Essential+Biology+05.5+-+Classification October 12th
advertisement
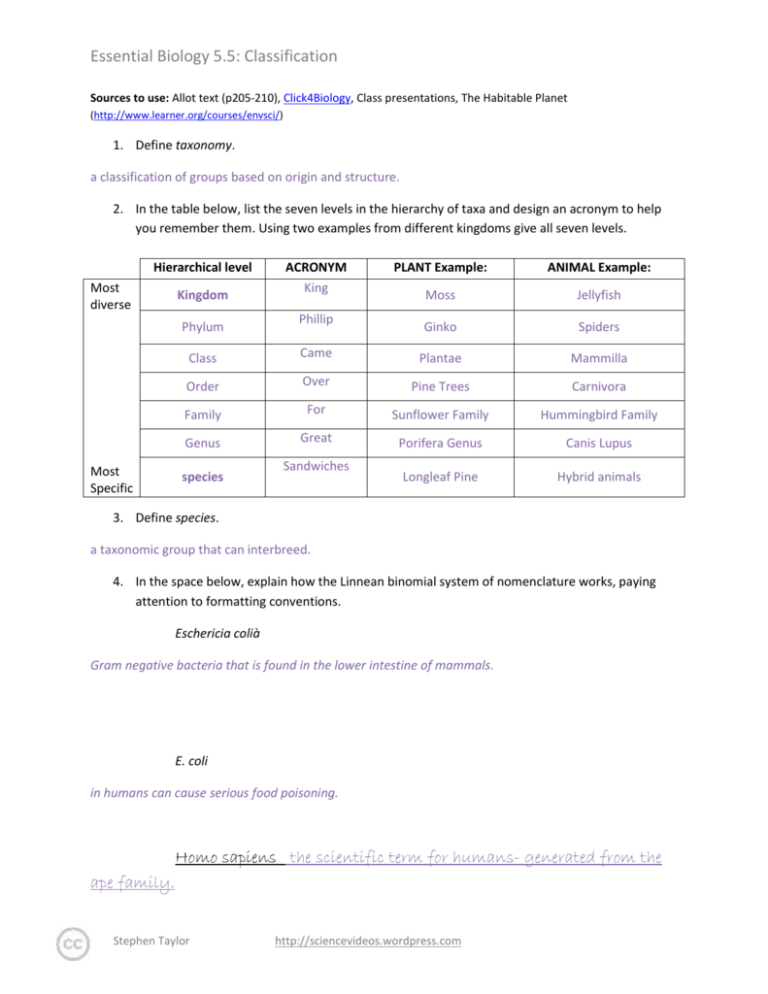
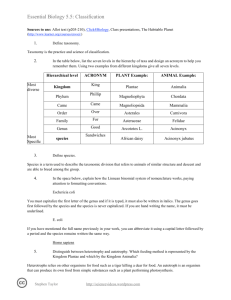
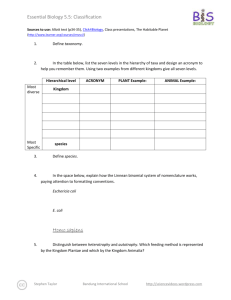
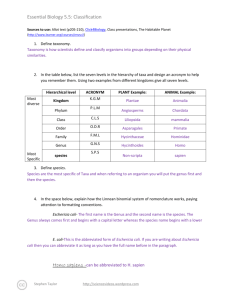
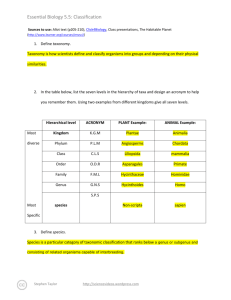
Essential Biology 5.5: Classification Sources to use: Allot text (p205-210), Click4Biology, Class presentations, The Habitable Planet (http://www.learner.org/courses/envsci/) 1. Define taxonomy. a classification of groups based on origin and structure. 2. In the table below, list the seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa and design an acronym to help you remember them. Using two examples from different kingdoms give all seven levels. Hierarchical level Most diverse Kingdom Phylum Most Specific ACRONYM King Phillip PLANT Example: ANIMAL Example: Moss Jellyfish Ginko Spiders Class Came Plantae Mammilla Order Over Pine Trees Carnivora Family For Sunflower Family Hummingbird Family Genus Great Porifera Genus Canis Lupus Longleaf Pine Hybrid animals species Sandwiches 3. Define species. a taxonomic group that can interbreed. 4. In the space below, explain how the Linnean binomial system of nomenclature works, paying attention to formatting conventions. Eschericia colià Gram negative bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of mammals. E. coli in humans can cause serious food poisoning. Homo sapiens the scientific term for humans- generated from the ape family. Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 5. Distinguish between heterotrophy and autotrophy. Which feeding method is represented by the Kingdom Plantae and which by the Kingdom Animalia? Autography is the process in which a species can make its own food while heterotrophy is when the specie (humans) can't make their own food and have to get it from another source. 6. Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using external characteristics. Give examples. Bryophytes- simplest of plants and generally small, 15-20 cm in height, and most reproduction is asexual. Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification Filicinophytes- ferns, they reproduce by spores, and are less than 1 inch in diameter. Coniferophytes- needle like leaves, reproductive system is similar to a flower; there are male and female cones. Angiospermophytes- seed bearing plant. 7. Have a go at using a dichotomous key here: http://www.scenicoregon.com/webanic/pages/animals.html 8. Distinguish between the following phyla of animals, using external recognition features and giving examples. Check your answers here: http://www.scenicoregon.com/webanic/pages/map.html Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 9. Distinguish between these terms: Radial symmetry a form of symmetry . that is arranged around a centre. vs Bilateral symmetry vs Asymmetrical symmetry on a vertical plane. a lack of symmetry. Motile vs Sessile -ability to move independently while sessile means permanently attached to something. 10. Design and apply a dichotomous key to distinguish between these Queensland shark species: Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 11. Look at the species names for the sharks in the chart. a. Which of the following pairs is most closely related? A. Black Tip Reef Shark and White Shark B. Grey Reef Shark and Shortfin Mako C. Grey Reef Shark and Winghead D. Creek Whaler and Black Tip Reef Shark b. Explain your answer to a. because they both have the same genus. c. Which of the following is/are true for the Great Hammerhead and Scalloped Hammerhead? i. They are two subspecies of the same species A. B. C. D. ii. They are two species in the same genus iii. They are members of the same order iv. They are from different phyla i only i and ii ii and iii iv only d. Which of the following is/are true of all of the sharks in the chart? i. They are members of the same species ii. They are part of the same genus iii. They are part of the same class iv. They are part of the same kingdom B. i only C. i and ii D. ii and iii E. iii and iv Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com