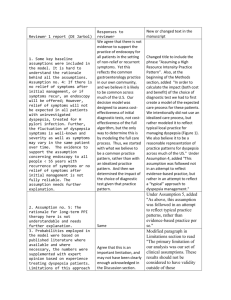
Hpylori
advertisement

Community Pharmacy Helicobacter Pylori ‘Test and Treat’ Enhanced Service Specification December 2005 Produced by: Medicines Management Team North Sheffield Primary Care Trust Firth Park Clinic North Quadrant Firth Park Sheffield S5 6NU Tel: (0114) 2716338 Fax: (0114) 2716293 Contents Page 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Introduction Service Description Rationale Aim and intended service outcomes Service Outline Duties of participating Surgeries Duties of participating Community Pharmacists Patient Pathway 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 8 9 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Management of patients with dyspepsia as per NICE guideline Who should be referred for endoscopy? Who should be referred for H. pylori ‘test and treat’ How should uninvestigated dyspepsia be managed? How should GORD be managed How should Peptic Ulcer Disease be managed? How should Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia be managed? How should patients be reviewed? 9 9 9 10 10 11 11 11 10 10.1 10.2 10.3 The 13C-Urea breath test Choice of test Description of breath test Supplies of test 12 12 12 12 11 12 13 14 15 16 Eradication therapy Training Untoward events and complaints Documentation Service funding and payment mechanism Duration of service 12 13 13 13 13 13 Appendix 1 Referral Form for Breath Test for Diagnosis of H pylori (HP1) 14 Appendix 2 Patient Information Leaflet – Instructions pre - H pylori breath test 15 Appendix 3 Standard Operating Procedure for H pylori breath test 16 Appendix 4 Procedure Form for Diabact UBT (HP2) 17 Appendix 5 Pharmacy record summary form (HP3) 19 Appendix 6 Standard Operating Procedure for supply of H pylori eradication therapy 20 2 Appendix 7 Patient Information Leaflet: Your H pylori treatment 21 Appendix 8 Communication Form: H pylori result (HP4) 22 Appendix 9 H pylori test and treat patient record 23 Appendix 10 Declaration of prescription exemption 24 Contacts 25 3 1. Introduction 1.1. NICE guidelines on the management of dyspepsia were published in August 2004 (NICE Clinical Guideline17). Two key priorities for implementation include Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication in appropriate patients and the appropriate use of endoscopy services. 2. Service Description 2.1. The pharmacy will carry out H. pylori breath tests on patients referred to them via a written direction from a general practitioner. 2.2. The pharmacist will subsequently treat H. pylori positive patients with eradication therapy under a Patient Group Direction (PGD). 2.3. The pharmacist will offer advice on the management of dyspepsia to patients. 2.4. The pharmacy will communicate the results in a routine and robust manner to the general practice. 3. Rationale 3.1. 40% of the population have dyspeptic symptoms. Of these the majority will have non-ulcer or functional dyspepsia on endoscopy, i.e. normal endoscopy. 3.2. More is spent on treating dyspepsia than on any other drug group. It accounts for 9-10% of the national drug budget. 3.3. Gastroenterology services in Sheffield are under considerable strain at present, especially the endoscopy waiting lists in relation to the management of patients with dyspepsia. As part of trying to improve gastroenterology services in Sheffield there is a desire to streamline services for patients with dyspepsia. 3.4. A significant number of patients currently have exploratory gastroscopies to check for underlying pathology. This procedure is unpleasant for patients and should be used efficiently and for appropriate patient groups. 3.5. The 13C-Urea Breath test is recognised as being the non-invasive test of choice for identifying H.pylori status and has completely superseded near-patient serology testing. Serology identifies antibodies to the H.pylori bacteria, however this does not show if the infection is active or not, merely that the person has had it in the past. Therefore serology should not be used if re-testing for H.pylori. 4 3.6. H.pylori is a bacteria strongly associated with peptic ulcer disease (PUD) – 95% of duodenal ulcers and 70% of gastric ulcers. Eradicating it from these patients reduces recurrence rates. Eradicating it from patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia (NUD) reduces symptoms. NICE recommends H.pylori testing and eradication in patients with PUD, NUD and as an intervention for uninvestigated dyspepsia. 4. Aim and intended service outcomes 4.1. To improve the care of patients with dyspepsia symptoms through the provision of a standardised effective & evidence based H. pylori test and treat service. 