Eukaryotic Cells
advertisement

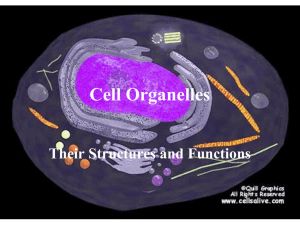
The Cell Overview Answer the following questions on a sheet of notebook paper in your lab notebook Objectives List the scientists who contributed to our knowledge of the cell, and explain their contribution in your own words. List the 3 components of the cell theory, then explain them to Mr. Allen Compare prokaryote to eukaryote cells, make a table and find similarities and differences. Sketch and Label a plant and animal cell Describe the functions of all cell organelles Early Contributions Robert Hooke - The first person to see cells, he was looking at cork and noted that he saw "a great many boxes. (1665) Anton van Leeuwenhock - Observed living cells in pond water, which he called "animalcules" (1673) Theodore Schwann - zoologist who observed that the tissues of animals had cells (1839) Mattias Schleiden - botonist, observed that the tissues of plants contained cells (1845) Rudolf Virchow - also reported that every living thing is made of up vital units, known as cells. He also predicted that cells come from other cells. (1850 ) The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cellss. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. *Why is the Cell Theory called a Theory and not a Fact? Cell Features Ribosomes - make protein for use by the organism Cytoplasm - jelly-like goo on the inside of the cell DNA - genetic material Cytoskeleton - the internal framework of the cell Cell membrane - outer boundary of the cell, some stuff can cross the cell membrane. Types of Cells Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotes are very simple cells, probably first to inhabit the earth. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a membrane bound nucleus. Bacteria are prokaryotes. DNA of bacteria is circular. The word "prokaryote" means "before the nucleus" Other features found in some bacteria: Flagella - used for movement Pilus - small hairlike structures used for attaching to other cells Capsule - tough outer layer that protects bacteria, often associated with harmful bacteria Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells are more advanced cells. These cells are found in plants, animals, and protists (small unicellular "animalcules"). The eukaryotic cell is composed of 4 main parts: cell membrane - outer boundary of the cell cytoplasm - jelly-like fluid interior of the cell nucleus - the "control center" of the cell, contains the cell's DNA (chromosomes) organelles - "little organs" that carry out cell functions Cell Structures The Nucleus Usually found at center of cell Has a nuclear membrane ;nuclear pores Contains cell's DNA in one of 2 forms o chromatin- DNA bound to protein (non-dividing cell) o chromosomes- condesed structures seen in dividing cell Also contains an organelle called nucleolus - which makes the cell’s ribosomes Mitochondria Energy center or "powerhouse" of the cell. Turns food into useable energy (ATP) Ribosome - make protein, located on the rough endoplasmic reticulum and throughout the cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus - processing, packages and secretes proteins; proteins are transported in vesicles Lysosome - contains digestive enzymes that can break things down, also called a "suicide sac" because the rupturing of the lysosome will cause the cell to destroy itself Endoplasmic Reticulum - Transport, "intracellular highway". Ribosomes are positioned along the rough ER, protein made by the ribosomes enter the ER for transport. Smooth ER - no ribosomes Rough ER - contains ribosomes Cytoskeleton - helps maintain the cells shape; supports the cell and aids in cell movement\ microtubules / microfilaments / centrioles microtubules are used to build cilia and flagella Vacuole - storage area for water and other substances, plant cells usually have a large central vacuole Protein Production The cell is like a factory. Its product is protein which goes to body to serve different functions. 1. 2. 3. 4. DNA has instructions to build; protein These instructions are sent to ribosomes The ribosomes build protein and send it through ER The proteins are delivered to& golgi where they are completed and tagged for export outside the cell Plant Cell Has all the components of animal cells with some additional structures. Chloroplast - Uses sunlight to create food, photosynthesis (only found in plant cells), contains green pigment chlorophyll Cell Wall - outside the cell membrane of plants and some bacteria, the cell wall serves as support Central vacuole - large water container, helps maintain a turgor (stiffness) in the plant Animal Cell versus Plant Cell ORGANELLES WITH DNA The Mitochondria and Chloroplasts have their own DNA ENDOSYMBIOSIS THEORY - eukaryotic cells evolved from the engulfing of bacteria cells, thus creating additional cell parts CELL MEMBRANE Function: to regulate what comes into the cell and what goes out Composed of a double layer of phospholipids and proteins