Leptin and Satiety
advertisement

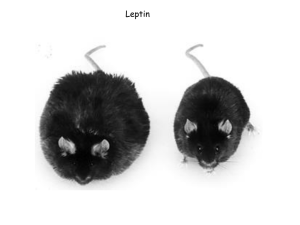
Leptin Exhibits Pluripotent Effects on Appetite and Metabolism. Research documents Leptin’s critical role in mediating Appetite, Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome Attributes In a Nutshell References Hunger Urges & Cravings The arcuate nucleus (ARC) is a key hypothalamic area for mediating leptin’s inhibition of food intake. In the ARC are neurons that both stimulate appetite – through two hormones: neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP), and inhibit appetite – through proopiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons that activate the appetite suppressing pathway which includes the satiety hormone α-MSH (alpha melanocyte-stimulating hormone). The ventral tegmental area (VTA) contains dopamine neurons that are important in modulating motivated behavior, addiction and reward. VTA dopamine neurons express leptin receptors, thus respond to leptin with activation of an intracellular JAK-STAT pathway and a reduction in firing rate causing decreased food intake. In the hippocampus leptin is shown to directly affect the appetite reward pathway – an example being a reduction in sugar cravings. (1) Leptin has potent effects on lipid metabolism and acutely increases glucose metabolism. (2) Research shows that leptin increases the activation state of key lipogenic enzymes, such as (1) fatty acid synthase, (2) ATP citrate lyase, and (3) hormone sensitive lipase (HSL) via the phosphorylation of the serine residues 563 and 660. Myers MG, Leibel RL, et al. Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010 (Nov); 21(11):643-651. Appetite Desires & Reward Motivation Increase in Thermogenesis Visceral Fat Oxidation Leptin increases the activation state of key lipogenic enzymes, such as: fatty acid synthase, ATP citrate lyase, and hormone sensitive lipase (HSL) via the phosphorylation of the serine residues 563 and 660. Nicotine, Leptin & Metabolism Dysfunctional Hormonal Signaling Nicotinic drugs decrease food intake primarily through activation of POMC neurons and melanocortin pathways. Insulin Resistance (1) Leptin has potent effects on lipid metabolism and acutely increases glucose metabolism. Thus it is also a strong indicator of insulin levels. (2) Leptin decreased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in studies on islets and β-cells. Leptin improves insulin sensitivity, and decreases insulin secretion by potentiating hypothalamic leptin and insulin signaling by stimulating IRS2 phosphorylation. Leptin Resistance and the Yo-Yo Effect of Dieting (1) Once the body becomes overweight or obese there is impeded transport of serum leptin across the blood brain barrier, creating dysfunctional signaling in areas of the brain expressing leptin mRNA. It is thought some neural systems that modulate energy balance may become ‘reset’ to a new and elevated level which would ‘defend’ the higher level of adiposity or body fat. (1) Leptin influences the number of both inhibitory and stimulatory synaptic inputs onto neurons (axonal projections and neurite outgrowth) within the arcuate nucleus – which is the ‘feeding center’ of the brain. Obesity creates leptin resistance which impairs leptin-mediated hippocampal synaptic transmission, thus affecting appetite reward pathways. Impaired Hippocampal Synaptic Transmission The appetite-stimulating hormone NPY has an inhibitory action within the hypothalamus, where it is released by specific neurons to suppress GH release. This is done by stimulation of somatostatin release by alpha 1 and beta-adrenergic receptor-mediated mechanisms. Hommel JD, Trinko R, Leptin receptor signaling in midbrain dopamine neurons regulates feeding. Neuron. 2006 (Sep);51(6):801-810. (1) Kamohara S, Burcelin R, et al. Acute stimulation of glucose metabolism in mice by leptin treatment. Nature. 1997;389:374-377. (2) Buettner C, Muse ED, Cheng A. et al. Leptin controls adipose tissue lipogenesis via central, STAT3independent mechanisms. Nat Med. 2008; 14(6):667-675. Buettner C, Muse ED, Cheng A. et al. Leptin controls adipose tissue lipogenesis via central, STAT3independent mechanisms. Nat Med. 2008; 14(6):667-675. Nicotine decrease food intake through activation of POMC neurons. Science. 2011 (Jun);332(6035):1330.1332. Rettori V, Milenkovic L, Aguila MC, McCann SM. Physiologically significant effect of neuropeptide Y to suppress growth hormone release by stimulating somatostatin discharge. Endocrinology. 1990 May;126(5) 2296-2301 (1) Kamohara S, Burcelin R, et al. Acute stimulation of glucose metabolism in mice by leptin treatment. Nature. 1997;389:374-377. (2) Park SM, Hong SM, et al. Long-term effects of central leptin and resistin on body weight, insulin resistance, and βcell function and mass by modulation of hypothalamic leptin and insulin signaling. Endocrinology. 2008;149(2):445-454. (1) Myers Jr MG, Leibel RL, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW. Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Nov; 21(11): 643-651. (1) Morrison CD, Leptin signaling in brain: a link between nutrition and cognition? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 May;1972(5):401-408. Leptica’s Homeopathic Leptin complements every weight management program safely & effectively. Visit www.LepticaResearch.com for more information.