4.2. To ensure that all patients with dyspepsia requiring a H. pylori test as per NICE guidelines have access to this test in primary care and are given eradication therapy if positive. 4.3. To ensure that all requests for endoscopy are appropriate and only those patients with ALARM symptoms are referred to secondary care. An individualised approach to endoscopy has to be adopted. 4.4. To provide a means by which H. pylori 13C-Urea breath testing can be performed in primary care. 4.5. To improve access and choice for patients. 4.6. To improve primary care capacity by reducing medical practice workload related to the management of dyspepsia symptoms. 5. Service Outline 5.1. The pharmacy must have a consultation area, which provides a sufficient level of privacy and safety. 5.2. The pharmacy must have continuity of pharmacist providing the service. 5.3. The pharmacy contractor has a duty to ensure that pharmacists and staff involved in the provision of the service have relevant knowledge and are appropriately trained in the administration of the H. pylori breath test and all other aspects of the service. 5.4. The pharmacy contractor has a duty to ensure that pharmacists and staff involved in the provision of the service are aware of and operate within the protocols and guidance detailed in the service specification. 5.5. The pharmacy will maintain records of the consultations performed and any medicines supplied (using the HP forms provided), to ensure effective ongoing service, delivery and audit. 5 5.6. The agreed PGDs will be used and only pharmacists who have gained accreditation in providing eradication treatment under a PGD issue to treatment and advice to H. pylori positive patients. 5.7. The pharmacy will: Provide advice to patients on the management of dyspeptic symptoms. Refer to general practitioner where appropriate. 5.8. The PCT will provide training on the administration of the H. pylori breath test to pharmacists and pharmacy staff. 5.9. The PCT will provide accredited training on the PGD for eradication therapy for pharmacists 6. Duties of participating Surgeries 6.1. GPs should refer patients who meet the criteria identified in this service specification for a H. pylori breath test to a participating pharmacy. 6.2. Surgeries should record the test results and all other relevant information in the patients’ medical notes. 6.3. Surgeries should co-operate and liase with community pharmacists operating the service. 7. Duties of participating Community Pharmacists 7.1. Patients should only be accepted into the service on presentation with a referral card (form HP1; appendix 1) signed by a GP of a participating surgery. 7.2. A member of the pharmacy team who has been trained in undertaking the H. pylori breath test will perform the test as per the protocols detailed in the service specification and complete procedure form (form HP2; appendix 4). 7.3. A pharmacist will deal with results. 7.4. Patients with positive H. pylori results will be contacted and managed by a pharmacist accredited to issue eradication therapy under a PGD to arrange an appropriate consultation time for the patient to present for treatment. 7.5. Patients requiring eradication therapy will be charged prescription charges as appropriate. Pharmacists should ensure that patients exempt from prescription charges have completed and signed the declaration of exemption of prescription charges (see example form in appendix 10). 6 7.6. The pharmacy will complete the appropriate communication forms (form HP4; appendix 8) and send to GP. 7.7. The pharmacists will submit claim/activity forms monthly (form HP3; appendix 5). 7.8. The pharmacy will audit the service annually. 7.9. The pharmacy will keep records of all consultations. A summary record form may be used to assist with this – see appendix 9. 7 8. Patient Pathway Patient presents to the GP with dyspepsia. No Alarm symptoms and symptoms not suggestive of GORD. GP completes referral form (appendix 1) and refers patient to community pharmacy for a H. pylori breath test. GP also gives patient information leaflet ‘Your Helicobacter Pylori Breath Test’ with pre-test instructions (appendix 2). Patient presents at pharmacy with referral form Member of the pharmacy team undertakes H. pylori breath test as per standard operating procedure (SOP) (appendix 3) and completes procedure form (appendix 4). Member of the pharmacy team completes summary form (appendix 5). On receipt of a H. pylori breath test result, pharmacist to contact patient by telephone and inform of the results. If result positive Pharmacist to invite patient back to pharmacy for eradication therapy as per Patient Group Direction. Refer to SOP for eradication therapy (appendix 6). Provide patient with ‘Your Helicobacter Pylori Treatment’ information leaflet (appendix 7). If result negative Pharmacist to offer patient diet and lifestyle advice and OTC therapy if appropriate. Advise patient to see GP if symptoms persist. Pharmacist to complete communication form and send to GP (appendix 8). Member of the pharmacy team to complete and submit summary form monthly. – (see appendix 5). 