PARTS OF SENTENCE – projector notes
advertisement

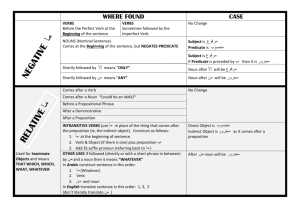
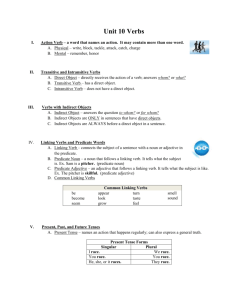
Projector Notes PARTS OF A SENTENCE / ENGLISH 8A Basic English Language Word Order Subject Verb Object SUBJECT ☼ Definition – Who or what the sentence is about; *If you can identify the verb in the sentence, find it, and then ask “who?” or “what?” to find the subject. ☼ Simple vs. Complete Subject - Simple subject is the main noun or pronoun. Complete subject consists of simple subject plus any modifiers or phrases that go with it. ☼ Compound Subject – occurs when multiple subjects share the verb phrase(s) in a sentence ☼ Understood Subject – In imperative sentences (they give commands), the subject is often understood to be the person or persons being addressed. * Written as (you) in grammar exercises ☼ Inverted Word Order – Sometimes the subject can be at the end. *When a sentence starts with the expletive “there” or “here” watch for subjects to be later in the sentence. *Questions can also invert the word order. ☼ The subject can NEVER be the object of a preposition!!! ☼ Be mindful! Questions often invert the word order and cause the verb to be split. PREDICATE /VERB ☼ Definition – Part which says something about the subject; Either the action being completed or the definition or description linked to the subject ☼ Simple vs. Complete Predicate – Simple predicate (known as the verb) is the verb phrase (including auxiliary verbs). Complete predicate consists of the simple predicate plus any modifiers or phrases that go with it. ☼ Compound Verb – occurs when multiple verb phrases are shared by the subject(s) in a sentence OBJECTS ☼ Direct Object – word(s) that names the receiver of the action of a transitive verb *Always a noun or pronoun Example: College students study the subjects of their choosing. ☼ Indirect Object – Used only with a direct object, the indirect object tells to whom or for whom the action of the transitive verb is done *Always a noun or pronoun Example: I gave the teacher my homework. COMPLEMENTS ☼ Object(ive) Complements – Used only with a direct object, word(s) that complete the direct object’s meaning by renaming or describing it *Can be a noun, pronoun or adjective – (usually found with verbs “consider, make, name, give” or their synonyms) Example: Professors often give reading assignments that are lengthy. ☼ Subject(ive) Complements – word(s) that complete the meaning of the subject by renaming or describing it; either a noun (predicate noun) or an adjective (predicate adjective) *Used with linking verbs Example: Last night’s sunset was beautiful. (PA) Kasey was the student body president. (PN) *Direct Objects only found w/ transitive (usually action) verbs. *Subject Complements only found w/ linking verbs (always intransitive). *Objective Complements only found w/ direct objects. *Indirect Objects only found w/ direct objects.