Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry-
advertisement

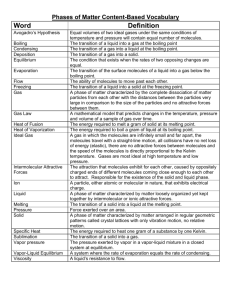
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry6th Edition – McMurry CHAPTER 8 VOCABULARY: Gases, Liquids, and Solids List created by: Tina Stewart - Spring 2010 Change of State- The change of a substance from one state of matter (gas, liquid, or solid) to another. Melting point (mp)- The temperature at which solid and liquid are in equilibrium Boiling point (bp) -The temperature at which liquid and gas are in equilibrium Kinetic-molecular theory of gases- A group of assumptions that explain the behavior of gases Ideal gases- A gas that obeys all the assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory Pressure (P)- The force per unit area pushing against a surface Gas laws- A series of laws that predict the influence of pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) on any gas or mixture of gases Gas constant (R) The constant R in the ideal gas law, PV = nRT Partial pressure- The contribution of a given gas in a mixture to the total pressure Intermolecular force- A force that acts between molecules and holds molecules close to one another Dipole- dipole force- The attractive force between positive and negative ends of polar molecules London dispersion force- The short- lived attractive force due to the constant motion of electrons within molecules Hydrogen bond- The attraction between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative O, N, or F atom and another nearby electronegative O, N, or F atom Vapor- The gas molecules in equilibrium with a liquid Vapor pressure- The partial pressure of gas molecules in equilibrium with a liquid Normal boiling point- The boilinh point at a pressure of exactly 1 atmosphere Crystalline solid- A solid whose atoms, molecules, or ions are rigidly held in an ordered arrangement Amorphous solid- A solid whose particles do not have an orderly arrangement Heat of fusion- The quantity of heat required to completely melt one gram of a substance once it has reached its melting point Heat of vaporization- The quantity of heat needed to completely vaporize one gram of a liquid once it has reached its boiling point