Classification worksheet WORD
advertisement

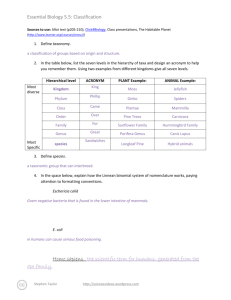
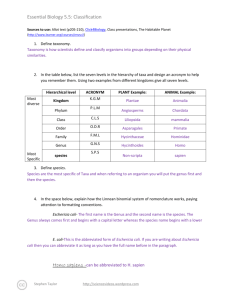
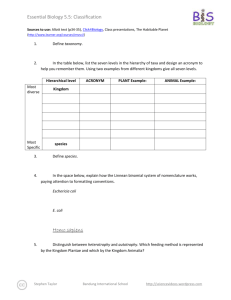
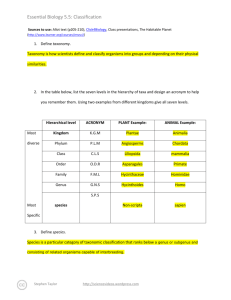
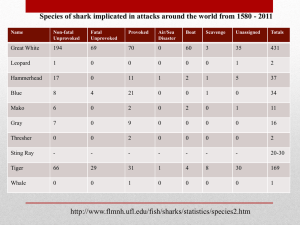
Essential Biology 5.5: Classification Sources to use: Allot text (p205-210), Click4Biology, Class presentations, The Habitable Planet (http://www.learner.org/courses/envsci/) 1. Define taxonomy. Taxonomy is the practice and science of classification. 2. In the table below, list the seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa and design an acronym to help you remember them. Using two examples from different kingdoms give all seven levels. Hierarchical level Most diverse Kingdom Phylum Most Specific 3. ACRONYM King Phillip PLANT Example: ANIMAL Example: Plantae Animalia Magnoliophyta Chordata Came Came Magnoliopsida Mammalia Order Over Asterales Carnivora Family For Asteraceae Felidae Genus Good Arcototos L. Acinonyx African daisy Acinonyx jubatus species Sandwiches Define species. Species is a term used to describe the taxonomic division that refers to animals of similar structure and descent and are able to breed among the group. 4. In the space below, explain how the Linnean binomial system of nomenclature works, paying attention to formatting conventions. Eschericia coli You must capitalize the first letter of the genus and if it is typed, it must also be written in italics. The genus goes first followed by the species and the species is never capitalized. If you are hand writing the name, it must be underlined. E. coli If you have mentioned the full name previously in your work, you can abbreviate it using a capital letter followed by a period and the species remains written the same way. Homo sapiens 5. Distinguish between heterotrophy and autotrophy. Which feeding method is represented by the Kingdom Plantae and which by the Kingdom Animalia? Heterotrophs relies on other organisms for food such as a tiger killing a dear for food. An autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food from simple substances such as a plant performing photosynthesis. Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 6. Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using external characteristics. Give examples. Non- vasuclar plants are plants without the systems required to circulate fluids such as veins, these plants are generally close to the ground because they cannot support a lot of growth such as moss. Vascular plants have the required systems to transport water throughout the plant and can grow much larger such as trees. 7. Have a go at using a dichotomous key here: http://www.scenicoregon.com/webanic/pages/animals.html Take the opportunity to build your vocabulary while completing this task. Think of an animal, answer the questions and work through the classification. No roots or stem, very simple, small leaves, furry appearance Roots, leaves and short stems. No lignin (no wood) Leaves are divided into sections and may be curled up Woody trees, have pine needles for leaves Roots, stems and leaves. Produce flowers. Stephen Taylor 50 cm 15 m 100m 100m http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Spores released from capsule at end of stalk (sporangium) Spores produced in sporangia, capsules under the leaves Seeds develop in female cones Seeds dispersed through fruits Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 8. Distinguish between the following phyla of animals, using external recognition features and giving examples. Check your answers here: http://www.scenicoregon.com/webanic/pages/map.html Invertebrates do not have a skeleton to support them such as jelly fish. Vertebrates have a skeleton that gives them support such as millipedes who have an exoskeleton. 9. Distinguish between these terms: Radial symmetry vs Bilateral symmetry vs Asymmetrical Radial symmetry is the symmetry about an axis (starfish). Bilateral symmetry is symmetry about a vertical plane (mirror image). Asymmetrical is the lack of symmetry. Motile vs Sessile Motile is the ability to move spontaneously and independantly. Sessile is the lack of movement independantly. 10. Design and apply a dichotomous key to distinguish between these Queensland shark species: 11. Look at the species names for the sharks in the chart. a. Stephen Taylor Which of the following pairs is most closely related? http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification b. Stephen Taylor A. Black Tip Reef Shark and White Shark B. Grey Reef Shark and Shortfin Mako C. Grey Reef Shark and Winghead D. Creek Whaler and Black Tip Reef Shark Explain your answer to a. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification The Black Tip Reef Shark and Grey Reed Shark are the most closely related because out of the 4 pairs they were the only two who shared the same genus making them the closest to the same species. c. Which of the following is/are true for the Great Hammerhead and Scalloped Hammerhead? i.They are two subspecies of the same species ii. They are two species in the same genus iii. They are members of the same order iv. They are from different phyla A. i only B. i and ii C. ii and iii D. iv only d. Which of the following is/are true of all of the sharks in the chart? i. i. They are members of the same species They are part of the same genus ii. They are part of the same class iii. They are part of the same kingdom Stephen Taylor B. i only C. i and ii D. ii and iii E. iii and iv http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com