8 9. Management of patients with dyspepsia as per NICE guideline 9.1. Who should be referred for endoscopy? Urgent referral for endoscopy is indicated for patients of any age with dyspepsia presenting with ALARM symptoms. o Alarm symptoms: Chronic gastrointestinal bleeding Progressive unintentional weight loss Progressive difficulty swallowing Persistent vomiting Iron deficiency anaemia Epigastric mass Suspicious barium meal Patients over 55 with unexplained* and persistent** recent onset dyspepsia. *’Unexplained’ is defined as a symptoms and or sign that has not led to a diagnosis being made by the primary care professional after initial assessment of the history, examination and primary care investigations (if any). ** ‘Persistent’ refers to the continuation of specified symptoms and/or signs beyond a period that would normally be associated with self-limiting problems. The precise period will vary depending on the severity of symptoms and associated features, as assessed by the healthcare professional. In many cases, the upper limit the professional will permit symptoms and/or signs to persist before initiating referral will be 4-6 weeks. (Extracted from NICE Clinical Guidelines 17) 9.2. Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia and without alarm signs is not necessary. Who should be referred for H.pylori ‘test and treat’? 9.2.1. Patients who should be tested Patients (aged 18+) with dyspepsia (no ALARM symptoms) and without typical reflux symptoms. Patients (aged 18+) with dyspepsia (no ALARM symptoms) without typical reflux symptoms whose symptoms have not improved with lifestyle advice or antacid/H2RA / PPI trial. Patients who have received antibiotics for H pylori (detected at endoscopy or by previous breath test) but have continuing symptoms. To confirm eradication the test must be carried out at least 4 weeks after completing the course of treatment. 9 Patients with previously documented evidence of gastric ulcer (but not had H. pylori eradication) and no recent change in symptoms. 9.2.2.Patients who should not be tested 9.3. 9.4. Patients with ALARM features; these patients should be referred. Patients aged under 18 (not licensed) Patients with previous diagnosis of duodenal ulcer: eradication therapy without prior testing is now recommended for those patients that have not had eradication therapy before. Patients with symptoms typical of gastro-oesophageal reflux. There is insufficient evidence of benefit (and some evidence of harm) in eradicating H. pylori from patients with GORD. Patients who have received antibiotic therapy for any reason within the previous 4 weeks - this may suppress H pylori and thus give a falsely negative result. These patients may be tested 4 weeks after completion of their course of antibiotics. Patients who have received treatment with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) within the previous 2 weeks - they may suppress H pylori and thus give a falsely negative result. These patients may be tested 2 weeks after stopping PPIs. How should uninvestigated dyspepsia be managed? Patients with dyspepsia without alarm signs and symptoms not suggestive of GORD should be tested and treated for H.pylori. Patients who have had eradication but whose symptoms recur should be managed with a PPI and stepped down to the lowest dose required to control symptoms. Patients who test negative for H.pylori should be offered a PPI for one month and then reviewed. How should GORD be managed? Patients with GORD should be given a full-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) for 1 or 2 months and then reviewed. If symptoms recur after initial treatment a maintenance dose PPI should be used to control symptoms, with a limited number of repeat prescriptions. 10 9.5. 9.6. How should PUD be managed? Patients with PUD should stop their NSAIDs if used. Patients with PUD should be tested for H.pylori infection and offered eradication if positive. An endoscopy to confirm healing post eradication therapy is only needed in patients with gastric ulcer. If symptoms persist and patients are H.pylori negative then a maintenance dose PPI should be used as required. How should NUD be managed? 