Essential+Biology+05.5+-+Classification
advertisement
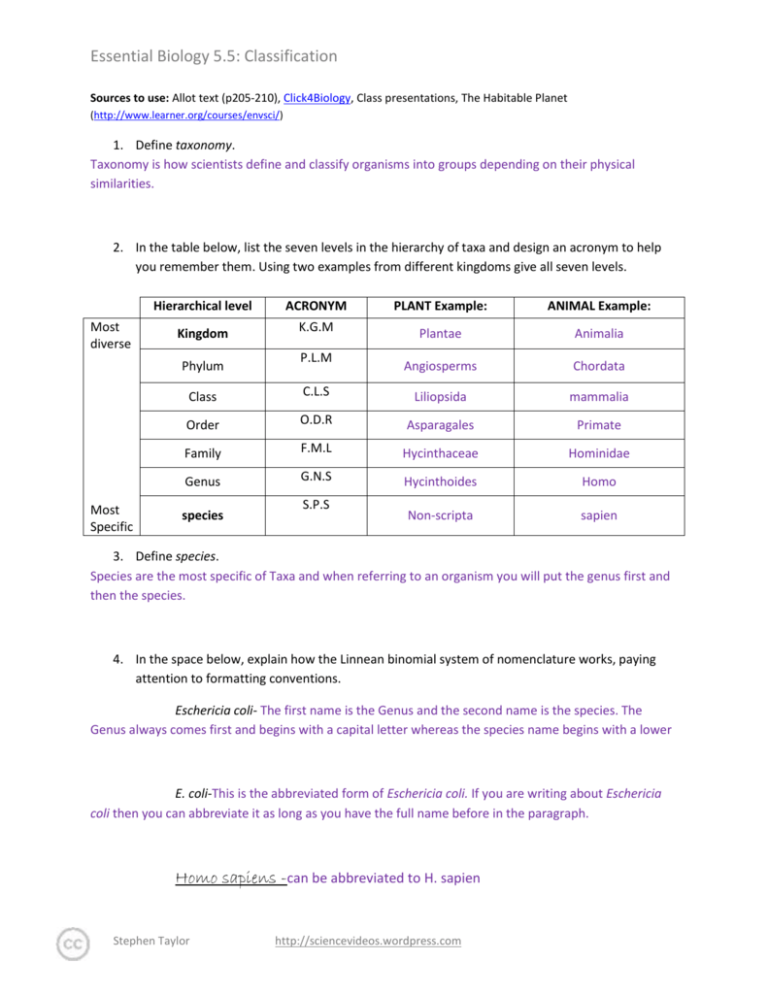
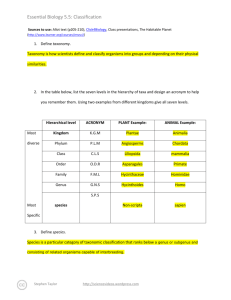
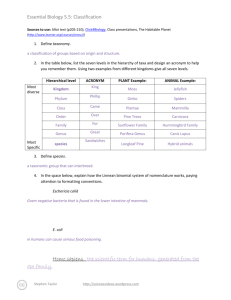
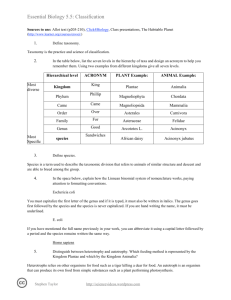
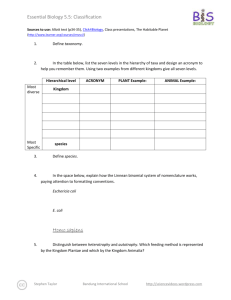
Essential Biology 5.5: Classification Sources to use: Allot text (p205-210), Click4Biology, Class presentations, The Habitable Planet (http://www.learner.org/courses/envsci/) 1. Define taxonomy. Taxonomy is how scientists define and classify organisms into groups depending on their physical similarities. 2. In the table below, list the seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa and design an acronym to help you remember them. Using two examples from different kingdoms give all seven levels. Hierarchical level Most diverse Kingdom Phylum Most Specific ACRONYM K.G.M P.L.M PLANT Example: ANIMAL Example: Plantae Animalia Angiosperms Chordata Class C.L.S Liliopsida mammalia Order O.D.R Asparagales Primate Family F.M.L Hycinthaceae Hominidae Genus G.N.S Hycinthoides Homo Non-scripta sapien species S.P.S 3. Define species. Species are the most specific of Taxa and when referring to an organism you will put the genus first and then the species. 4. In the space below, explain how the Linnean binomial system of nomenclature works, paying attention to formatting conventions. Eschericia coli- The first name is the Genus and the second name is the species. The Genus always comes first and begins with a capital letter whereas the species name begins with a lower E. coli-This is the abbreviated form of Eschericia coli. If you are writing about Eschericia coli then you can abbreviate it as long as you have the full name before in the paragraph. Homo sapiens -can be abbreviated to H. sapien Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 5. Distinguish between heterotrophy and autotrophy. Which feeding method is represented by the Kingdom Plantae and which by the Kingdom Animalia? Heterotrophs are organisms that consume other organisms for food (Kingdom Animalia). Autotrophs are organisms that make their own food (Kingdom Plantae). 6. Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using external characteristics. Give examples. No roots have stems and leaves 2 cm20cm asexual Stems, leaves and roots 15 meters asexual Roots, stems and leaves 6cm tall asexually Roots, stems and leaves 1 meter sexual 7. Have a go at using a dichotomous key here: http://www.scenicoregon.com/webanic/pages/animals.html Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification Take the opportunity to build your vocabulary while completing this task. Think of an animal, answer the questions and work through the classification. Flamingo -kingdom: Animalia -phylum: -class: aves -order: Ciconiiformes -family: Phoenicopteridae -Genus: Phoenicopterus -Species: ruber 8. Distinguish between the following phyla of animals, using external recognition features and giving examples. Check your answers here: http://www.scenicoregon.com/webanic/pages/map.html none Surface covered in pores. radial Tentacles around mouth. bilateral Body-flat, thin .no blood system bilateral Blood vessels visible bilateral Hard radula for feeding. bilateral Segmented body and legs. Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 9. Distinguish between these terms: Radial symmetry vs Bilateral symmetry vs Asymmetrical Radial- circular symmetry Bilateral- the left half is identical to the right half. Asymetrical- both sides are different. Motile vs Sessile Motile- organisms that re mobile and can move around. Sessile- organisms that stay in one place such as a plant that cannot move around on its own. 10. Design and apply a dichotomous key to distinguish between these Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification Queensland shark species: 11. Look at the species names for the sharks in the chart. a. Which of the following pairs is most closely related? A. Black Tip Reef Shark and White Shark B. Grey Reef Shark and Shortfin Mako C. Grey Reef Shark and Winghead D. Creek Whaler and Black Tip Reef Shark b. Explain your answer to a. They are in the same Genus. c. Which of the following is/are true for the Great Hammerhead and Scalloped Hammerhead? i. They are two subspecies of the same species ii. They are two species in the same genus iii. They are members of the same order iv. They are from different phyla A. i only Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification B. i and ii C. ii and iii D. iv only d. Which of the following is/are true of all of the sharks in the chart? i. They are members of the same species ii. They are part of the same genus iii. They are part of the same class iv. They are part of the same kingdom B. i only C. i and ii D. ii and iii E. iii and iv Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com