LOOKING INSIDE CELLS - Conackamack Middle School
advertisement

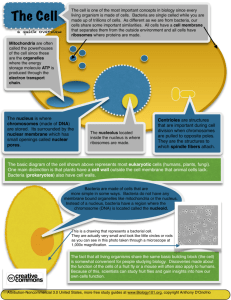
LOOKING INSIDE CELLS pages 60-67 RECALL: All living things are made up of cells. • There are two MAJOR types of cells – Prokaryotes – cells that lack a nucleus ex. Bacteria – Eukaryotes – cells with a nucleus ex. plant and animal cells • There are two types of EUKARYOTIC CELLS – PLANT and ANIMAL Structure of a Plant Cell • Shape – more rectangular; rigid; (strong/tough) because the cell wall is made up of cellulose fibers. Structure of an Animal Cell • Shape – more round; but they come in many different shapes. Brain cell Female egg cell Blood cell Liver cell Differences between Plant and Animal Cells • Plant cells have a cell wall which surrounds their cell membrane. • Animal cells do not have a cell wall but they do have a cell membrane. Cell Membrane Cell Wall Differences between Plant and Animal Cells • Plant cells have chloroplasts, animal cells don’t. – Structure – large, green – Function – trap energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell • Plant cells have a larger vacuole. Differences between Animal and Plant cells • Animal cells contain lysosomes. – Function – break down larger food particles into smaller ones. • Animal cells usually have more mitochondria. Lysosomes shown below in yellow. CELL ORGANELLES • Organelles: tiny cell structures that carry out specific functions in the cell TYPES OF ORGANELLES • CELL MEMBRANE – Structure – plant cell: within the cell wall animal cell: outside boundry – Function – controls which substances go in and out of the cell; substances travel through pores (holes) – “selectively permeable” • Nucleus – control center of the cell – Function – controls all cell activities – Structure – oval structure in the center of the cell • Three parts to the nucleus – Nuclear membrane – surrounds the nucleus – Chromatin – contains genetic material – Nucleolus – inside the nucleus, where ribosomes are made • Cytoplasm – Structure – gel-like fluid; constantly moving – Function – contains all cell organelles • Mitochondria – the “Powerhouse” - Structure – rod-shaped - Function – provide most of the energy cells need to carry out its functions • Ribosome – the “Protein FACTORIES” – Structure – small grain-like bodies – Function – produce proteins – Made in the nucleolus • Endoplasmic Reticulum(ER) – the protein TRANSPORTER – Structure – maze of passageways • Smooth ER – no ribosomes • Rough ER – ribosomes – Function – carry proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another. • Golgi Bodies – the “protein MAILROOM” – Structure – flattened sacs and tubes – Function – receive proteins, package them for the job they need to do and deliver them to other parts of the cell • Vacuoles – “Storage House” – Structure – water-filled sacs – Function – store food, water, and other materials Let’s Review ALL the cell parts… PROKARYOTIC CELLS • BACTERIA CELLS – Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic • Size – bacteria are MUCH smaller • No nucleus – genetic material found in the cytoplasm • No organelles except for ribosomes – Similarities • Has a cell wall • Has a cell membrane