Air Pressure Notes - Delran Middle School
advertisement

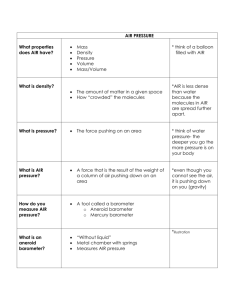
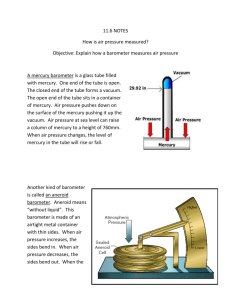
CHAPTER 3 THE ATMOSPHERE LESSON 2 AIR PRESSURE Air has mass, and also has density and pressure. Density = D = Mass = M Volume V Density - the amount of mass in a given volume. The greater the number of air molecules = the greater the density The lower the number of air molecules = the lower the density Pressure- a force applied to an area Air pressure- caused by the weight of air pushing on an area The air pressure at sea level is 14.7 lbs. per square inch. MEASURING AIR PRESSURE Barometer – an instrument used to measure air pressure 1. Mercury Barometer a long glass tube closed at one end and open at other closed end is almost a vacuum as air pushes down the level goes up 2. Aneroid Barometer “without liquid” an air tight metal chamber that is sensitive to changes in air pressure WEATHER REPORTS Forecasts- “uses inches of mercury” Maps- use millibars 1 inch of mercury = 33.86 millibars (ex; 980 mb) AIR PRESSURE AND ALTITUDE Altitude – the distance above sea level Air pressure decreases as you move further from the Earth’s surface (the air spreads out), so the density goes down Air pressure increases as you move closer to the Earth’s surface (the air molecules are closer), so the density goes up Cold air = more dense = higher air pressure Warm air = less dense = lower air pressure