9.7. Patients with endoscopically determined NUD should be tested for H.pylori and treated if positive, followed by symptomatic management and periodic monitoring. How should patients be reviewed? Patients requiring long-term management of symptoms for dyspepsia should be offered an annual review of their condition, encouraging them to try stepping down or stopping treatment. A return to self-treatment with antacid or alginate therapy (prescribed or over the counter) may be appropriate. Patients should be offered lifestyle advice, including advice about healthy eating, weight reduction and smoking cessation. 11 The 13C-Urea breath test 10. 10.1. Choice of test The 13C-Urea Breath test is recognised as being the non-invasive test of choice for identifying H.Pylori status and has completely superseded near-patient serology testing. In a systematic review of 30 published studies, 13C-urea breath tests were more accurate than serological tests. The 13C-Urea breath test can also be used post eradication to confirm that treatment has been successful. Serological tests are of no value in confirming successful eradication as the antibody remains in the blood stream long after successful eradication. 10.2. Description of 13C-Urea breath test 10.3. On the basis of convenience and cost, DIABACT UBT is the Urea breath testing kit of choice. The test involves the collection of breath samples before and after the ingestion of a 13C-Urea tablet. If H. pylori is present in the stomach it produces the enzyme urease, which breaks down the ingested 13C-Urea to ammonia and 13CO2. The samples are sent away for laboratory analysis and a result is provided within 48 hours. The post dose breath sample will contain this 13CO2 if H. pylori is present. Analysis and test tubes for breath samples are included in the kit provided. 13C-Urea 13C- is a stable isotope and therefore has no associated radioactivity. Supplies of test Breath tests will be obtained under contract by the PCT and supplied to providers For practices participating in this service breath tests should NOT be prescribed on FP10 unless a patient is unable to swallow the Diabact tablet. An alternative breath test could then be prescribed by FP10. 11. Eradication therapy 11.1. For patients who test positive, a 7-day, twice-daily course of treatment consisting of lansoprazole 30mg, amoxicillin 1 g and clarithromycin 500 mg (HeliclearTM) should be given under a PGD. For patients 12 allergic to penicillin the PGD for lansoprazole, clarithromycin and metronidazole should be used. 11.2. Eradication is effective in 80–85% of patients. 11.3. Pharmacists will be reimbursed the cost of the Heliclear™ (or individual components where used) plus VAT. Requirements for patients who normally pay for NHS prescription charges also applies under a PGD. 12. Training 12.1. The PCT will provide training to the community pharmacists participating in the scheme. 12.2. Each community pharmacy manager must ensure that all staff involved in providing any aspect of care under the scheme have the necessary training and skills to do so. 13. Untoward events and complaints 13.1. It is a condition of participation in the pilot service that pharmacists and GPs give notification to the PCT clinical governance manager of any clinical governance issues or untoward events in relation to the pilot. 13.2. All complaints in relation to the service should be submitted to the complaints manager at North Sheffield PCT. 14. Documentation 14.1. Pharmacies are to complete summary form and submit to the PCT monthly. 14.2. Practices are to document procedure in the patients’ notes on receipt of the communication form from the pharmacy. 15. Service Funding and Payment mechanism 15.1. The PCT agrees to pay £15 per breath test and to reimburse the pharmacy for the cost of the Heliclear™ (or individual components used) plus VAT, minus prescription charges where applicable. 15.2. The payments will be made monthly as per the Service Level Agreement. 16. Duration of Service 16.1. The service will run to the date specified in the service level agreement. 