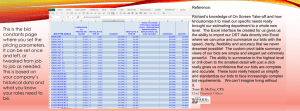
Q1(4 marks) / What is the problem of the share space algorithm in
advertisement

Philadelphia University Lecturer: Dr. Nameer N. EL-Emam Internal Examiner: Dr. Raad Alwan Module Name: Adv.Operating System Module Number: 750434 Second Exam 14/5/2015 Faculty of Information Technology Department of CS Marking Scheme Semester two 2014-2015 One hour Basic Part Objective: The aim of this part is to check student abilities to understand the basic of Processors allocation algorithm in DOS. Q1(5 marks) / Bidding algorithm tries to turn the computer system into a small economy, processors picking the highest bid from all bids sent before. Answer the following: a) What is the benefit of selecting the highest bid? b) What is the expected system performance if a processor selects a bid randomly? c) What is your suggestion to improve the bidding algorithm if we have more than one highest bid? d) Some time the kernel increases or decreases the process’s bid with respect to the time. Explain the circumstances for this dynamic bedding. Ans: A) Processors, which auction their cycles off to the highest bidder to gain high profit. If we select bids randomly then the processor profit will be down. B) The benefit of selecting the highest bids is to assign the process to the most proper processor with respect to many features (speed, memory size, presence of floatingpoint hardware, and other features). C) If we have more than one highest bids, scheduling all bids with the same level in the one queue of selected processor according to the policy FCFS to avoid starvation, or assign the equivalence bids to different processors with the same features. D) The kernel increases or decreases the process’s bid with time due to the amount of available resources in the system that are needs by process. Where the amount of resources are changed through the time, and if we have enough resources then the process’s bid is high. Q2(5 marks) / Find the objective function of the figure below using Bokhari's algorithm. The edge (e) in the processes graph has two weights, w1(e) and w2(e). Calculate the values of two weights of the above processes graph. OF= max(6+7, 2+8+9) + 3 = max(23,19)+3=19+3= 22 3 w1(e) Sm y 2 8 y 10 m 1 process 1 can move to P 2 then y 6 w1(e) 6 10 16 w 2( e ) C 3 3 Familiar Part Objective: The aim of this part is to check student abilities to understand processors’ scheduler and process policy algorithms in DOS. Q3(5 marks) / Let us define the following information of six processes working on two parallel processors. Apply ELS and ETS to show the time analysis of each processor with load balance and minimum time (if possible) Unfamiliar Part Objective: The aim of this part is to check student abilities to compute the system performance in DOS. Q4(5 marks)/ Assume we have application run on 10 processors with the total computation time of the concurrent portion is equal to 50 sec. Compute the optimal sequential processing time if the optimal concurrent processing time at ideal system is equal 20 sec. and the ratio of the total computation time needed for parallel algorithm to the time for the optimal sequential algorithm is 10. According to above given data then, - n=10 processors - total computation time of the concurrent portion = - optimal concurrent processing time at ideal system is OCPTID=20 sec - RP is the ratio of the total computation time needed for parallel algorithm to the time for the optimal sequential algorithm is =10 - Find optimal sequential processing time OSPT p i OSPT OSPT RP p RP i 50 5 10 OR p i OSPT OCPTid n n OCPTid RP pi OCPTid n OSPT n OCPTid RP 50 20 10 10 20 5 10 p i 50 sec