Genetics Notes

Genetics Unit
Genetics = the field of biology devoted to understanding how characteristics are
transmitted from parents to offspring
- was founded by the work of Gregor Mendel
Heredity = the transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring
Mendel
- “father” of modern genetics = laid the groundwork
- experimented with garden peas
- looked for traits = specific characteristics
- P
1 generation = parental generation
- F
1 generation = offspring of the parental generation
- F
2
generation = offspring of the F
1
generation
- Mendel’s 1 st Law = Law of Segregation
1) Organisms inherit two copies of each gene, one from each parent
2) Organisms donate one copy of each gene in their gametes.
- Mendel’s 2 nd Law = Law of Independent Assortment
1) The presence of one trait does not affect the appearance of another trait
Basics of Genetics
- Gene = a segment of DNA on a chromosome that controls a specific trait
- because chromosomes come in pairs, genes come in pairs
- Allele = each of several forms of a gene
- aka: letters
- capital letters = dominant alleles - lowercase letters = recessive alleles
- each allele has a specific location on a chromosome (= locus)
- Homozygous = both alleles are alike
- homozygous dominant = both capital letters = BB
- homozygous recessive = both lowercase letters = bb
- Heterozygous = alleles are different = Bb
- Genotype = genetic makeup of an organism
- consists of alleles (letters)
- Phenotype = the appearance of an organism as a result of its genotype
- aka: what does it look like
- human phenotype can be altered by behavior
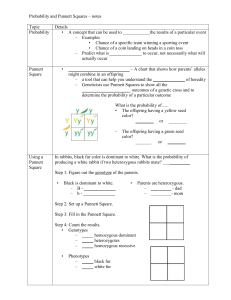
- Probability = # of desired outcomes
# of possible outcomes
- can be expressed as a fraction, decimal, ratio, or percentage
- example: If a bag of M&M’s has 30 yellow, 22 red, 13 brown, 6 orange, and 4 blue M&M’s, what is the probability of selecting a yellow M&M?
Monohybrid Cross = a cross between individuals that involves one pair of traits
Example: Black hair (B) in guinea pigs is dominant to brown hair (b)
Example 1: Homozygous Dominant X Homozygous Dominant
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Example 2: Homozygous Recessive X Homozygous Recessive
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Example 3: Homozygous Dominant X Heterozygous
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Example 4: Homozygous Recessive X Heterozygous
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Example 5: Heterozygous X Heterozygous
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Example 6: Testcross
= an individual of unknown genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual
- can be used to determine the genotype of any phenotype that is dominant b b
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Example 7: Incomplete Dominance
= the F
1
Generation will have a phenotype in between that of the parents
Example: Red flowers (R ) and White flowers (r ) can make Pink flowers (Rr )
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Example 8: Codominace
= when both alleles for a gene are expressed in a heterozygous offspring
Example: Red coat color (R ) in horses is codominant with white coat color (R’)
to make a horse that shows a mix of red and white coat (RR’).
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Dihybrid Cross = a cross between individuals that involves two pairs of traits
Example: Black hair (B) in guinea pigs is dominant to brown hair (b) and rough coat (R ) is dominant to smooth coat (r )
Example 1: Homozygous Dominant x Homozygous Recessive
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio
Example 2: Heterozygous x Heterozygous
Genotypic Ratio
Phenotypic Ratio