Issues Chart
advertisement

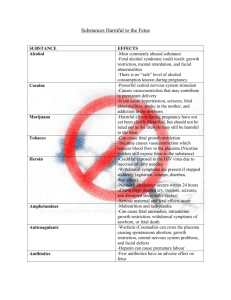
“Issues in Prenatal Development” For each of the 7 general causes of congenital anomalies, fill in the chart with definitions, types, descriptions and facts. Be sure to define the terms in the shaded column headings Genetic Disorders Chromosomal Errors Teratogens: Maternal Diseases – agents Teratogens: Drugs which cause damage to embryo or a fetus Autosomal disorders – disorders caused by recessive genes are PKU (causes developmental delay) baby has difficulty digesting phenylalanine; found in Caucasian babies Sickle-cell disease – African infants – causes red blood cell deformities; can’t carry enough oxygen to tissues; few live to 20 years Tay-Sachs disease – E. Jewish children; Fr. Cdns.; severe intellectually delayed and blind; live to 3 yrs Trisomies – a condition where 3 copies of a specific autosome; Viruses: may pass through the placental filters and attack the embryo or fetus Down Syndrome most common; 3 copies of chromosome 21; 1 in 800 children in Canada; intellectually delayed, distinctive features, plus other health concerns Also Trisomy 13 and 18 – more severe; death by 1 year old Sex-chromosome Anomalies- associated with the sex chromosomes; Huntington’s – causes brain to deteriorate; risk 1 in 10 000; 50% chance if parent has it Sex-linked disorders – caused by recessive genes; colour blindness; hemophelia (blood will not clot); Fragile-X syndrome (developmental delayed – males more often affected Most common is an XXY pattern Called Klinefelter’s syndrome; 1-2 in every 1000 males Intellectually delayed, at puberty experience enlarged penis and breasts Turner’s syndrome is single X patter; anatomically female but show stunted growth and usually sterile Imbalance in cognitive skills 1 in 1000 boys have extra Y chromosome – taller, large teeth, normal puberty and intelligence Rubella or german measles; can be deadly for a fetus; may cause deafness, cateracts, heart anomalies Cytomegalovirus (CMV); herpes group; transmitted thru bodily fluids 10% of infected newborns display serious symptoms (deafness, damage to nervous system, intellectual delay) STD’s – sexually transmitted organisms that can be passed frommotherto fetus HIV: can cross the placenta andenter the fetus’s bloodstream, or infant can contact the virus in the brith canals during labour, or virus can be passed thru breast milk; 3-4 per 10 000 births in Canada Infants become ill within first 2 years; weakens immune systems; children must restrict exposure to viruses and bacteria Others: syphilis, genital herpes, gonorrhea: cause variety of anomalies Prescription drugs: must be careful what you take when pregnant; doctors recommend avoiding drugs Thalidomide in 1960’s – prescribed for morning sickness; caused malformations of the limbs Drugs for anxiety and depression have been associated with increase risks of preterm delivery, low birth weight, low Apgar score Tobacco – smoker mothers are on average give birth to babies of lower birth weight; also higher rates of miscarriage, stillborn, premature babies, neonatal death; even second-hand smoke provides risks to baby Alcohol – can adversely affect an ovum prior to ovulation; mothers who drink heavily are at significant risk to delivering FAS baby; smaller brains, hear anomalies, hearing losses, faces with distinctive features, smallish looking, wide-set eyes; often have learning and behavioral difficulties; SAFEST course is no alcohol at all Psychotropic drugs – heroin, methadone can cause miscarriage; babies addicts; Cocaine, marijuana (mixed results; not implicated as a human teratogen) Teratogens: Others Teratogens: Mutagenic, etc….. Paternal Influences Fetal Assessment & Treatment Diet – some nutrients vital to prenatal development; Mutagenic (agents that cause changes to genomic DNA) Father’s role – at least a portion of unknown causes of malformations are related to paternal factors Diagnostic tests Spina bifida: folic acid deficiency during early stage pregnancy Low birth weight – due to insufficient calorie intake; connected also to development of mental illnesses adulthood Greatest impact of malnutrition is on the nervous system Women should gain 11.5 to 16 kilograms during pregnancy Age – trend in Canada – women having babies in their 30’s; average age is now 29.3 years Most older moms have no complications Low birth weight is potential Congenital anomalies (nervous system, female genetalia anomalies, cleft lip or club foot) But teenage moms can have poor prenatal care, unhealthy diets, smoke, drink or do drugs…can be factors Chronic illnesses – emotional or physical Severe depression can lead to slow fetal growth and premature labour Less likely to feel attached to their fetuses Heart disease, diabetes, lupus, epilepsy can also affect prenatal development Hence: Fetal-maternal Medicine: helps manage pregnancies of women with such conditions listed above Exposure to radiation, chemical toxins can cause mutations that interfere with conception and embryo/fetal development Environmental (agents can damage cells or disrupt or damage cell development) Can cause such things as disruption of neural networks in the brain Epimutagenic (agents that cause abnormal gene silencing or expression without changing DNA) Ex. Infertility, miscarriage, congenital abnormalities Higher percentage of risk with men working in certain occupations (janitors, painters, printers, firefighters, woodworkers) Also agriculture, gardeners, butchers, the arts Exposed to solvents, preservatives, pesticides, hydrocarbons, etc. 2/3rds “unknown” factors Eg. A mother’s diet can produce enduring changes on successive generations - i.e. our diet may impact our grandchildren Sperm – may be toxins in the seminal fluids that can be transmitted during intercourse DNA damage to sperm can contribute to congenital anomalies Also concern over impact of father’s age Evidence links adverse birth outcomes with both teenage fathers and older fathers Physical abuse – abuse of mother during pregnancy Can lead to premature labour Premature breaking away of the placenta Low birth weight 6% of pregnant Canadian women affected 2/3rds perpetrated by husband, boyfriend, or “ex” Preconception and first trimester screening assay the potential for developmental complications Tests can identify chromosomal errors for many disorders o chorionic villus sampling (CVS): Cells are extracted from the placenta amniocentesis – done at 14-16 weeks; needle extracts amniotic fluid ; can diagnose chromosomal and genetic disorders maternal blood, urine, and amniotic fluid can help monitor fetal development Fetoscopy – insertion of a tiny camera into the womb to observe development – can be used for fetal blood transfusions and bone marrow transplants Maternal emotions: anxiety and depression lead to changes in body chemistry May eat less, weakened immune system – can retard fetal growth