SBI 3U REVIEW SHEET – GENETICS
advertisement

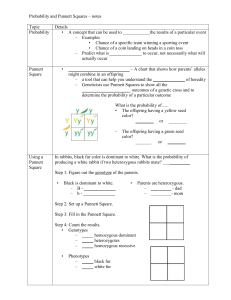
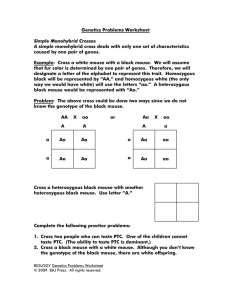
SBI 3U REVIEW SHEET – GENETICS 1. Terms you should know: hybrid Punnet Square allele purebred incomplete dominance F1 generation Gregor Mendel P generation multiple alleles codons nitrogen bases cell cycle cytokinesis haploid diploid monohybrid dihybrid gene dominant heterozygous recessive homozygous F2 generation DNA structure nucleotides mitosis anaphase telophase crossing over non-disjunction 2. Imagine a disease controlled by a dominant allele. Babies born with this disease die before they are born. What implication does this have (e.g. dominance when the allele kills those who carry it)? With respect to this allele, what would your genotype be? The genotypic ratio of the class? 3. How are mitosis and meiosis different? Similar? What is the purpose of the extra division in meiosis? 4. With the treatment of diseases such as haemophilia, more people bearing these genes are surviving to reproductive age. What will happen to the numbers of recessive disease-carrying alleles in the human population as a result of this? Explain. Problems 1. In rabbits, short hair is dominant over long hair. If a heterozygous short-haired rabbit is crossed with a longhaired rabbit, what percentage of the F1 generation will be long-haired? 2. In sheep, a white coat is dominant to a black coat. A white ram (male sheep) is mated with 3 ewes (female sheep). Ewe A, which is black, gives birth to a white lamb. Ewe B, also black, gives birth to a black sheep. Ewe C, which is white, gives birth to a black sheep. What are the genotypes of the four parents? 3. In humans, brown eyes are dominant to blue and the ability to float in mid air is recessive to the inability to float. A blue eyed man who cannot float (but is heterozygous for that trait), and a woman with brown eyes (homozygous) who can float, are planning on having a family. The woman would really like a child that has blue eyes and can float a) What is the probability that she will get her wish? b) State the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of the offspring. 4. In turtles, thick shell is dominant over thin shell, and the ability to tango is dominant over inability to dance the tango. A female turtle that has a thin shell and is homozygous for ability to dance the tango is mated to a trait sex chromosome genotype phenotype sex-linked characteristic probability gamete co-dominance meiosis interphase prophase centriole spindle fibres epigenetic polygenetic male turtle that has a thick shell and cannot dance the tango. You know that the male turtle’s mother had a thin shell. a) Give the genotype and phenotype of the parents. b) What is the probability of producing thick-shelled, tangodancing turtles? c) Give the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of the F1 generation. 5. In chocolate rabbits, the allele for type of chocolate is a type of incomplete dominance. Purebred bunnies can be dark chocolate or white chocolate, but people have seen some light brown “milk” chocolate bunnies. If a dark chocolate bunny is mated with a milk chocolate bunny what are genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the F1 generation. 6. In bees, the alleles for body colour display co-dominance. When a yellow-bodied bee is crossed with a black-bodied bee, the offspring are all striped black and yellow. a) If a baby bee is striped, what are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of its parents? b) If a baby bee is black, then what are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of its parents? 7. A woman with blood type O and a man with blood type AB have 8 children. How many of them will have type O like their mother? AB like their father? Type A? Type B? 8. John with blood type A and Julie with blood type B have children. If John’s mother and Julie’s father both had type O blood, what is the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of their children? 9. In rats, the ability to talk is a recessive, sex-linked (X) allele. a) Show the cross between a talking male and a non-talking (homozygous) female. Of the offspring, how many males/females can talk? b) Show the cross between a speechless male and a talking female who is heterozygous for the trait. Give the genotypic and phenotypic ratios for F1. Unit Review p179-183