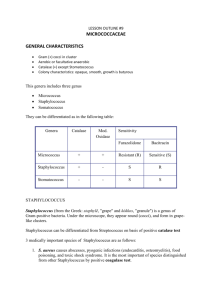
Introduction: Although the majority of microorganisms are either
advertisement

Introduction: Although the majority of microorganisms are either harmless or beneficial, certain species are capable of causing disease. The human body is home to approximately 90 trillion microbial cells some of which are opportunistic pathogens. Opportunistic pathogens are organisms that do not normally cause infections in healthy individuals, only when they enter into the body were they are not normally found or if a patient is immune-compromised do they cause infection. Modern clinical diagnosis of bacterial infections usually involves the use of the Gram stain and observation of cellular morphology, colony morphology, and biochemical testing. The Gram stain is the first step in identifying an unknown microorganism, based on the Gram stain reaction the proper battery of biochemical tests are used for further diagnosis. Cellular and colony morphology allows microbiologists to narrow the search when identifying the disease causing organism. Biochemical tests are tests that differentiate between bacterial species based on metabolic by-products. Biochemical testing is however based on percentages therefore they must be used in combination with the Gram stain and colony morphology in order for the correct identification of the disease causing bacteria. In this case study a patient presented to the hospital with a severe skin wound infection on the upper forearm. The wound area showed swelling localized to the site of infection with redness spreading from the wound. Applying pressure to the wound resulted in pain and oozing pus. The infection site was swabbed and Gram stained, additional swabs were taken for diagnostic testing. Based on the signs and symptoms and the initial Gram stain showing Gram-positive coccus arranged in clusters indicates the skin wound infection is most likely caused by an organism from the genus Staphylococcus. The following biochemical tests that will be discussed will determine if the causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus epidermidis which will allow for proper treatment. Materials and Methods: Sugar fermentation tubes A pure culture of the suspected pathogen was used for all biochemical tests. Sugar fermentation tubes include glucose, lactose, sucrose, and mannitol these are biochemical tests which test for an organisms ability to ferment sugar. A positive test is indicated by a color change from red to yellow indicating the production of an acid by-product. The pH must drop below 6.8 in order for a change to occur. Weak positives may present if the pH is close to 6.8, indicated by a color change from red to yellow-orange. To test for sugar fermentation capabilities one loopful of organism was aseptically inoculated into each of the four sugar tubes. Sugar tubes were then incubated for 24 hours at 37 degrees Celsius. Test for Motility Motility agar was used to test for the presence of flagella. A positive test is indicated by growth and media color change to violet/red. A spreading pattern into surrounding media may also be observed. Motility agar was incubated for 5 days at 37 degrees Celsius. Test for oxygen usage A fluid thioglycolate tube was used to test for this organisms capability to use oxygen during cell respiration. The upper portion of the agar medium contains the greatest amount of free oxygen because the gas may easily diffuse into the medium from the atmosphere. The large center zone contains a decreasing amount of oxygen because the gas has more difficulty reaching that portion of the medium. If turbid growth is only seen at the top of the media, this indicates an aerobic organism. If growth is observed throughout the entire media this indicates a facultative anaerobe. Fluid thioglycolate tubes were inoculated with one loopful of bacteria directly below the surface of the media, the loop was not agitated in the media only dipped as to not introduce oxygen into the lower portion of the media. The tube was then incubated at 37 degrees Celsius for 24 hours. Continue describing the tests you performed using the above format!!! Results (put in same order as you did for the materials and methods) Sugar fermentation Following incubation of the sugar fermentation tubes the results show that this organism fermented glucose, lactose, and sucrose indicated by the media changing to a yellow color. Gas was not recovered in the gluscose broth durham tube indicating a slow fermentation rate. The mannitol fermentation tube was weakly positive showing a yellow/orange color. Test for motility Following incubation of the motility agar results show this organism is non-motile indicated by growth only along the stab line from the inoculating needle. No swarming affect was observed. Continue describing your results using the above format!!!! Discussion (must compare results to Bergey’s manual for diagnosis!) Things to include: What was your organism? General description of your unknown: recap some of the major findings that helped you determine your unknown. Discussion of erroneous results. Provide a statement like I have below Analysis of biochemical testing indicates results consistent with Staphylococcus aureus. As mentioned biochemical testing is based on percentages 90% of the results reported are consistent with the characteristics described in Bergey’s Manual for Systematic Bacteriology. Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram positive coccus shaped bacterium that is usually characterized as catalase positive. The catalase test is one of the key tests used to differentiate Gram positive organisms such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus organisms. According to Bergey’s Manual S. aureus is classified as a Mannitol fermenter. The strain causing the skin wound infection described earlier only weakly fermented Mannitol. Longer incubation may have resulted in a strong positive result. The key test to conclude the causative agent for the skin wound infection described earlier was the growth and fermentation of Mannitol on Mannitol Salt Agar. The fermentation of Mannitol confirmed the organism was Staphylococcus aureus not Staphylococcus epidermidis. Name some notable diseases caused by this organism Discussion of virulence factors Propose Treatment Conclusion The human body is composed of approximately 100 trillion cells, only 10 percent of those cells are actually human cells the remaining 90 percent of cells are microorganisms which are mainly harmless or beneficial. When given the opportunity some species of normal microbiota are capable of causing disease. One such organism is Staphylococcus aureus, S. aureus is a Gram-positive coccus arranged in clumps. This organism is considered to be normal microbiota and equally known to cause diseases such as skin wound infections, Toxic shock syndrome, and food borne intoxication. Often infections caused by S. aureus are easily treated with antibiotics however, resistance to antibiotics such as methicillin is becoming more prevalent. Humans are constantly exposed to potential disease causing microbes including some found on the human body itself. To avoid a severe skin wound infection caused by S. aureus, such as the one described in this study, proper wound care should be administered promptly upon becoming injured.