13 Appendix 1. (Form HP1) Referral Form for Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobacter Pylori infection. Patients Name: Patients Address: NHS number: Date of Birth: Telephone no: I confirm that the patient has dyspepsia but none of the following: ALARM symptoms GORD symptoms Over 55 with unexplained and persistent recent onset dyspepsia. I authorise that the above person be tested for Helicobacter Pylori infection by using Diabact UBT 13C-urea breath test. (Read Code: 3167) I understand that if the H.pylori test is positive the patient will be offered H pylori eradication therapy under a PGD. Does the patient have: An allergy to penicillins? Y/N An allergy to metronidazole, clarithromycin or lansoprazole? Y/N Severe renal or hepatic impairment? Y/N If this service were unavailable would this patient have been referred for a gastroscopy? Y/N GP Name: ____________________________________ Signed: ______________________________________ Date: _______________________________________ GP stamp: 14 A list of participating pharmacies will be printed on the reverse of the referral form. Appendix 2: Instructions pre – Helicobacter pylori breath test. What do I have to do before the test? W hat will happen next? So that the test works properly it is important that you make sure that: send away your The pharmacy will test and a r range to contact you you have not eat en for 6 hours before taking the test — It is a good idea if possible to arrange to have your test in the morning and delay your breakfast until after the test. a f ter about a you have not taken any What if I still have any questions ? of your stomach medicines (e.g. Omeprazole or Lansoprazole) for two weeks. week and give you your r e sults. At this point the pharmacist will discuss with you if you will need treatment or not. If you have any further questions about H pylori, your test or your result ask y ou have not taken any your community pharmacy antacids such as Peptac or Gaviscon in the last 24 hours staff, GP or practi If you are in any doubt about which medicines ma y interfere with the test then ask your pharmacist Helicobacte r Yo u r d o c t o r w i l l h a ve d i s c u s s e d w i t h yo u w h y t h e y h a ve r e f e r r e d yo u t o b e t e s t e d f o r H P yl o r i . T h e m o s t comm on reasons ar e: I f yo u h a ve a s t o m a c h ulcer I f yo u h a ve s ym p t o m s o f indigestion that won’t go a w a y d e s p i t e h a vi n g u s e d m edication I t i s t h o u g h t t h a t H P yl o r i alters the linin g of the stom ach and can be t he cause of st om ach ulcers a nd indigestion. breath test. H elicobacter pylori is, explain about the test and tell you what you need to do before you have the test What is a b reath test? T h e H P yl o r i b r e a t h t e s t i s w h e r e a s a m p l e o f yo u r b r e a t h i s t e s t e d t o s e e i f yo u a r e i n f e c t e d w i t h H P yl o r i . How do I arrang e m y test? Go to on e of the c om m uni ty pharm acies listed o n th e back o f yo u r r e f e r r a l c a r d . T h e y w i l l d i s c u s s w i t h yo u w h e n y o u c a n h a ve t h e t e s t . Before doin g an y othe r tests fo r indig estion Why is it a prob lem? Your doctor has referred you for a Helicobacter pylori This leaflet will tell you what Medicines Management Team North Sheffield PCT Firth Park Clinic North Quadrant Sheffield S5 6NU Telephone 0114 2716338 Review Date: Dec 2007 Who ne eds to be test ed for H Py lori? It is one of the m ost com m on infections in the UK alt hough m o s t p e o p l e d o n o t e ve n k n o w t h a t t h e y h a ve i t . Patient Information ce nurse. What is Hel icoba cte r Pylo ri? p yl o r i ( o r H P yl o r i a s i t i s m ore com m only called) refe rs t o a b ac te rial infec tion that can be foun d in t he stom ach or sm all intestine. Your Helicobact er Pylor Breath i Test Yo u r d o c t o r w i l l d e c i d e i f yo u n e e d a n y f u r t h e r t e s t s afte r this one How can I b e tested fo r H Pylori? B y yo u r d o c t o r r e f e r r i n g yo u to the com m uni ty pha rm acy yo u c a n h a ve a s i m p l e b r e a t h t e s t t o s e e i f yo u a r e i n f e c t e d w i t h H p yl o r i o r n o t . What w ill I hav e to do? F i r s t yo u w i l l b e a s k e d t o b l o w into a tube. After this is do ne yo u w i l l b e a s k e d t o swallow a whole tablet w ith a d rink of w ater. After waiting fo r 10 m inutes yo u w i l l b e a s k e d t o b l o w i n t o anothe r tube. It’s a sim ple as tha t \\Pctnorth\data\Library\Shared\Prescribing Folder\Pharmacy\H pylori Pilot\Forms,PILs,Quest\Amended docs\Pre PIL final.pub 15 Appendix 3: Standard Operating Procedure Summary of Helicobacter pylori breath test Procedure Pre-dose breath samples taken in duplicate Patient takes the 13C-urea tablet and waits 10 minutes Post dose breath samples taken in duplicate 1. Check that the patient is over 18 years of age. 2. Check that the patient can swallow tablets. If not refer the patient back to the GP who can prescribe an alternative test. 3. Certain medicines taken before the test may lead to false negative results. For example, the test should not be performed within 28 days of an antibacterial drug, within 14 days of a PPI (omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole) or within 24 hours of an antacid or H2 antagonist (ranitidine, cimetidine). Patients should be counselled to avoid taking their PPI for two weeks prior to the test. 4. Ideally the patient should have fasted overnight i.e. no breakfast on the day of the test and advised to attend for the test first thing in the morning. The patient should not have eaten for at least 6 hours before the test is performed. 