Genetics Blank Study Guide
advertisement

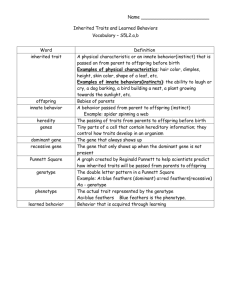
Name: _________________________ Pd. _________ The Basics of Genetics KEY CONCEPTS: -Heredity is the passing of traits from ___________________to offspring. -Some traits are inherited Example: _____________________________________________________________________________ -Some traits are __________________ (or developed through your life; not born with it) Examples: ____________________________________________________________________________ **You can NOT pass on acquired traits through DNA** -Individuals do not receive the traits, themselves, from their parents. They receive the genes that code for the traits it has. -Each human has _________ pairs of chromosomes -The 23rd pair are the ___________ ____________________—yes, these chromosomes determine the gender of the offspring, however, they do play other roles as well. -______________ __________________-founder of the idea behind genetics and performed multiple experiments with breeding plants to witness the different traits produced. KEY TERMS: ________________ _____________________: the type of reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells combine to form offspring with genetic material from both cells. Gene: the basic unit of heredity that consists of a segment of ___________ on a chromosome. Heredity: The passing of genes from parents to offspring; the genes are expressed in the traits of the offspring. Chromosomes: come in pairs. Each member in that pair is called a homolog. _________________: alternate forms of the same gene (example: Bb, Hh, Tt...etc.) Phenotype:______________________________________________________________________(examples: eye color, color of flower, height...etc.) ________________________: the genes that an organism has (Example: BB, Hh, TT...etc.) ______________________: one version of the gene trumps the other (always written in capital letters: B, H, T) Recessive: the allele is not expressed in the _____________________ when combined with a dominant form of a gene. Punnett Square: a visual representation of how the parents’ alleles might combine in offspring. Consists of squares that are used to create combinations of genes, such as recessive and dominant. Ratio: compares or shows the relationship between two quantities (usually written as 4:4 or four to four) Probability: the likelihood, or chance, of a specific outcome in relation to the total number of possible outcomes. Percentage: a ratio that compares a number to a 100. It states the number of times a particular outcome might happen out of 100 chances. Basics to Punnett Squares 1. Begin by drawing a table that has 4 boxes--> 2. Recognize that each box makes up 25% or 1/4 (think of adding the 4 together, you’re given 100% or 4/4. This will help you with determining the end probability/ratio/percentage. 3. Read the information that is provided to you. Example: There are two parent bunnies. Each parent bunny has one dominant allele for black fur (B) and one recessive allele for brown fur (b) **Remember, dominant genes will be written with capital letters, whereas recessive genes will be written with lower case letters. ** 3. After reading the information, begin properly filling in your Punnett square (male’s genes usually go on the top). 4. After you fill in your Punnett square, determine the probability/ratio/percentage of which trait will be passed onto the offspring. 5. What will its phenotype be? How can you determine this?