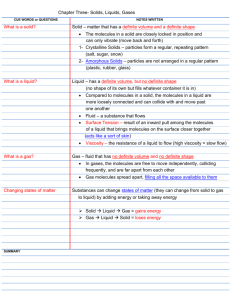
IGCSE Chemistry 1 The particulate nature of matter 1 Demonstrate understanding of the terms atom and molecule. atom – element – molecule – compound – particle – any small piece of a substance; it could be a molecule or billions of molecules mixture – solute – solvent – solution – solution – filtrate – residue – saturated solution – concentration – colorless – purity - 4.1 States of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. 4.2 Molecular model Describe qualitatively the molecular structure of solids, liquids and gases. Relate the properties of solids, liquids and gases to the forces and distances between molecules and to the motion of the molecules. solid liquid gas description fixed volume, own shape fixed volume, takes shape of container any volume takes shape of container arrangement of particles in a regular patter called a lattice random random separation of particles close together, touching movement of particles vibration around a fixed position attractive forces between particles stronger than the liquid phase still close together, just slightly farther apart than those in the solid phase slow movement in a random way from place to place, sliding past each other slightly weaker than the solid phase separated, far apart fast random movement no attractive forces between particles When the temperature of a solid increases, so does the energy of the particles. At the melting point the particles have enough energy to move past each other and change positions. Liquids can flow and change their shape. When a liquid is heated, the energy of the particles increases. At the boiling point the intermolecular forces can no longer hold the particles together, so the particles separate & become a vapor or gas. The particles can change position and move apart. Gases can flow and expand to fill any space. supply heat energy solid supply heat energy liquid heat energy given to surroundings gas heat energy given to surroundings Interpret the temperature of a gas in terms of the motion of its molecules. The higher the temperature, the faster the speed of the molecules. Temperature is a measure of the average speed of the molecules. Temperature is how hot something is; heat is energy that flows from hot substances to cold substances. Describe qualitatively the effect of a change of temperature on the pressure of a gas at constant volume. The higher the temperature, the larger the volume of gas at a constant pressure. Describe qualitatively the pressure of a gas in terms of the motion of its molecules. At a constant temperature, gas molecules move at a constant average speed, so that the force of the collision is the same ( on average ). If the gas is compressed into a smaller volume, there are more frequent collisions on each unit of area, so that the total force per unit area increases and the pressure increases. If a gas expands to a greater volume at a constant temperature, the pressure decreases.