5. The timing of post dose breath samples needs to be accurate- the manufacturers of Diabact UBT advise that they are collected 10 minutes after ingestion of the 13C-Urea tablet. 6. The two pre-dose and two post-dose samples are returned to the laboratory for analysis as per the method detailed in the Diabact UBT kit. 7. Complete procedure form. 16 Appendix 4 Procedure Form for Diabact UBT (Form HP2) Patient Details Patient name:………………….. NHS number: ….………… Patient Address:………………………………….. ……………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………… Postcode……………………… Tel no (home):………………………… Tel No (mobile):…………… GP name………………………………………………………… GP Tel No:………………………………………………………. Diabact UBT Batch number: Expiry Date: Questions pre test: Y N Questions to ask patient before the test is commenced 1. Have you had anything to eat in the last 6 hours? 2. Have you had antibiotics in the last 4 weeks? 3. Have you had a PPI in the last 14 days? 4. Have you had an antacid e.g. Gaviscon in the last 24 hours? If any of the above has been answered yes then do not proceed with the test. 17 Test Procedure 1. Begin the procedure by blowing into the two empty “00 minutes” tubes (BLUE LID) a) Unscrew the stopper b) Unwrap the straw and place it in the bottom of the tube c) Blow into the tube until the inside of the sample tube steams up d) Continue to breath through the straw while removing it from the tube and immediately seal the tube with the stopper. e) Repeat for 2nd tube Blue tube 1 Blue tube 2 2. Swallow the tablet together with a glass of water and wait 10 minutes Start time End time 3. Blow into the two empty “10 minutes” tubes (RED LID) a) Unscrew the stopper b) Unwrap the straw and place it in the bottom of the tube c) Blow into the tube until the inside of the sample tube steams up d) Continue to breath through the straw while removing it from the tube and immediately seal the tube with the stopper e) Repeat for 2nd tube Red tube 1 Red tube 2 4. Place the four tubes into the box. 5. Fill in the leaflet entitled “Patient details for breath analysis at Glasgow Royal Infirmary” 6. Stick the barcode label onto the leaflet 7. Close the white box with the leaflet inside and attach security sticker. 8. Place inside blue box. Attach address label and pharmacy stamp. Test carried out by:…………………………… Date…………….. Checked by……………………………………. 18 Appendix 5: Pharmacy Record Summary Form (Form HP3) Patient Gastroscopy Diabact Date Identifier Avoided? UBT test Y/N test done done Y/N Date test result received H. pylori result +/- Eradication therapy given Y/N/n/a Prescription Advice Comments Fee Eradication charge given claimed fee levied Y/N for H. claimed Y/N/n/a pylori Y/N/n/a test Y/N Totals: If the patient normally pays prescription charges, the same applies under the PGD – total claimed is the eradication fee minus the prescription charge. I confirm that I have carried out the above service and claim the following fee: £ Name: Date: Signature: Please make cheque payable to: Approved by PCT:……………………………………Date:……………………………. Please keep a copy for your records 19 Appendix 6. Standard Operating Procedure Summary of eradication therapy supply to patient under PGD Upon receipt of a positive result from Glasgow Royal Infirmary Recall patient to see pharmacist who is authorised to supply as per the HeliclearTM or the H. pylori eradication therapy PGD. Go through the exclusion criteria. If the patient is not allergic to penicillin use the HeliclearTM PGD. If HeliclearTM is out of stock use the H. pylori eradication therapy PGD and supply the individual drug components i.e. amoxicillin, lansoprazole, and clarithromycin. If the patient is allergic to penicillin supply metronidazole, lansoprazole, clarithromycin. Check cautions Check contra-indications If after checking interactions, cautions and exclusions the pharmacist has any concerns as to the suitability of eradication therapy, the GP should be consulted and informed of any potential consequences. If necessary then therapy should be withheld until such a time, as the pharmacist is satisfied as to the safety of supplying the drugs. Label the drugs to be supplied. Check if the patient normally pays NHS prescription charges, complete exemption form if patient exempt from charges. Supply to the patient, giving a Patient Information Leaflet and any relevant counselling and advice. The summary form should be completed. 