Cells Study Guide
advertisement
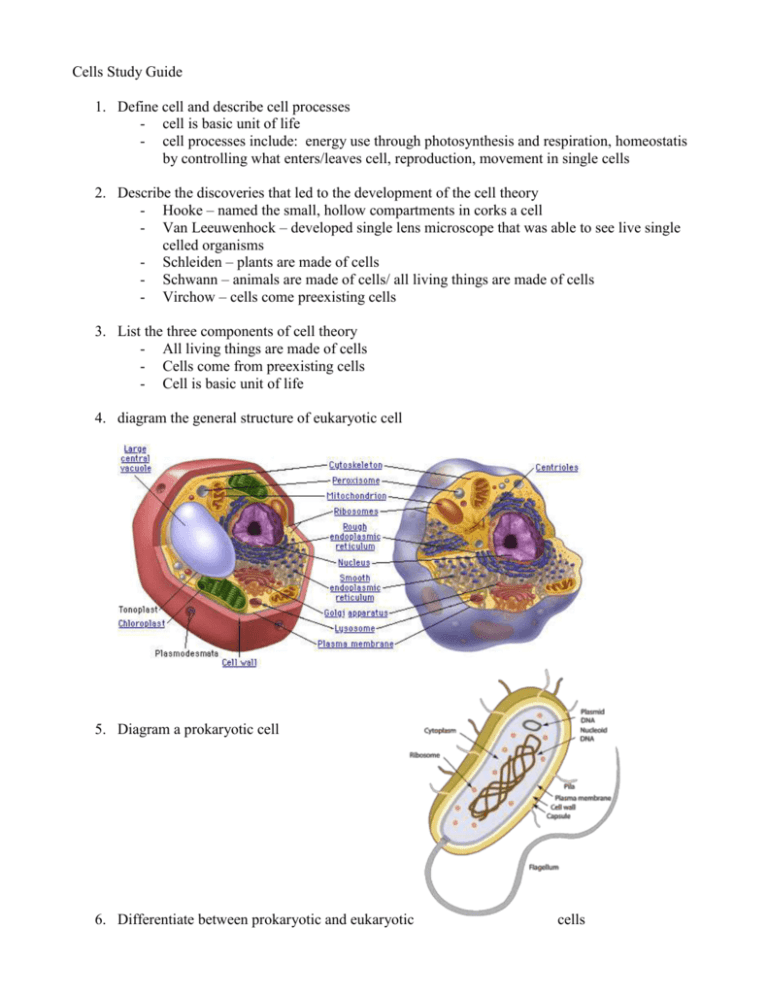
Cells Study Guide 1. Define cell and describe cell processes - cell is basic unit of life - cell processes include: energy use through photosynthesis and respiration, homeostatis by controlling what enters/leaves cell, reproduction, movement in single cells 2. Describe the discoveries that led to the development of the cell theory - Hooke – named the small, hollow compartments in corks a cell - Van Leeuwenhock – developed single lens microscope that was able to see live single celled organisms - Schleiden – plants are made of cells - Schwann – animals are made of cells/ all living things are made of cells - Virchow – cells come preexisting cells 3. List the three components of cell theory - All living things are made of cells - Cells come from preexisting cells - Cell is basic unit of life 4. diagram the general structure of eukaryotic cell 5. Diagram a prokaryotic cell 6. Differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells - Eukaryotic cell: plant/animal/fungus/protist cells, have nucleus, have membrane bound organelles, many different organelles with different functions, DNA in nucleus - Prokaryotic cell: bacteria cell, no nucleus, no membrane bound organelles, have ribosomes, DNA spread throughout the cell - ALL CELLS have a cell or plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA 7. describe how cell structure helps different cells function - red blood cells: biconcave shape so flexible to squeeze into small places and increased surface area for oxygen/carbon dioxide exchange - white blood cells: round/different shapes that squeeze into infected tissue to engulf invaders - skin cells – thin cells in a thick layer to provide protection - nerve cell – long thin with covering that speeds up impulse in one direction 8. relate cell parts/organelles to their function - cell or plasma membrane: controls what goes in and out of cell - nuclear membrane: controls what goes in and out of nucleus - nucleus: controls all cell processes - nucleolus: makes ribosomes - cytoplasm: jellylike substance that holds organelles in place - mitochondria: makes energy for cell (respiration) - endoplasmic reticulum: synthesizes and transports ribosomes/material around the cell - golgi body: packages proteins/carbs for export from the cell - lysosome: digests material not needed - ribosome: makes proteins - vacuole: stores water, food, nutrients - cell wall: provides structure in plant cells - chloroplast: traps light to make glucose for plant - cytoskeleton: support and give cell its shape - centrosome: makes microtubules and contains centriole - flagella: tail that helps cell move - cilia: hairs around cell that help it move 9. distinguish between plant cells, animal cells, bacteria, and virus - plant cells have cell wall and chloroplasts but animal cells do not have these organelles - 1 large vacuole in plant cell and many small ones in animal cell - Both animal and plant cells are eukaryotes and bacteria is a prokaryotic cell - Animal and plant cells have a nucleus containing the DNA but bacteria does not have a nucleus so DNA floats around in center of cell - Animal cell, plant cell, and bacteria have a cell membrane, DNA, ribosomes, and cytoplasm - Animal cell, plant cell, bacteria, and virus contain DNA - Virus cell is non-living and requires a host cell to reproduce but animal cell , plant cell, and bacteria can reproduce by themselves through the processes of mitosis