Physical Science Unit Outline Welcome to High School Science
advertisement

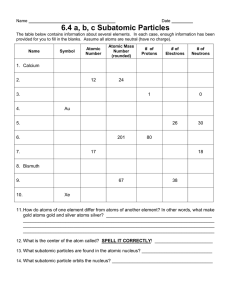
Physical Science Unit Outline Welcome to High School Science 1. Compare the fields of chemistry and physics. 2. What are the three main ingredients of science? 3. Give five specific examples of how science applies to your program area. 4. Compare direct and indirect observations and give an example of each from your program area. 5. Why are math skills important for scientists. 6. Why are reading and writing important skills for scientists? 7. How are theories, laws, and hypotheses related? 8. A theory ______________ be proven. 9. ______________ describe. ____________________ explain. 10. What does the acronym STEM stand for? Chemistry 1. Compare mass and volume. 2. Compare mass and weight. 3. Explain the concept of density and how it is calculated. 4. Explain the difference between physical properties and chemical properties. 5. Compare the three states of matter based on their properties 6. Compare elements, compounds, and mixtures. 7. Compare heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures. 8. All objects and materials in the world are made up of ___________________ 9. The basic building block of all matter is the _________________ 10. Explain why we use models to discuss atomic theory 11. Atoms are made up of subatomic particles called: 12. Compare the charges, masses, and location of these subatomic particles 13. Relate subatomic particles to the Atomic Number and Atomic Mass of an atom. 14. Come atoms, ions, and isotopes. 15. Compare and contrast ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. 16. Explain the difference between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds 17. Compare physical changes and chemical changes 18. When looking at a chemical equation, how do you tell the reactants from the products 19. Explain the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions 20. Compare acids and bases Energy 1. The ability to do work is called ______________ 2. Compare kinetic and potential energy 3. List and describe the major forms of energy 4. Describe the three normal states of matter in terms of energy, particle motion, and phase transitions 5. The source of practically all the energy on Earth is ________________ 6. Compare renewable and nonrenewable sources of energy 7. Compare and contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion 8. A byproduct of light is often _____________ and a byproduct of heat is often ____________ 9. Compare temperature and heat 10. Heat moves from an area of ______________ temperatures to an area of ____________ temperatures 11. An increase in temperature results in a _______________________ in kinetic energy 12. Describe the law of conservation of energy 13. Compare convection, conduction, and radiation 14. Electrical current is a result of the flow of ________________ 15. List at least five electrical conductors and five electrical insulators from your program area. 16. Compare series and parallel circuits 17. Compare the reflection, refraction, and absorption of light 18. Describe the electromagnetic spectrum in terms of wavelength, energy, and type 19. Compare the characteristics of sound through a solid, liquid, and gas 20. Compare the wave nature of light and sound 21. Explain how waves transfer energy without transferring matter 22. Describe the Doppler Effect Physics 1. Explain how an object’s change in motion can be observed and measured 2. All movement must be compared with a _______________________________ 3. Any change in position relative to the frame of reference is called _____________________ 4. Apply Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation to the forces between two objects 5. The rate at which an object changes its position is called ____________________ 6. What are the two parts of velocity 7. Explain how momentum is related to the forces acting on an object 8. Forces that are opposite and equal are _____________ forces