The Cell Study guide 2014
advertisement
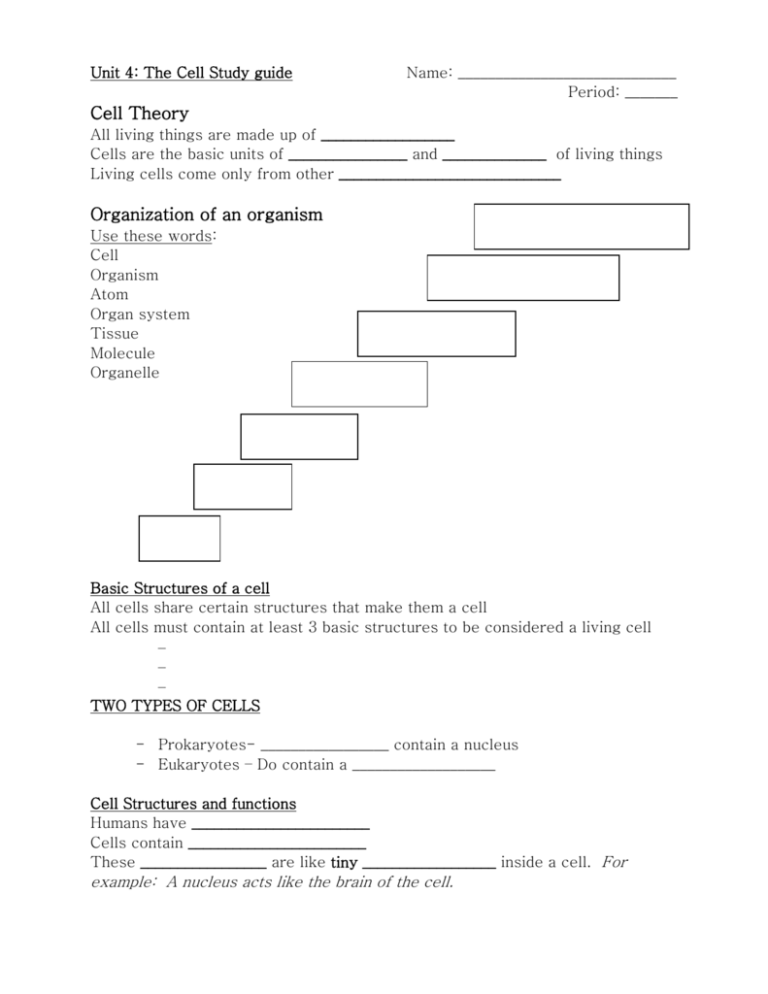
Unit 4: The Cell Study guide Name: _____________________________ Period: _______ Cell Theory All living things are made up of __________________ Cells are the basic units of ________________ and ______________ of living things Living cells come only from other ______________________________ Organization of an organism Use these words: Cell Organism Atom Organ system Tissue Molecule Organelle Basic Structures of a cell All cells share certain structures that make them a cell All cells must contain at least 3 basic structures to be considered a living cell – – – TWO TYPES OF CELLS - Prokaryotes- _________________ contain a nucleus - Eukaryotes – Do contain a ___________________ Cell Structures and functions Humans have ________________________ Cells contain ________________________ These _________________ are like tiny __________________ inside a cell. For example: A nucleus acts like the brain of the cell. Match the organelles with functions. _____ 1. makes proteins a. lysosome _____ 2. assembles and passes on cell products, like an assembly line _____ 3. converts food into energy for the cell (cellular respiration) b. endoplasmic reticulum (ER) c. golgi apparatus d. mitochondrion _____ 4. cleans up cell waste and breaks down materials e. ribosome _____ 5. acts as shipping and packaging for the cell ___________________________________ _______________ _____ 6. provides support and protection for the cell; made of cellulose f. nucleus g. centriole _____ 7. Helps cell perform division by creating spindles. _____ 8. controls what enters and leaves the cell; made of two layers of lipids/ proteins h. chloroplast i. cell wall j. cell membrane _____ 9. the control center of the cell; contains DNA _____ 10. turns solar energy into food for the cell (photosynthesis) ____________________________________ _____ 11. membrane enclosed structure inside of a cell that has a specific function. Name means “little organ” _______________ a. vacuole b. prokaryote _____ 12. the jellylike material that fills the space inside a cell c. eukaryote _____ 13. cells that do have a nucleus d. organelle _____ 14. cells that do not have a nucleus e. cytoplasm _____ 15. Storage area for water, food, etc. Cellular Movement & Homeostasis Directions: Fill in the correct letter in the blank that best answers the question. (2 points each) _________1. The movement of substances from an area of high concentration to low concentration is called: a. diffusion b. endocytosis c. exocytosis d. osmosis ________ 2. The movement of water molecules across a membrane is: a. exocytosis b. endocytosis c. osmosis d. diffusion ________ 3. A substance that moves by passive transport tends to move: a. away from equilibrium b. away from low concentration c. away from high concentration ________ 4. Cell transport that requires a source of energy is called: a. active transport b. energetic transport c. passive transport