ch3 B5 funct react
advertisement

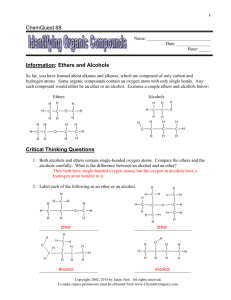
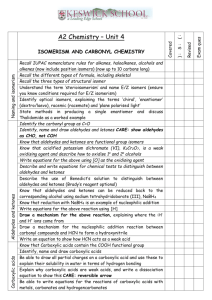
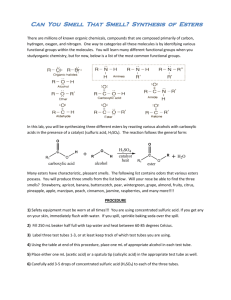
Unit 3 Chemistry – Reactions of Functional Groups Reactions of chloro-alkanes the presence of a highly electronegative Cl atom makes the chloroalkane a polar molecule the chlorine draws electrons away from its attached carbon, making the carbon susceptible to attack from negative ions, such as hydroxide ion OHchloromethane H H – C+– Cl– H – OH CH3OH + Clmethanol hydroxide R–Cl + OH- R-OH + Cl- chloroalkane hydroxide alkanol this reaction is a substitution reaction … OH being substituted for Cl polar molecules, such as water H2O and ammonia NH3 can also attack the C-Cl bond -----------------------------------------------------H chloroethane H3C – C+– Cl– H NH3 CH3CH2NH2 + HCl aminoethane ammonia R–Cl + chloroalkane NH3 ammonia R–NH2 + HCl amine --------------------------------------------------------------chloroethane H H3C – C+– Cl– H OH2 CH3CH2OH + HCl ethanol water R–Cl chloroalkane + H2 O water R–OH + HCl alkanol -------------------------------------------------------- Reactions of Alkanols ethanol has a highly polar molecule and is soluble in water alkanols, like ethanol, can undergo substitution reactions … methanol H silica catalyst H – C – OH CH3NH2 + H2O H aminomethane NH3 ammonia R–OH + alkanol NH3 ammonia R-NH2 + H2O amine ------------------------------------------------------- primary alkanols are oxidised to carboxylic acids a primary alcohol is one in which the OH group is attached to the end of the alkyl chain [or the end of an alkyl side chain] atmospheric oxygen can be the oxidant, but acidified dichromate or permanganate are the preferred laboratory oxidants CH3CH2OH(aq) [O2] ethanol in wine CH3COOH(aq) vinegar, so cork your wine! Note: the equation above is not a balanced redox equation … it is simply a schematic representation of the reaction path from alkanol to carboxylic acid CH3CH2CH2OH(aq) 1-propanol [Cr2O72-/H+] CH3CH2COOH(aq) propanoic acid ------------------------------------------------------------------------Reactions of Carboxylic Acids all carboxylic acids are weak acids, partially ionizing in water to form a weakly acidic solution CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+(aq) being acids, carboxylic acids react with bases, reactive metals and carbonates R-COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) R-COO.Na(aq) + H2O(l) carboxylic acids react with alkanols to produce esters [esterification reaction] Esters esters are volatile organic compounds [smells or flavours] esters contain the ester functional group and have the general structure … -CO-O-R ester functional group Forming Esters [condensation reaction; esterification] esters are formed by the condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and alkanol [ sulfuric acid often used as a catalyst] H2SO4 catalyst R-COOH(aq) + HO-R’(aq) carboxylic acid R-COO-R’(aq) + H2O(l) alkanol ester water the reaction is called a condensation reaction because water is a product esters are named by replacing the “anol” of an alkanol with “yl” and the “ic acid” of the carboxylic acid with “ate” propanol + ethanoic acid propyl ethanoate In the name, the alkanol name comes first, but sthe structure is usually shown with the carboxylic acid to the left. Polyesters a polyester is a copolymer made by the condensation polymerisation of a di-acid with a diol … HOCH2OH + HOOCCH2COOH + HOCH2OH + HOOCCH2COOH + etc. etc. diol di-acid diol … OCH2O-OCCH2CO-OCH2O-OCCH2COO… polyester polymer di-acid + lots H2O Reactions of Functional Groups 1. Using structural formulas for the reactants and products, illustrate the following organic reactions:(a) propan-1-ol, from 1-chloropropane (b) 2-aminobutane, from 2-chlorobutane (c) aminoethane, from ethanol ------------------------------------------------------------------------2. Butanoic acid can be formed from butan-1-ol. (a) Name the reaction involved in converting butan-1-ol to butanoic acid. (b) Name suitable reactants that could be used to facilitate this change. (c) Explain why butan-2-ol cannot be oxidised to form butanoic acid. ------------------------------------------------------------------------3. Write an equation illustrating that CH3CH2CH2COOH(aq) is a weak acid. ------------------------------------------------------------------------4. Synthetic pineapple flavour is the organic compound, ethyl butanoate. (a) Name the two reactants used to produce ethyl butanoate. (b) Name the type of reaction [give 2 alternative names] involved in the formation of synthetic pineapple flavouring. (c) Using structural formulas for all reactants and products, illustrate the formation of ethyl butanoate, including any catalyst employed (d) On the structural formula of ethyl butanoate, highlight and name the linking functional group. ------------------------------------------------------------------------5. Using structural formulas for all reactants and products, illustrate the formation of synthetic rum flavour, ethyl methanoate. -------------------------------------------------------------------------