Meteorology
advertisement

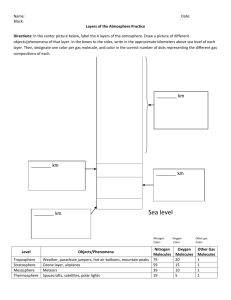
Name ______________________________ Period _________ Meteorology and Atmospheric Energy A. Meteorology Defined 1. Meteorology is the science that deals with the ___conditions____ of the __atmosphere____ at a specific moment in ___time____. Ex) Today’s weather and tomorrow’s forecast. 2. Climatology deals with the ___average_______ conditions of the atmosphere. Ex) Rain forests and deserts B. Atmospheric Gases 1. The atmosphere is a ___mixture______ of gases held to the surface of the Earth by __gravity______. 2. Up to __80__ km, there are two main gases, __nitrogen___ and __oxygen___. Above this, the mixture of gases changes. A layer of oxygen reaches to about _1000__ km. Above this a layer of __helium___ reaches to about __2400__ km. 3. Determine the percent (%) by volume of each gas in the lower atmosphere (up to 80 km). Also, identify the number of atoms per molecule and the molecular (or atomic) weights of each gas: Atmospheric Gas Chemical Formula (or Symbol) % Number of Atoms Molecular (or Atomic) Weight Nitrogen N2 78 2 28 Oxygen O2 21 2 32 Argon Ar 1 40 Carbon Dioxide CO2 3 44 Hydrogen H2 2 2 Methane CH4 5 16 Ozone O3 3 48 Water Vapor H2O 3 18 Radon Rn 1 222 Sulfur Dioxide SO2 3 64 1% 4. As a result of gas molecules being squeezed together, 99 % of the atmosphere’s weight is found within about __32__ kilometers of the earth’s surface. Half the atmosphere’s weight is within __5.5__ kilometers. C. Layers of the Atmosphere 1. The layers of the atmosphere are on page ___14__ of your ESRT’s. 2. The layers of the atmosphere are : a. ___Troposphere______ c. ____Mesosphere______ b. ___Stratosphere________ d. ____Thermosphere____ 3. The layers appear to be separated by reversals in __temperature__ D. Characteristics of the Layers 1. Troposphere (means __change__) a. Begins at the __surface____ to __12___ kilometers up (17 km near the equator to 7 km at the poles). b. All __weather_____ occurs in this layer. c. Gets its heat energy from the _Earth___; not the Sun. d. Temperature decreases as you go higher in altitude at a rate of _6.5 deg C/km__ (adiabatic lapse rate). 2. Stratosphere (means ___layers____) a. from approximately ___12____ km up to ___50___ km. b. Temperature increases as you go higher due to the ___ozone__ layer absorbing ultraviolet light (16-60km). 3. Mesosphere (means __middle____) a. from approximately ___50____ km up to ____80___ km. b. Temperature decreases to __-90C___ as you go up. c. Heated by the ___Sun___. d. Meteors ___burn___ up here (shooting stars). 4. Thermosphere (means ___heat_____) a. from approximately ___80 km___ and higher b. Temperature __increases_____ as you go up. c. Heated by the ___Sun____. d. Ten __million____ times less air particles than at the surface, and is considered a __vacuum___. 5. Layers within the upper layers a. Ionosphere – Layers of ___ionized___ gases found in the lower thermosphere. b. Exosphere – Top of the thermosphere where the atmosphere blends into ___outer space_______. c. Magnetosphere – Upper atmosphere influenced by the Earth’s ___magnetic field_____. E. Atmospheric Variables and Instruments 1. Temperature – Measures the __motion____ of molecules (kinetic energy). a. Mercury thermometer - best in __warm___ climates b. Alcohol thermometer – best in _cold___ climates c. Bi-metalic thermometer – Brass and steel strips that twist due to different ___expansion____ rates. 2. Air Pressure – The __weight___ of air molecules per unit area. Air molecules are ___colliding____ with your body. a. Mercury barometer – measures the height of a column of ___mercury____ b. Aneroid barometer – measures pressure with a sealed __can__ (vacuum inside) 3. Humidity – The amount of __invisible__ water molecules in the air (gas state). a. Sling psychrometer – Has a wet and a dry bulb thermometer. Takes advantage of the __cooling____ process of evaporation. b. Hair hygrometer – Measures how much a blonde __human___ hair stretches. 4. Wind speed a. Anemometer – 3 or 4 cups that spin 5. Wind direction a. Weather vane – Points __into_ the wind. 6. Precipitation – Any __falling__ form of water (rain, sleet, snow,etc) a. Rain gauge – Records to the nearest 1/100 of an inch. Snow accumulates in inches. F. Convert the following air pressure readings (p. 13 of your ESRT’s) Inches of Hg 30.45 29.21 30.03 29.42 30.55 ___29.53___ ___28.53___ ___28.67___ ___29.92___ Millibars ___1031.2_ ___989.2__ ___1017.0__ ___996.4__ ___1034.6__ 1000.0 966.1 970.9 1013.2