SOCIAL RISKS MITIGATION draft
advertisement

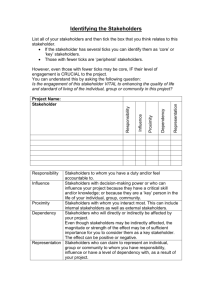
SOCIAL RISKS MITIGATION & STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT PLAN I. Introduction G Sampath (1990) on his statement identified the business activity is an economic activity that intended to make profit. It will be awkward if the companies or entrepreneurs doing business without thinks about profit oriented. Based on that point, then it is undeniable that every companies must be trying to protect their business activities from any kinds of risks that can be threatened their profits. In avoiding the risk threats is not easy, a company is required to have an innovative business strategy to be free from those threats. One of the strategy that usually used by the companies is implementation of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). CSR is performed to confirm the companies’ commitment to achieve sustainable development. CSR is a proof contribution in promoting and establishing a balance position among economy, social and environment. In the implementation of CSR, the companies usually facing a dilemma situation since they should be fair in repaired the environment destruction without compromising the companies’ goal which is profit-oriented. However, in CSR practicing the companies activities usually lead to the new problems. For instance in the mining companies in Indonesia, such as PT Weda Bay Nickel Indonesia in Halmahera and several project location of PT Medco Energi International. Both of them usually facing the problems especially related to the land acquicition for their business activities. Instead of obtaining the ease of doing business, those companies are regarded as the trigger of the environmental and natural resources destruction which owned by the region. Reflecting to these cases, then it is required comprehensive knowledge from the companies to recognize their stakeholders’ as well as the risks that brought by them. This paper would like to give a complete overview related to the risks and issues identification from each stakeholder, as well as the instrument that can be used by the companies in mitigating their social risks. This instrument becomes important to be well-known by the companies to the related parties as an approaching method before the companies implementing their business activities, especially in CSR application. II. Conceptual Framework a. Definition of Business The Business definition become important to understand, since this paper discussed about the company’s or organization’s activities to achieve their profit and benefit. Hughes and Kapoor (…) stated that business is the organized effort of individuals to produce and sell for a profit, the goods and services that satisfy society’s needs. The general term business refers to all such efforts within a society or within an industry. In addition, Brown and Petrello (….) stated that business is an institution which produces good and services demanded by people. Regarding to those concepts, the authors defined business as an organization that produces or provides goods and/or services to meet the community’s demand and needs. Based on those definition, then it is required several component to declare that an organization is doing business, such as (1)it is related with goods and/or services, (2)there is transferred of goods and/or services from the organization to an individual or other organization, (3)there is a system management that regulated the business activities, (4)profit oriented, and (5)the organization get any benefit, either materials and/or immaterial (…..). a. Risks Theory In the implementation of business activities usually the companies are facing the unpredictable options. The companies have not been known what is the significant impact that will be occurred in the future. This situation can be categorized as a risk. Vaughan (1978) has been stated several definition about risks. On his definitions, the essences of risks are the uncertain and unpredictable situation that will bring the companies to gain a loss. The statement of uncertain and unpredictable situation become significant since the expected result can be same as the prediction or it can be completely different to the expectation. Based on this condition, then the companies may be indicated gain the risks if the results obtained are not accordance with the companies’ expected results. Regarding to that definitions, there are several risks resources that can be lead to companies’ loss, such as (1)social risks which is the risks that arise from others (individual or community) actions and because of their actions the companies can not achieve their goals; (2)physical risks (force majeure) which is the risks that arise due to the natural phenomena; and (3)economical risks which is the risks that arise due to the economic situation of its country such as inflation, monetary crisis, etc. Due to the lack of CSR implementation, then this paper is focused on social risks. It is because the risks arise since the interference from the outsiders who will threaten the business activities and company’s sustainability. b. Social Risk Management One of the methods that can be used in reducing the level of risks is through the risks identification, such as understanding the nature of risks and the impacts that will be occurred for the companies’ sustainability. The theory of risks management in economic perspective gives several companies’ provision in facing and managing the risks, which are; 1. Risks avers, which is the calculation of the amount of risks and benefits that will be received by the companies 2. Risks neutral, which is the rational attitude of the companies in facing the risks. In this case the companies taking into account the expectation to be gained and to be loosed that will be received by the companies. 