File
advertisement
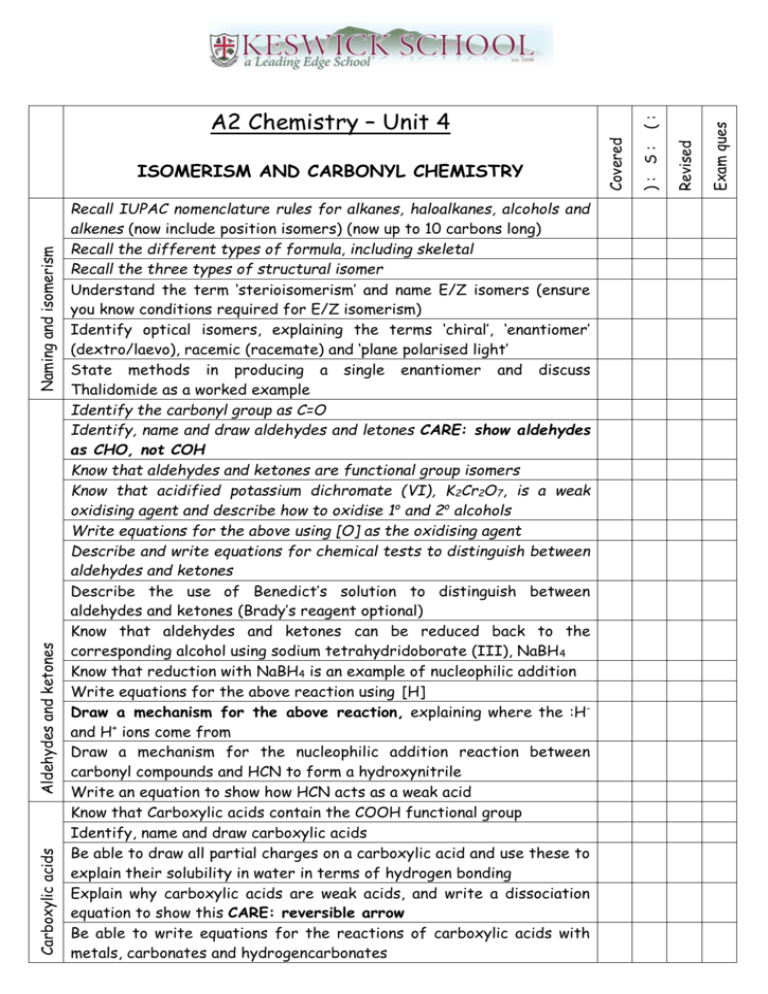
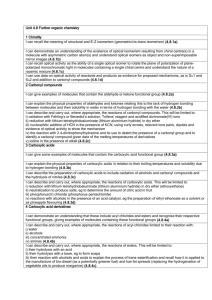
Carboxylic acids Aldehydes and ketones Naming and isomerism Recall IUPAC nomenclature rules for alkanes, haloalkanes, alcohols and alkenes (now include position isomers) (now up to 10 carbons long) Recall the different types of formula, including skeletal Recall the three types of structural isomer Understand the term ‘sterioisomerism’ and name E/Z isomers (ensure you know conditions required for E/Z isomerism) Identify optical isomers, explaining the terms ‘chiral’, ‘enantiomer’ (dextro/laevo), racemic (racemate) and ‘plane polarised light’ State methods in producing a single enantiomer and discuss Thalidomide as a worked example Identify the carbonyl group as C=O Identify, name and draw aldehydes and letones CARE: show aldehydes as CHO, not COH Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional group isomers Know that acidified potassium dichromate (VI), K2Cr2O7, is a weak oxidising agent and describe how to oxidise 1o and 2o alcohols Write equations for the above using [O] as the oxidising agent Describe and write equations for chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones Describe the use of Benedict’s solution to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones (Brady’s reagent optional) Know that aldehydes and ketones can be reduced back to the corresponding alcohol using sodium tetrahydridoborate (III), NaBH4 Know that reduction with NaBH4 is an example of nucleophilic addition Write equations for the above reaction using [H] Draw a mechanism for the above reaction, explaining where the :Hand H+ ions come from Draw a mechanism for the nucleophilic addition reaction between carbonyl compounds and HCN to form a hydroxynitrile Write an equation to show how HCN acts as a weak acid Know that Carboxylic acids contain the COOH functional group Identify, name and draw carboxylic acids Be able to draw all partial charges on a carboxylic acid and use these to explain their solubility in water in terms of hydrogen bonding Explain why carboxylic acids are weak acids, and write a dissociation equation to show this CARE: reversible arrow Be able to write equations for the reactions of carboxylic acids with metals, carbonates and hydrogencarbonates Exam ques Revised ): S: Covered ISOMERISM AND CARBONYL CHEMISTRY (: A2 Chemistry – Unit 4 Esters Fats, oils and biodiesel Acyl chlorides Know that carboxylic acids and esters are functional group isomers Know that esters contain the –COO- functional group Identify, name and draw esters Describe how to make an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, stating the role of the concentrated sulphuric acid Write equations for the above reactions, identifying which sections of the ester come from each of the reactants CARE: reversible Explain why the above reaction is a condensation reaction Give some properties and uses of esters State what a hydrolysis reaction is Describe the acid hydrolysis of an ester to produce a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, related to Le Chatelier’s principle Know that esters can be hydrolysed with bases e.g. NaOH, to produce a carboxylate salt and an alcohol CARE: reflux needed Write equations for the above reactions Know what saturated and unsaturated fatty acids are and the difference between a fat and an oil Know the structure of glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol) Show how a triglyceride (triester) can be made from glycerol and three fatty acids CARE: condensation to form 3 water Show the hydrolysis for the above reaction with NaOH to make glycerol, soap and fatty acids Describe how to react a triglyceride with methanol to make biodiesel Write an equation for the above reaction Evaluate how carbon neutral biodiesel may be Know that acyl chlorides contain the –COCl group, have the general formula CnH2n-1OCl, and how to name and draw them Write equations for the substitution reactions of acyl chlorides with water, alcohols, ammonia and amines (HCl produced) Explain why the above reactions are examples of nucleophilic additionelimination Draw mechanisms for the above reactions Know the structure for and how to name simple acid anhydrides Write equations for the reactions of acyl chlorides with water, alcohols, ammonia and amines (Carboxylic acid produced) Know equations for the formation of aspirin from ethanoic anhydride Discuss why aspirin is not made using an acyl chloride