Ch 7 Cell Review 6.0
advertisement

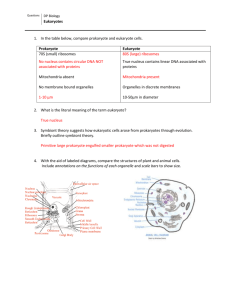
Chapter 7 Cell Review (Section 7.1, 7.2, 7.4) Name: Biology 6.0 Date: Period: Matching terms with their definitions: _____ 1. Cell a. organism whose cells contain a nucleus _____ 2. Cell membrane b. granular material visible within the nucleus _____ 3. Cell wall c. the basic unit of all forms of life _____ 4. Nucleus d. specialized structures within a cell that perform important cell functions _____ 5. Cytoplasm e. organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus _____ 6. Prokaryote f. strong layer around the cell membrane that protects the cell _____ 7. Eukaryote _____ 8. Organelle _____ 9. Chromatin g. uses energy from sunlight to create energy rich food molecules h. large structure that contains the cell’s genetic information _____ 10. Chloroplast i. thin, flexible barrier around the cell; regulates what goes in/out of the cell j. material inside the cell membrane, not including the nucleus Matching organelles with their definitions: _____ 11. Ribosome a. Modifies, sorts and packages proteins and lipids for storages or transport out of the cell _____ 12. Endoplasmic reticulum b. Maintains the cell shape; moves cell parts; helps cells move _____ 13. Golgi apparatus _____ 14. Lysosome c. Saclike structure that stores materials d. Made of microtubules; helps with cell division; only found in animal cells _____ 15. Vacuole e. Converts chemical energy in food to usable compounds _____ 16. Mitochondria _____ 17. Centrioles _____ 18. Cytoskeleton f. Small particle of RNA and protein that produces proteins following instructions from nucleus g. Filled with enzymes used to break down food particles or “clean up” damaged cell parts h. An internal membrane system in which components of the cell membrane (lipids) and proteins are constructed 1 Structural Comparisons Word Part pro karyon eu Meaning before nucleus or kernel true 19. Determine the meaning of prokaryote: 20. Determine the meaning of eukaryote: 21. Identify a structural difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells that is directly related to their difference in size. 22. Describe one similarity between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells that is independent of size. 23. Describe the steps involved in the synthesis, packaging and export of a protein from a cell. (page 200-201) 2 Structure Function Prokaryote Eukaryote Animal Plant Nuclear Envelope Nucleus Cellular Control Center Nuclear Pores Chromatin Nucleolus Cytoplasm Vacuole Organelles that store, Clean-up, and Support Vesicles Lysosomes Cytoskeleton (microtubules I microfilaments) Centrioles 3 Structure Function Prokaryote Eukaryote Animal Plant Ribosomes Organelles that build proteins Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Organelles that capture and release energy Chloroplasts Mitochondria Cell Wall Cellular Boundaries Cell Membrane 4 Multiple Choice 24. Which row in the chart below contains a cell structure paired with its primary function? Row 1 2 3 4 Cell Structure Ribosome Vacuole Nucleus Mitochondria Function Protein synthesis Production of genetic information Carbohydrate synthesis Waste disposal 25. The diagram to the right represents a cell of a green plant. Solar energy is used to produce energy-rich compounds in structure A, B, C or D? 26. Within which structure shown in the diagram below are energy-rich organic compounds used to produce ATP? 27. In the diagram to the right, structure B represents cells, only cells and tissues, only an organ with cells and tissues a complete system with organs, tissues and cells a. b. c. d. 28. The cells of unicellular organisms are Specialized to perform different tasks Larger than those of multicellular organisms Able to carry out all of the functions necessary for life Unable to respond to changes in their environment a. b. c. d. 29. Which list represents the levels of organization in a multicellular organism from the simplest level to the most complex level? a. cell, tissue, organ system, organ c. tissue, organ, organ system, cell b. organ system, organ, tissue, cell d. cell, tissue, organ, organ system 30. Which part of the lipid bilayer faces the watery environment? 31. Which part of the lipid bilayer faces away from the watery environment? 5 Label the following diagrams This is a cell This is an cell This is a cell 6