Thirteen Colonies Study Guide
advertisement

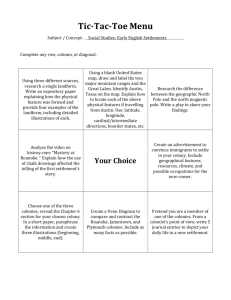
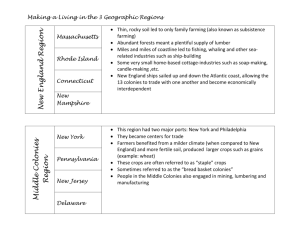
Thirteen Colonies Study Guide 1. Identify the location and region of each of the colonies. Be able to lable these on a blank map. New England Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Middle New York Pennsylvania New Jersey Delaware Southern Maryland Virginia North Carolina South Carolina Georgia 2. Briefly describe the climate, geography, and natural resources of each region. New England * Long, cold winters and short growing season * Rocky soil made farming difficult. Subsistence farming was common. * Thick forests provided wood for ship building. There was good fishing and whaling off the coast. These were some of the industries that supported the people. Middle * Mild winters and longer growing seasons; lots of sun and plenty of rain * Fertile soil made farming easy and allowed farmers to cash crops. * Wide rivers allowed farmers to transport their crops for sale and trade. * Sometimes these colonies were called the “Breadbasket Colonies” because they provided much of the food eaten in all thirteen colonies. Southern * Warm weather and very long growing seasons * The tidewater area near the coast was very good for growing and exporting crops * The backcountry was harder to farm, but many people had small family farms * The Southern colonies had small farms and large plantations where crops like tobacco, Indigo, and rice. * Southern colonies depended on slavery to provide most of the labor. 4. Know who these people are: Roger Williams and Anne Hutchinson: Dissenters who left Massachusetts & founded Rhode Island Metacomet (aka King Philip): Wampanoag leader who fought colonists over land Jonathan Edwards and Georgie Whitfield: ministers who led the “Great Awakening” William Penn: Quaker; Founder of Pennsylvania; believed in religious tolernace and freedom Benjamin Franklin: Philadelphia’s famous citizen (printer, scientist, inventor, government leader) James Oglethorpe: Proprietor and founder of Georgia 3. Define these terms * Town meeting: a gathering where colonists met to make decisions and vote on laws * Self-government: when people make laws for themselves * dissenter: a person who does not agree with the beliefs of his or her leaders * banish: to force someone to leave * proprietor: a person who owned and controlled all of the land in a colony * representative: someone chosen to speack and act for others * treaty: an official agreement between people or groups * free market economy: the people, not the government, decide what will be produced * free enterprise: system in which the people may start any business that they believe * artisan: a person who is skilled at making something by hand * laborer: person who does hard physical word * apprentice: someone who studies with a master to learn a skill or business * debtor: a person who owes another person money * import: a product brought INTO one country from another * export: a product SENT to another country and sold * Triangular trade: trade routes among Europe, Africa, North America, and the West Indies 5. Facts: Great Britain was the country that controlled the Thirteen Colonies Religion was an important part of the government in the Massachusetts Bay Colony Some people disagreed with Puritan leaders and left Massachusetts to form New Colonies The settlement of New England led to war with American Indians Philadelphia was the largest colony in the British Colonies The Middle Colonies were very diverse: people from many countires lived and worked together. Georgia was founded to help debtors and poor people (a debtor’s colony) Charles Town (now Charleston) was the largest and most important port city in the south. 6. Be able to explain the “Triangular Trade” and the role of slavery in the colonies ***Study the map on page 175*** There were slaves in all of the Thirteen Colonies The Triangular Trade route was between Europe, Africa, North America, and the West Indies Slaves were brought from Africa to the West Indies, and then on to the colonies The journey from Africa to the West Indies was called the Middle Passage Many slaves died during the journey due to disease and mistreatment The colonies depended on slaves to provide labor; eventually there were more slaves in the Southern colonies because they had mostly agricultural economies.