Chapter 6: Review
advertisement
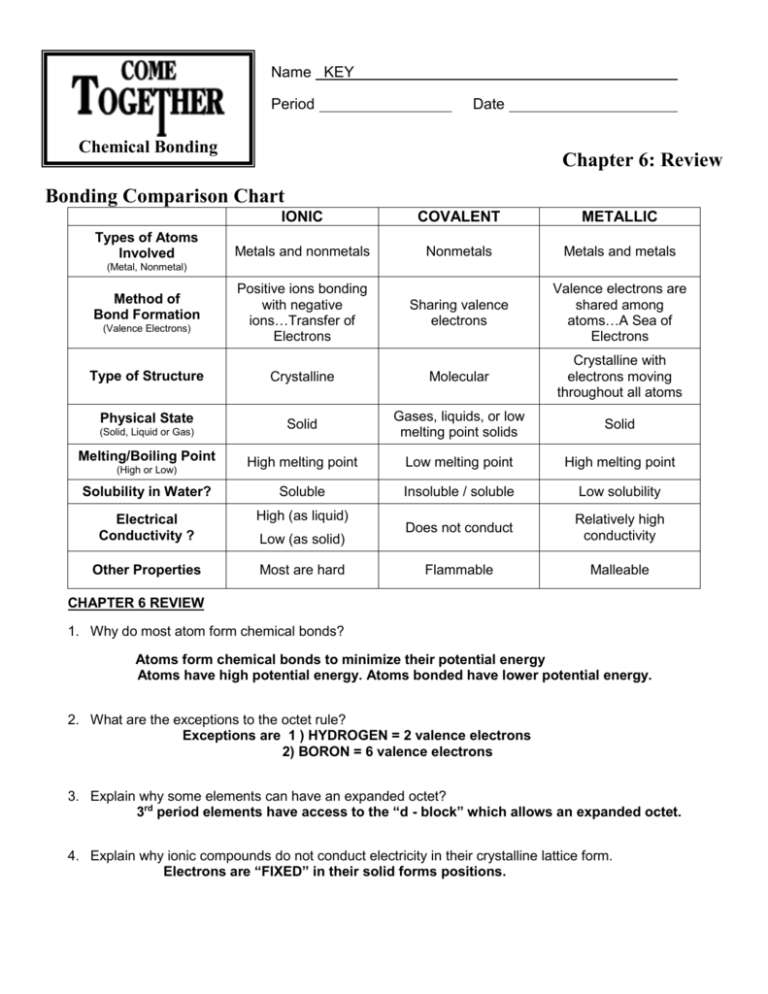
Name KEY Period Date Chemical Bonding Chapter 6: Review Bonding Comparison Chart IONIC COVALENT METALLIC Metals and nonmetals Nonmetals Metals and metals Positive ions bonding with negative ions…Transfer of Electrons Sharing valence electrons Valence electrons are shared among atoms…A Sea of Electrons Type of Structure Crystalline Molecular Crystalline with electrons moving throughout all atoms Physical State Solid Gases, liquids, or low melting point solids Solid High melting point Low melting point High melting point Solubility in Water? Soluble Insoluble / soluble Low solubility Electrical Conductivity ? High (as liquid) Does not conduct Relatively high conductivity Other Properties Most are hard Flammable Malleable Types of Atoms Involved (Metal, Nonmetal) Method of Bond Formation (Valence Electrons) (Solid, Liquid or Gas) Melting/Boiling Point (High or Low) Low (as solid) CHAPTER 6 REVIEW 1. Why do most atom form chemical bonds? Atoms form chemical bonds to minimize their potential energy Atoms have high potential energy. Atoms bonded have lower potential energy. 2. What are the exceptions to the octet rule? Exceptions are 1 ) HYDROGEN = 2 valence electrons 2) BORON = 6 valence electrons 3. Explain why some elements can have an expanded octet? 3rd period elements have access to the “d - block” which allows an expanded octet. 4. Explain why ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in their crystalline lattice form. Electrons are “FIXED” in their solid forms positions. 5. Identify bond types as either ionic, metallic or covalent HCN:__Covalent___ Fe: _Metallic___ PbO:_Ionic___ Si: _Covalent____ 6. A molecule of which of the following compounds contains a double bond? a) C3H8 c) C2H4 b) C2H6 d) C2H5OH e) CH4 7. A compound that exhibits resonance is: a) SO2 b) N2 c) CO2 d) HCl e) NH3 8. The best example of a non-polar molecule containing polar bonds is a) F2 c) CO2 b) SO2 d) PCl3 9. Which of the following is non-polar molecule? a) F2O b) PCl3 d) NO21+ e) NO21- c) PCl3 d) PCl5 e) SO3 c) O2 2- d) HO2 1- c) SO2 10. Which of the following compound has an expanded octet? a) H2O b) PH3 11. Which contains the shortest oxygen-oxygen bond? a) O2 b) O3 12. Which of the following molecules has the shortest bond length? a) N2 b) O2 c) Cl2 d) Br2 e) l2 13. Which of the following has zero dipole moment (i.e. is non-polar molecule)? b) NO21- a) H2O d) SO3 2- c) CCl4 e) HF 14. Ionic bonds are the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged atom. What determines their ionic strength? Explain 1) SIZE (distance) of the atom 2) ↑ size (distance) α ↓electrostatic force Magnitude (amount) - PRODUCT of the charges involved 15. Arrange the following types of attractions in order of increasing strength: Covalent, Electrostatic, Ionic, Dipole-dipole, Hydrogen and London Dispersion forces. IONIC Electrostatic (Ion-Ion) COVALENT Hydrogen Bonding Dipole-Dipole London Dispersion w/ FON POLAR NONPOLAR 16. What is the difference between intramolecular and intermolecular bonding? INTRAmolecular force: holds atoms together in an ionic, covalent or metallic bond. INTERmolecular force: force is BETWEEN molecules or formula units. 