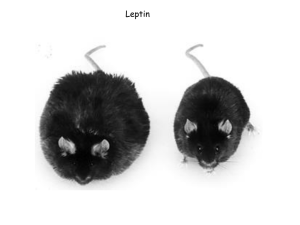
Diverse applications for Leptin
advertisement

Applications In Brief References Alzheimer’s Leptin benefits the functional characteristics and viability of neurons that degenerate in AD. Leptin protects cortical neurons from AB(1-42) and promotes tau clearance. (1) Leptin receptors have been detected on human platelets. Leptin at high serum (blood) concentrations corresponding to those of obese individuals was found to act synergistically with ADP to promote platelet aggregation – a component of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Leptin appears to activate multiple cell signaling pathways within the cell. Thus, activities such as: (1) protection against oxidative stress, (2) loss of dopamine neurons, and (3) cognitive (behavior, learning, memory) function are all influenced by leptin. (1) In laboratory research with rodents, leptin has been reported to normalize blood sugar and inhibit insulin secretion when added to the culture of isolated pancreatic islet cells. Leptin has been shown to inhibit the insulin-stimulated synthesis of fatty acids and total lipids. (1) Leptin protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by epilepsy. Doherty GH et al. Leptin prevents hippocampal synaptic disruption and neuronal cell death induced by amyloid B. Neurobiol. Aging. 2013(Jan);34(1):226-237. (1) Nakata M, Yada T, Soejima N, Maruyama I. Leptin promotes aggregation of human platelets via the long form of its receptor. Diabetes. 1999 Feb;48:426-429. Atherosclerosis Cognitive Impairment Diabetes Mellitus I & II Epilepsy Arteriogenic Erectile Dysfunction Pluripotent Hormonal Influences Hypertension A-ED is caused by an impaired ability of blood vessels to open and allow a normal blood flow; obesity is a major contributing factor. Excess serum leptin might be related to plaque build-up in blood vessels, thereby restricting flow. Leptin plays a significant permissive role in the physiological regulation of several neuroendocrine axes, including the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal, thyroid, growth hormone, and adrenal axes. (1) One of the peripheral functions of leptin includes the regulation of blood pressure via endothelial cells. (2) Leptin infusion was shown to reduce blood pressure and heart rate, and to stimulate NO in the cardiovascular system. Infertility Leptin may be of importance in obesity-associated dysfunction of the reproduction system. It is possible that leptin acts on the reproductive system both at the hypothalamic-pituitary level (GnRH-FSH/LH) and directly on the ovary. Insomnia Short sleep duration has been found to be related to metabolic disorders such as obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance, which are all influenced by leptin. (1) Leptin improves insulin sensitivity, and decreases insulin secretion by potentiating hypothalamic leptin and insulin signaling by stimulating IRS2 phosphorylation. This sets up a stimulating/inhibiting feedback loop between leptin and insulin. Data from research studies support the hypothesis that leptin may exert direct action on insulin resistance, insulin secretion, insulin hepatic extraction, and insulin delivery. Leptin influences all aspect of MS: (1) visceral adipose tissue – central obesity, (2) hyperlipidemia – raised triglyceride levels, (3) insulin resistance – raised fasting glucose levels, (4) hypertension. (5) reduced HDL cholesterol, and (6) increased blood pressure. Adipocytes and osteoblasts are derived from a common multipotential mesenchymal stem cells. Excess obesity-associated leptin may increase adipocyte differentiation and fat accumulation while decrease osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. (1) Leptin can reverse dopaminergic cell loss and functional behaviors via the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Insulin Resistance Metabolic Syndrome Osteoporosis Parkinson’s Premature Puberty Leptin serves as the adipose-brain signal for the onset of sexual maturation. Leptin influences FSH and IGF-1 stimulated progesterone production. Visit www.LepticaResearch.com for more information. Morrison CD, Leptin signaling in brain: a link between nutrition and cognition? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 May;1972(5):401-408. (1) Emilsson V, Liu YI et al.Expression of the functional leptin receptor mRNA in pancreatic islets and direct inhibitory action of leptin on insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1997;46:313-316. (1) Diano S, Horvath TL, Anticonvulsant effects of leptin in epilepsy. J Clin. Invest. 2008;118:2628. Dozio E, et.al, Adipokines, hormonal parameters and cardiovascular risk factors: similarities and differences between patients with erectile dysfunction of arteriogenic and nonarteriogenic origin. J Sex Med. 2012(Sep);9(9):2370-2377. Khan, SM, Hamnvik OR, et al. Leptin as a modulator of neuroendocrine function in humans. Yonsei Medical Journal, 2012 (Jul);53(4):671-679. (1) Lembo G, Vecchione C, Leptin induces direct vasodilation through distinct endothelial mechanisms. Diabetes. 2000;49:293-297. (2) Fruhbeck G, Pivotal role of nitric oxide in the control of blood pressure after leptin administration. Diabetes. 1999;48:903-908. Zachow RJ, Magoffin DA. Direct intraovarian effects of leptin: impairment of the synergistic action of insulin-like growth factor-1 on follicle stimulating hormone-dependent estradiol-17B production by rat ovarian granulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1997;138:847-850. Reynolds AC, Dorrian J, et al. Impact of five nights of sleep restriction on glucose metabolism, leptin and testosterone in young adult men. PLos One, 2012(Jul);7(7):1-10. (1) Park SM, Hong SM, Sung SR, Jung HK. Long-term effects of central leptin and resistin on body weight, insulin resistance, and β-cell function and mass by the modulation of hypothalamic leptin and insulin signaling. Endocrinology. 2008;149(2):445-454. Bae YJ, Kim SH, et.al., Evaluation of adiposityrelated biomarkers as metabolic syndrome indicators. Clin Nutri Res. 2013;2:91-99. Cao JJ, Effects of obesity on bone metabolism. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011 (Jun); 6(30): (1) Weng ZF, Signore AP et.al, Leptin protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic cell death via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J of Biol Chem. 2007 (Nov); 282 (47): 34479-34491. Mantzoros CS, et al. A longitudinal assessment of hormonal and physical alterations during normal puberty in boys. Rising leptin levels may signal the onset of puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:1266-1070.