Unit 4 - Review Notes Answers4
advertisement

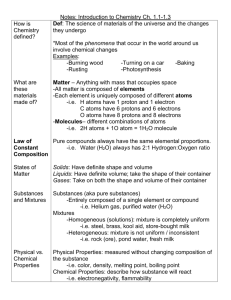
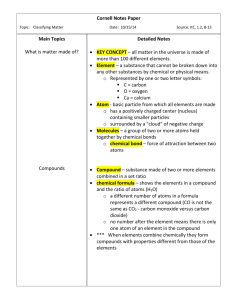
Unit 4: Interactions of Matter – Review Notes Main Idea 1. What is a chemical? name:_______________________ period: ______________ Supporting Details/Answer Anything made of matter is a chemical. 2. What is a chemical formula? A short way of writing chemical symbols for atoms that have bonded together. (e.g. H20) 3. How can you use chemical symbols and numbers in a chemical formula to figure out how many atoms of different elements are bonded? (e.g. C6H12O6) Use the periodic table to determine the name of an element based on its symbol. Numbers (called subscripts) tell you how many atoms of the element are present. The number refers to the symbol to the left. 4. How many types of mixtures are there? 3 types of mixtures 5. List the different types of mixtures and describe them. Solution: very small particles, homogeneous, no light scattering, no particle settling Colloid: small particles, homogeneous, light scattering, no particle settling Suspension: larger particles, heterogeneous, light scattering, particle settling Heterogeneous (hetero = other, generous = kind): possible to see the different parts of a mixture (e.g. trail mix) Homogeneous (homo = same, generous = kind): appears to be a single substance (e.g. salt water) Solutions and colloids: evaporation; the particles are not chemically combined, so evaporating one of them will leave the other; particles are too small to filer Suspension: filters, mechanical separation (e.g. tweezers), magnets, screens, etc. ; particles are big! Solute: The substance that is dissolved into a solvent to 6. What does it mean for a mixture to be heterogeneous or homogeneous? 7. How can you separate the different types of mixtures? Why do these methods work? 8. What are solutes and solvents? Give an example. 9. What does it mean for a chemical to be “soluble”? (e.g. solubility is the ability of a chemical to…) Is solubility a physical or chemical property of matter? 10. Describe what is happening when a solute dissolves in a solvent. Is this a physical or form a solution. (Kool-Aid powder in Kool-Aid) Solvent: The substance in which a solute is dissolved to form a solution. The chemical that is the greatest amount. (Water in Kool-Aid) The chemical has the ability to dissolve in another substance. Solubility is a physical property of matter. Dissolving salt into water does not create a new substance through chemical bonding. The particles are dispersed without bonding. Dissolving is a physical change where the particles of the substances mix equally but do not chemically Unit 4: Interactions of Matter – Review Notes name:_______________________ period: ______________ chemical change? Is a new chemical formed or do the substances equally disperse? Draw a picture. combine. 11. Why do chemical equations need to be balanced? Chemical equations need to be balanced because all of the ingredients (reactants) must be present in the products. In chemical reactions, no atoms are created or destroyed. Bonds between atoms are created and destroyed. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that all atoms must be accounted for. 12. Practice balancing equations: http://funbasedlearning.com/chemistry/chembalancer/ http://www.chem.vt.edu/RVGS/ACT/notes/scripts/bal_eq1.html 13. Describe the Law of Conservation of Mass In regular chemical and physical changes, no matter and how it applies to chemical and physical (mass) can be created or destroyed. This means that changes. even though atoms may move or recombine to form new substances (chemical) or change form (physical), all of the atoms must be accounted for. Example: 1 block of cheese = 100g ; cut it into two pieces and together, the pieces will still = 100g 14. What are properties of matter? Properties of matter are ways of describing matter. 15. Define chemical property of matter: 16. Define physical property of matter: 17. What are some clues of a chemical reaction? 18. What are the three possible outcomes when mixing chemicals together? 19. How can you slow down or speed up a reaction? A chemical property of matter can only be observed by reacting matter with other matter to create a new type of matter. Chemical properties describe the ability of a type of matter to react with other matter. A physical property can be observed without changing the matter into a new substance. (color, texture, density, solubility, state of matter, etc.) Clues: bubbling, foaming, new gas formed, precipitate (new solid), energy change (hot, cold, light, explosion, etc.), unexpected color or odor change There are three main outcomes: mixing, non-mixing, and chemical reaction. Speed up: add energy (heating); increase surface area (stirring, crushing); adding a catalyst (chemical that helps the reaction go faster) Slow down: remove energy (cool down); decrease Unit 4: Interactions of Matter – Review Notes name:_______________________ period: ______________ surface area 20. Describe the role energy plays in chemical changes. All reactions need energy to get started. Exothermic: releases energy (feels hot, emits light; etc.) Endothermic: continues to absorb energy (feels cold) 21. How are physical and chemical changes Physical Change: easier to reverse; can be reversed different? with a physical change; changes physical properties of a chemical; no new substance formed Chemical Change: results in a new substance; chemical change needed to reverse; original substances do not maintain properties; new substance has new properties 22. How are atoms, elements, compounds, Atom: basic unit of matter molecules and mixtures similar and Element: specific types of atoms with different different? Draw a picture or use symbols to numbers of protons, electrons, and neutrons and illustrate. physical/chemical properties (O, C, H or O2) Compound: 2 or more different elements chemically bonded to make a new substance (CO2) Molecule: elements chemically bonded; can be a new substance (H20) or same substance (O2); characterized by covalent bonds (not covered in class) Mixture: 2 or more substances combined without chemical bonds 23. Describe the process of making new When two or more substances react to make a new substances. What happens to chemical substance, the bonds between atoms may be bonds and what do we need to make new broken. This takes energy. The original atoms may substances? move around to recombine with different atoms. New bonds are formed which takes energy. The new substance(s) (products) are different than the original substances (reactants). No atoms are destroyed in the process due to the Conservation of Mass. This chemical reaction can be written by a chemical formula.