17. Identify the types of INTERMOLECULAR forces for the following chemical compounds (HINT: Dipole-Dipole, Electrostatic, Hydrogen or London Dispersion) NaCl : ____ELECTROSTATIC CO2: ___L.D. _____________________ H2CO : __L.D. \ DIPOLE-DIPOLE NH3: _L.D. \ DIPOLE-DIPOLE \ _HYDROGEN 18. True or False ___T___ a) Water is a polar molecule ___F____ b) Pyramidal molecules have two unshared electron pairs on the central atom. ONE LONE PAIR ___F___ c) A molecule cannot be non-polar if it contains only polar bonds. ___T___ d) A molecule consisting of 2 atoms is always linear. ___T__ e) Polar molecules have stronger attractions for each other than non-polar molecules have. 19. Describe the TWO factors that determine whether a molecule is polar or non-polar. 1) SYMMETRY 2) ELECTRONEGATIVITY DIFFERENCE 20. Define electronegativity. How does it relate to the intermolecular force between molecules? Electronegativity – is a relative scale used to determine an element ability to grab electrons. ↑ ΔEN α ↑ intermolecular force (dipole - dipole force) 21. Explain why Chlorine (Cl2) is a gas, bromine (Br2) is a liquid, and iodine (I2) is a solid. Be very specific! Intermolecular force (IMF) is responsible for the different states of the halogens. Chlorine, Bromine & lodine are all NONPOLAR MOLECULES which implies their only intermolecular force is LONDON DISPERSION FORCE. ↑ Atomic size α ↑ London Dispersion Force 22. Rank the following substance from strongest to weakest intermolecular force: He NH3 NF3 NaCl __NaCl_ > __ NH3___ > __ NF3___ > __ He ___ Electrostatic Hydrogen Dipole London Dispersion 23. Rank the following substances from strongest to weakest intermolecular force: HF F2 FCl ____HF____ > ___FCl___ > ____F2_____ Hydrogen Dipole London Dispersion 24. CENTRAL ATOMS – Most of the time SINGLE atoms become the central atom. However if you are required to determine the central atom, it must meet the best two out of three requirements: 1) Atom with the largest number of valence electrons 2) Atom with the largest atomic radius 3) Least electronegative atom **Note: _Hydrogen___ and __Halogens____ can not be central atoms. 25. Explain why nonpolar molecules usually have much lower surface tension than polar ones. Nonpolar molecules have NO attraction for each other, therefore they have a significantly lower surface tension (invisible skin) than polar molecules. 26. Rank the molecules from lowest to highest polarity. PH3 PF3 NH3 NF3 ___PH3____ < __ NH3 ____ < __ NF3____ < ___ PF3 _____ ΔEN = 0 ΔEN = 0.9 ΔEN = 1.0 ΔEN = 1.9 27. Which of the following has dispersion forces as its only intermolecular force? CH4 HCl C6H13NH2 NaCl CH3Cl 28. Rank the following substances from strongest to weakest intermolecular force Calcium Chloride Potassium Chloride Sodium Chloride __CaCl2_____ > ___KCl____ > ___NaCl____ 29. CH3CH2CH3 (propane) or CH3CH2CH2CH3 (butane) has the highest melting point because they both have the same IMF (London Dispersion) however butane has the higher molecular weight. 30. Draw the lewis structure, identify the shape, state whether it is polar or nonpolar and identify the one with lowest boiling point? PH3 H2S HCl SiH4 ΔEN = 2.1 – 3.0 = 0.9 Lowest Boiling Point SHAPE: SHAPE: Trigonal Pyramidial SHAPE: Bent SHAPE: Linear Tetrahedral NONPOLAR or POLAR NONPOLAR or POLAR NONPOLAR or POLAR NONPOLAR or POLAR