Protein Synthesis: Translation Process Explained
advertisement

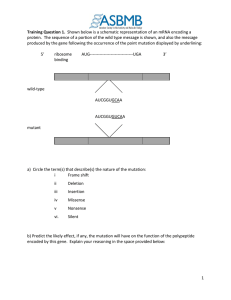
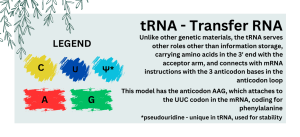
What is Protein Synthesis? Protein Synthesis or Translation is process in which the sequence of nucleotides on the mRNA is used to make different protein of different functions. How does it work? When transcription ends mRNA is produced and then the mRNA moves to the ribosome to start the translation process. Step 1 Translation begins at AUG (codes for methionine), the start codon. Each tRNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to the bases of a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon and then a lot of tRNA try matching their complementary anticodon until one matches. The ribosome then continues matching tRNAs to mRNAs. Step 2 The ribosome joins two amino acids together forming a peptide chain and breaks the bond between the previous amino acid and its tRNA. Then that tRNA leaves the ribosome allowing the next tRNA to match its anticodon to the mRNAs codon. Step 3 This process continues until the stop codon is found (UAA, UAG, UGA) which code for no amino acid, indicating that the polypeptide chain is done and the mRNA is released from the ribosome. And from there one the amino acid chain is formed making a protein. Done By: Ismail Mousa Osama Al-Amoudi Ahmed Saber Abdulaziz Omran Jihad Omara