d. osmosis ________ 5. The words describing that a membrane can choose what enters or exits a cell: a. Selectively Flexible b. Impermeable c. Selectively Permeable ________6. When cells move material to keep a constant and equal internal environment it is: a. Homeostasis b. equilibrium c. Movement ________7. When cells are in a state where all materials are balanced and equal it is in: a. Homeostasis b. equilibrium c. Movement ________8. Movement without energy is called: a. Active Draw a cell that will do diffusion: b. Stationary c. Passive Draw a cell in equilibrium: Cellular Nutrition & Energy ____1. Organisms that make their own food A. Chloroplasts ____2. Site of photosynthesis B. Aneorobic ____3. Process occurs in a mitochondrion C. Aerobic ____4. C6H12O6 D. Glucose ____5. Process does not require oxygen E. chlorophyll ____6. Process requires oxygen F. Fermentation ____7. Energy storing molecule G. Respiration ____8. The anaerobic process of splitting glucose and forming lactic acid or alcohol H. ATP ____ 9. The pigment that traps sunlight I. Autotrophs ____10. Organisms that eat for food J. Heterotrophs MAKING ENERGY Photosynthesis: Process where plants use ________________________ for food __________ + ___________ + ____________ ________ + __________ REMEMBER – PLANTS STILL COMPLETE RESPIRATION! USING ENERGY 2 types of Cellular Energy processes - Aerobic & Anaerobic (1) Aerobic Respiration Requires ___________________________________ Water and CO2 are _____________________ products ___________ + __________ _________ + _____________ + ___________ (2) Anaerobic Fermentation Does not require _____________ Yeast cells used to make bread Creates __________________ (makes bread rise), alcohol and ATP OR Creates __________________ and ATP in other organisms Cellular Reproduction & Growth TWO Types of Reproduction Mitosis (asexual reproduction) In order for an organism to ___________, the cells must ______________ and create more cells to add to the organism Each new cell is a _____________ of the parent cell. Meiosis (sexual reproduction) In order for organisms to reproduce sexually they must make _______ cells Each new cell is a ____________ then the parent cell with ________ the DNA Put the following stages of cell division in the correct order by adding a number beneath for which is 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th. Also include the name of the stage below. (8 points) Number: _____ ______ Name: _______________ _______________ _______ ________________ _______ ____________ 1. What are the large X’s in the pictures above called? (2 points) 2. What are the X’s made of? (2 points). 3. List two ways that Mitosis and Meiosis are different (2 points) Major differences between a PLANT and ANIMAL cells Plant cells have a _______________________ – animal cells do not. Plant cells have _________________________ – animal cells do not Plant cells have a large central ___________________ – animal cells do not