20 Appendix 7: Patient Information Leaflet for eradication therapy Your Helicobacter Pylori Treatment Patient Information What treatment will I need for H Pylori? For effective treatment you will need to take a combination of medicines, two antibiotics and a medicine to reduce the acid in your stomach, all at the same time. How long will I have to take this combination? You will need to take this combination of medicines for one week. What should I expect after I have finished my course of treatment? After taking your course of medicines you may suffer from further symptoms similar to those you had before treatment. How long will this last? Usually these symptoms will settle on their own within a few weeks. What if I don’t get any better? If the symptoms have not settled down after a month then please return to your GP. Please consult you pharmacist or GP if you have any concerns about this. Medicines Management Team North Sheffield PCT Firth Park Clinic Tel: 0114 2716338 Review date: Dec 2007 21 Appendix 8. Form HP4 Communication Form: Helicobacter pylori result Patient name:…………………………………………. Patient Address:………………………………………. ………………………………………… ………………………………………… NHS number…………………………………………… Referring GP:………………………………………….. GP address:……………………………………………. ……………………………………………… ……………………………………………… Date of test:……………………………….. I confirm that the above patient presented for a helicobacter pylori breath test and the result was: Positive Negative Therefore the patient was given: Eradication therapy under a PGD Advice* * Patient (Hp negative only) given diet and lifestyle advice plus over the counter medication where appropriate. Advised to see GP if dyspepsia symptoms persist. Patient should be managed as per NICE guidelines. Any other comments: …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… Please add to the patient’s medical records and read code accordingly: 4JM1 Helicobacter pylori GI tract infection. 8BAC Helicobacter eradication therapy. 4JM0 Helicobacter pylori negative Name of Pharmacist: Date: Signature of Pharmacist: Pharmacy Stamp: 22 Appendix 9: H Pylori ‘Test and Treat’ Patient Record 23 Patients Name: Contact Number: GP/ Surgery: Yes No Comments GP referral form (HP1) complete Patient given pre-test PIL (Appendix 2) Appointment made Date: Test undertaken (Appendix 3) Date: Test procedure form (HP2) completed Record test identification code: Commence summary form (HP3) Counselling given (test,result.implications) Test kit completed (Form, box sealed & addressed) Test kit posted Date: Result received Date: Test result +ve -ve Patient informed of result Date: Positive result: Appointment made Date Treatment prescribed Counselling given Treatment PIL given (A7) Negative result: Counselling given Summary form ( HP3) completed GP Informed (HP4) Notes: 24 Test Reference Number………. Adapted from J Stephen Hawkins Ltd 25 Appendix 10: Declaration of Prescription Exemption To be completed by the patient The patient doesn’t have to pay because he/she: A B C D E F G L H K M × × × × × × × × × × × N × is under 16 years of age is 16, 17 or 18 and in full-time education is 60 years of age or over has a maternity exemption certificate has a medical exemption certificate has a prescription prepayment certificate has a war pension exemption certificate is named on a current HC2 charges certificate gets income support gets income-based jobseekers allowance is named on a working families Tax Credit NHS exemption certificate is named on a disabled persons Tax Credit NHS exemption certificate I am the patient I am the patient’s representative To the Patient - Please complete the declaration below:1. I am exempt from charges for the reason specified above. I understand that this is an NHS service and that the NHS will retain data relating to my use of the service and may contact me for my views. Signed (Patient)…………………………………….Date………………………………………………. Evidence of Exemption Seen: YES NO 26 Contacts: For further forms and general enquiries contact: Susan Rutherford in the Medicines Management team: (0114) 2716338 (Please note: Forms HP1, 2,3,4 and patient information leaflets will be supplied by the PCT) For clinical governance issues contact: Michelle Black or Paul Schatzberger (0114) 2716275 27