Substances Harmful to the Fetus
advertisement

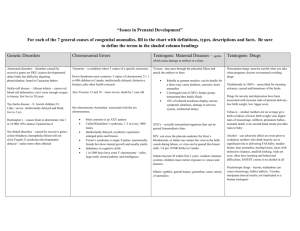
Substances Harmful to the Fetus SUBSTANCE Alcohol Cocaine Marijuana Tobacco Heroin Amphetamines Anticoagulants Antibiotics EFFECTS -Most commonly abused substance -Fetal alcohol syndrome could result: growth restriction, mental retardation, and facial abnormalities -There is no “safe” level of alcohol consumption known during pregnancy -Powerful central nervous system stimulant -Causes vasoconstriction that may contribute to premature delivery -It can cause hypertension, seizures, fetal abnormalities, stroke in the mother, and addiction in the newborn -Harmful effects during pregnancy have not yet been clearly identified, but should not be ruled out as the lifestyle may still be harmful to the fetus -Can cause fetal growth restriction -Nicotine causes vasoconstriction which reduces blood flow to the placenta (Nicotine patches still expose fetus to the substance) -Could be exposed to the HIV virus due to injection of dirty needles -Withdrawal symptoms are present if stopped suddenly (agitation, cramps, diarrhea, rhinorrhea) -Neonatal abstinence occurs within 24 hours of birth (high pitched cry, tremors, seizures, and disrupted sleep-wake cycles) -Serious maternal and fetal effects occur -Malnutrition and tachycardia -Can cause fetal anomalies, intrauterine growth restriction, withdrawal symptoms of newborn, or fetal death -Warfarin (Coumadin) can cross the placenta causing spontaneous abortion, growth restriction, central nervous system problems, and facial defects -Heparin can cause premature labour -Few antibiotics have an adverse effect on fetus Anticonvulsants Isotretinoin (Accutane) and Vitamin A derivatives Diethylstilbestrol Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (captopril, enalapril) Folic acid antagonists (methotrexate, amethopterin) Lithium Radiation -Tetracycline exposure after the 4th month gestation yellowing of teeth and hyperplasia of the enamel -Streptomycin and Kanamycin are associated with damage to the VIII cranial nerve and hearing loss in the newborn -Dilantin can cause craniofacial abnormalities and mental retardation in the fetus -Trimethadione (Tridione) and Paramethadione (Paradione) are contraindicated for use in pregnancy because of high risk anomalies -If taking valproic acid (Depakene) or carbamazepine (Tegretol) should have assessments for skeletal anomalies and neural tube defects -Neonatal withdrawal may occur if taking phenobarbital -Clearly associated with fetal anomalies and are contraindicated for use in pregnancy -Birth control is advised for a minimum of 3 months after isotretinoin therapy -Can cause uterine malformation, vaginal carcinoma, and testicular abnormalities in newborn -Can cause fetal kidney anomalies, growth restriction, and oligohydramnios (decreased amniotic fluid) -Cause spontaneous abortion and serious fetal anomalies -Associated with the development of congenital heart disease -Can be toxic to the thyroid and the kidneys of the fetus -Exposure before 6 weeks of gestation can cause serious fetal damage that includes leukemia, eye, and central nervous system anomalies, and fetal loss -Therapeutic radiation is contraindicated during pregnancy Leifer, G. (2015). Introduction to maternity & pediatric nursing. (7th ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier Saunders.