3. Risks seeker, different with the other two in this point the companies is looking for risks that to be received by them and will be taken the highest risks. In many literatures, it has actually delivered some common methods in dealing with the risks, such as (1)avoiding the cause of risks, (2)reducing the risk probabilities, and (3)shifting the risk into an insurance company. However for the latest one, it can not be implemented for the social risks. c. Reducing Social Risk The Independent Project Analysis (IPA) on their risk management and company’s sustainability studies stated that there are four important things to minimize the risk impact, which are (1)stakeholder assessment, (2)social baseline studies, (3)community engagement, & (4)grievance (communication) mechanism (Figure 1.) III. Result & Discussion Based on the key practices of IPA Global, it can be seen that there are four steps that should be taken by the company before running the stakeholder engagement. Those four steps are effective to minimize the risks that would be disturbed the business process. Herewith the explanation of each steps, there were: 1. Baseline Social Studies. It is the basic part before starting the stakeholder engagement. This part is important to do as the initial analysis to gain information about social impact assessment in the project areas and surrounding. In addition, this section also provides comprehensive information about the social aspects. 2. Stakeholder Identification. The important thing that needed to know by company is basic principle of stakeholder involvement. Identified to gain information can be from anywhere and everywhere, either individuals organizations. On this section, it could be worthy if the company’s recognize the the or the roles of each development actors. Comprehensive information of each development actors becomes important as the basic for the company’s strategy. While legitimacy (=normative appropriateness) is an important variable, two other factors must be considered when mapping out stakeholder class relationships. One factor consists in power defined as the ability to influence the actions of other stakeholders and to bring out the desired outcomes. This is done through the use of coercive-physical, material-financial and normative-symbolic resources at one's disposal. The other factor is that of urgency or attention-getting capacity. This is the ability to impress the critical and pressing character of one's claims or interests, goals that are time-sensitive and will be costly if delayed. These three "otherdirected" attributes (legitimacy, power, urgency) are highly variable; they are socially constructed; and they can be possessed with or without consciousness. Consequently, there are 8 different stakeholder groups: 1. Dormant stakeholders (Power, no legitimacy and no urgency) 2. Discretionary stakeholders (Legitimacy, but no power and no urgency) 3. Demanding stakeholders (Urgency, but no legitimacy and no power) 4. Dominant stakeholders (Power and legitimacy, but no urgency) 5. Dangerous stakeholders (Power and urgency, but no legitimacy) 6. Dependent stakeholders (Legitimacy and urgency, but no power) 7. Definite stakeholders (Power, legitimacy and urgency) 8. Nonstakeholders (No power, no legitimacy and no urgency) 3. Community Engagement. After the company having knowledge about the roles and risks level of the stakeholders, the next step is the process of stakeholders’ involvement to the company’s activities. On this engagement, the company can used which strategy that the most suitable for the company’s need and stakeholder interest. The essence of this stage is how to create the trust between both parties, which are the company and stakeholders. It is become required to establish the favorable conditions. Consequently, the company’s goals can be achieved without bothering the stakeholders’ interest. The International Association of Public Participation (IAP2) has been developed some important values for Public Participations practices. Through the public participation’s basic values, then the objectives of both side will be fulfilled. Furthermore, the public participation can be used as the medium to delivery the stakeholders’ desires and their expectations. Herewith the IAP2 basic values on public participation; 1. Public participation is based on the belief that those who are affected by a decision have a right to be involved in the decision-making process. 2. Public participation includes the promise that the public’s contribution will influence the decision 3. Public participation promotes sustainable decisions by recognizing and communicating the needs and interests of all participants, including decision makers. 4. Public participation seeks out and facilitates the involvement of those potentially affected by or interested decision. 5. Public participation seeks input from participants in designing how they participate. 6. Public participation provides participants with the information they need to participate in a meaningful way. 7. Public participation communicates to participants how their input affected the decision In order to increase the stakeholder engagement, IAP2 also introduce a spectrum that can be used as a standard in the decision-making process. Herewith the scheme: 4. Communication Mechanism. In order to build the trust, the company should need two-way communication with their all stakeholders. The best communication mechanism will give good results in gathering and delivering the information. The information can be related with the company’s report or stakeholders’ update. The company that is able to perform two-way communication with their stakeholders absolutely has their own perception. - Such as the companies are required to recognize the community association (if any) as a media to gain information from the community as well as to give information from the companies related to their activities or else. - If the association in community is not exist then the company can help the community to build the effective communication or dialogue with them. IV. Conclusion & Recommendation