Eukaryotic Cells: Structure, Function & Comparison Worksheet
advertisement
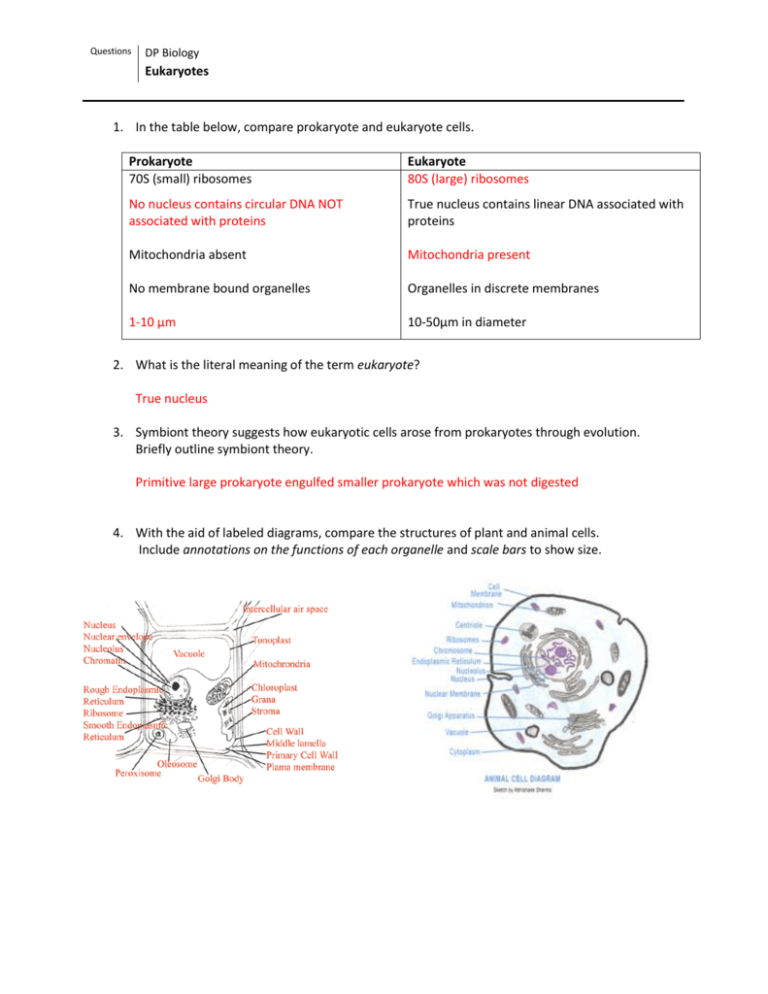
Questions DP Biology Eukaryotes 1. In the table below, compare prokaryote and eukaryote cells. Prokaryote 70S (small) ribosomes Eukaryote 80S (large) ribosomes No nucleus contains circular DNA NOT associated with proteins True nucleus contains linear DNA associated with proteins Mitochondria absent Mitochondria present No membrane bound organelles Organelles in discrete membranes 1-10 µm 10-50µm in diameter 2. What is the literal meaning of the term eukaryote? True nucleus 3. Symbiont theory suggests how eukaryotic cells arose from prokaryotes through evolution. Briefly outline symbiont theory. Primitive large prokaryote engulfed smaller prokaryote which was not digested 4. With the aid of labeled diagrams, compare the structures of plant and animal cells. Include annotations on the functions of each organelle and scale bars to show size. Questions DP Biology Eukaryotes 5. Complete the table below to describe various eukaryotic organelles. Organelle Nucleus Structure (description) Region of the cell containing chromosomes, surrounded by a double membrane, in which there are pores. Function of organelle Storage and protection of genetic information on chromosomes. Ribosome Small spherical subunit consisting of two subunits, some attached to membranes, others free. Protein synthesis Lysosome Spherical organelles surrounded by a single membrane, containing hydrolytic enzymes. Digestion of structures ad molecules that are not needed in the cell. Mitochondrion Organelles surrounded by two membranes, the inner of which is folded inwards. Cellular respiration Chloroplast Double-membrane containing layers of membranes (thylakoid stacks) and the pigment chlorophyll. Photosynthesis Rough Endoplasmic reticulum Large, folding membrane structure found close to the nucleus, with ribosomes attached to some surfaces. Ribosomes attached to surface make proteins, which are then transported around the cell in the flattened sacs Golgi apparatus Large, folded membrane structure found close to the plasma membrane, often with vesicles budding off the outer edge. Collection, packaging and distribution of substances within the cell Draw it Questions DP Biology Eukaryotes 6. The image below shows a TEM micrograph of a liver cell. a. Identify the labeled structures. b. Calculate the magnification of the image. Image (scale bar) Actual 24mm 1 24000 µm 1 µm X 24,000 c. Calculate the maximum diameter of the nucleus. 78 mm at widest point 3.25 X 1 µm = 3.25µm 78/24 = 3.25 7. State three differences between plant and animal cells. Plant Cell wall Permanent vacuole Chloroplasts Animal No cell wall Temporary vesicle No chloroplasts Questions DP Biology Eukaryotes No centrioles Centrioles 8. Extracellular components are materials or structures which extend beyond the plasma membrane. Outline the role of an extracellular component in a plant cell and an animal cell. Plant: Cellulose: provides support to the plant. Animal: Collagen: Allows cells to be anchored in place 9. In the space below, draw and label three specialized cells (two animal, one plant), outlining the relationship between structure and function in each case.