Molecular Basis of Inheritance Review
advertisement

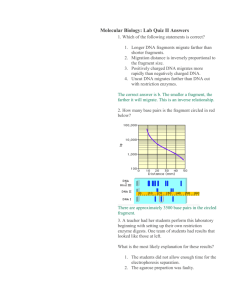
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Review Name ____________________________________ Define and explain the following processes Transcription Translation Transduction Translocation Transposon How does a typical virus (non-mutated ) infect and what does it infect? What is necessary for a DNA virus to complete a lytic cycle Define and give examples for each of the following: Prophage Provirus Vector What are the different kinds of viruses? What factors determine whether or not a gene is transcribed? Explain each of the following mutations and how they are different: Framshift Missense Nonsense Silent List the functions of the following: DNA ligase DNA Polymerase Primase Helicase Telomerase List the steps involved in PCR and briefly explain what happens in each. Explain the process of Gel Electrophoresis and how it is used to separate DNA fragments Describe the trp operon and the lac operon. What are there roles in the feedback mechanism that regulates protein product? Explain and draw the operon including the operator, and promoter regions What are prions? How do they work inside a cell? Give some examples. Explain the uses of RFLP’s (restriction fragment length polymorphisms) and cDNA (complementary DNA). Explain how retroviruses use reverse transcriptase. Why would it be beneficial to use reverse transcriptase to clone a human gene? What did the following scientists discover: Meselson and Stahl Rosalind Franklin Griffith Hershey and Chase Watson and Crick Chargaff List the roles of SNRPs, GTP, Poly A tail, exons, introns, codons, anticodons What acts as a primer to initiate the synthesis of a new strand of DNA? Where does a typical DNA virus make copies of its DNA in a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell? Look over the virus structure Practice Restriction Mapping 1. Below is a restriction map for the plasmid pGEN101 (total length=20 kb). Using this map as a guide, give the number of restriction fragments along with their associated lengths that would result from digesting pGEN101 with the restriction enzymes EcoRI, BamHI, and a combination of EcoRI + BamHI. Digest Performed: EcoRI……………………………….. BamHI……………………………… EcoRI + BamHI……………………. 2. Sizes of Fragments Obtained: Two freshman college students, interested in becoming gene jocks, performed the following set of restriction digests on a newly isolated plasmid, pBLA230. The reaction they carried out, along with the fragment obtained in single and double digest reactions were: Enzyme(s) HpaI HindIII HpaI + HindIII Fragment Lengths Obtained: 26 kb 13 kb, 6kb, 4kb, 3kb 7 kb, 6 kb (2), 4 kb, 3 kb Using this information, construct a restriction map of pBLA230. 3. As part of an undergraduate project, a student was attempting to construct a restriction map for the plasmid pUC23 using the restriction enzymes EcoRI and BamHI. After carrying out both single and double enzyme digest reactions and electrophoresing each reaction mix through an aragose gel, the picture below is obtained, showing the number of DNA fragments produced in each reaction, along with the sizes of each fragment. From this information, construct a restriction map of the pUC23 for enzymes EcoRI and BamHI.