Translation and Protein Synthesis: DNA to Protein
advertisement
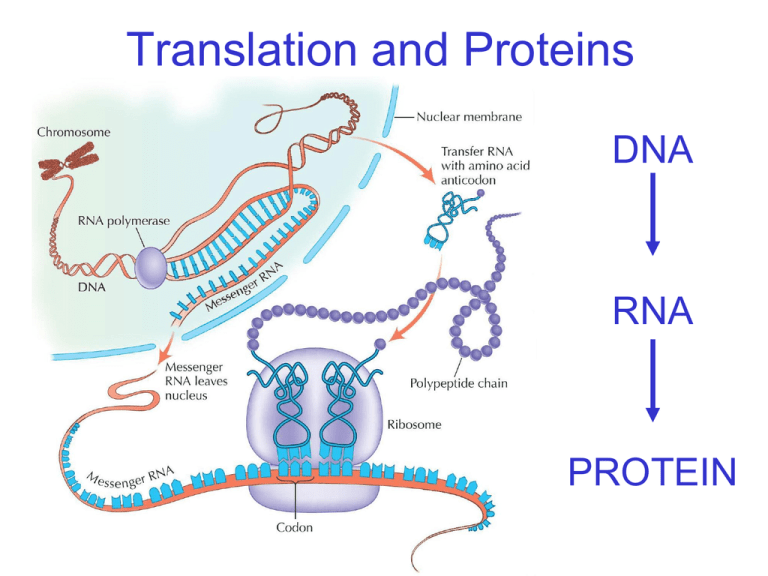
Translation and Proteins DNA RNA PROTEIN The Genetic Code • the language of RNA is read in groups of 3 bases – A, U, C, G Codon • a group of three bases on mRNA – Start Codon • signals the beginning of a protein chain • AUG • always brings the amino acid methionine – Stop Codon • signals for the end of protein synthesis • UAA, UAG, or UGA • does not code for any amino acids Anticodon • a group of three bases on tRNA that bind to the mRNA codon – bind in a complementary fashion • A with U • C with G • each tRNA brings a specific amino acid into place based on the genetic code The Genetic Code is… Based on Codons from mRNA Translation • decoding of an mRNA message into a chain of attached amino acids (protein) • cells use information from mRNA to produce a specific protein by linking amino acids together Steps of Translation Translation Animation Steps of Translation 1. a ribosome attaches to the mRNA 2. tRNA molecules bring specific amino acids to the ribosome in the right sequence as specified by the mRNA codons Steps of Translation 3. amino acids are continually hooked together by the ribosome until a stop codon is reached 4. the ribosome releases the new protein Translation and Proteins DNA RNA PROTEIN Replication, Transcription, & Translation Concept Map replication transcription DNA translation protein RNA Other Resources • Book pages for help on Transcription and Translation – Pg. 208-214