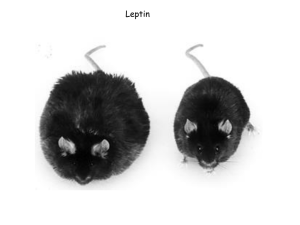
TESTING A LEPTIN PRODUCT
AS A NOVEL THERAPY FOR
ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
J. Wesson Ashford, M.D., Ph.D. (1)
Mark A. Smith, Ph.D. (2),
G. Casadesus, Ph.D. (2),
S.J. Greco, Ph.D. (3),
J.M. Johnston, Ph.D. (3),
N. Tezapsidis, Ph.D. (3)
(1) Stanford /VA Aging Clinical Research Center, VAPA-HCA,
Palo Alto, CA USA
(2) Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, USA
(3) Neurotez, inc., Bridgewater, NJ, USA
Disclosures
Drs. Ashford and Tezapsidis are coprincipal investigators on an NIHfunded SBIR to study the effects of
Leptin in Alzheimer patients
OVERVIEW
Numerous factors (particularly age and APOE) are
known to moderate the course of Alzheimer’s disease
(AD), but the pathophysiology of AD causation is
unknown.
Serum Leptin levels appear to protect against
cognitive decline in the elderly, and patients with AD
have lower Leptin levels.
Leptin injections in AD-transgenic mice protect
against both the development of amyloid and tau
pathology and reverse the cognitive impairments
found in these animals.
Therefore, Leptin may be a preventive therapy for AD
ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE COURSE
Estimate MMSE as a function of time
MMSE score
30
25
20
15
10
There is a prolonged period
during which loss of cognitive
function occurs.
5
0
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
Estimated years into illness
AAMI / MCI/ early AD -- DEMENTIA
Ashford et al., 1995
Ashford et al., 1998
J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.57:972
Serum Leptin levels and cognition in the elderly
AD
20
Severe
Moderate
MiId
10
Normal
Patients with AD have
lower serum leptin levels
compared to controls,
independent of BMI
(Power et al., 2001)
Data: Satoris, Inc.
Leptin (ng/ml)
In elderly, higher serum
leptin appears to protect
against cognitive decline
(5 yr prospective study,
2,871 elders, Holden et
al., 2009)
6
In vitro:
Leptin inhibits Ab production and stimulates Ab uptake
7
Fewlass et al., 2004
extra cellular
APP is a transmembrane
protein. It is first cleaved
by one of two enzymes.
intracellular
Lipid raft
(BACE)
Fewlas et al., 2004
Leptin receptors can
activate JAK/STAT3,
stimulate lipolysis,
modulatng lipid raft
composition,
decreasing BACE
activity
In vitro
Leptin is 270x more potent than Insulin
in down-regulating tau phosphorylation
Leptin, 4h
IC50=46.9nM
Greco et al., (2008) BBRC
Insulin, 4h
IC50=13mM
9
Animal studies
Chronic s.c. Leptin in Tg2576 reduces brain Ab
Fewlass et al (2004) FASEB J
10
Animal studies
Leptin reduces
hippocampal Amyloid
burden in TgCRND8 mouse
Leptin reduces
phospho-tau in
brain of
TgCRND8 mouse
11
Animal behavior studies
12
Animal behavior studies
Fear conditioning after 8 weeks leptin
Greco et al., Manuscript submitted
13
Summary of preclinical data
High density of Leptin receptors in the hippocampus
Leptin inhibits Ab production in neurons
Leptin promotes ApoE-dependent Ab neuronal uptake
Leptin inhibits tau phosphorylation
Leptin (chronic application) reduces brain amyloid load in
AD transgenic mice
Leptin (acute and chronic application) improves memory
in aged AD transgenic mice.
The clinical and preclinical data provide compelling
evidence to support a clinical trial of Leptin for AD
14
Alzheimer’s Disease:
Course, Pathology, Biomarkers
Clinical
State
Neuro
pathology
CSF
Biomarkers
Normal
PreSymptomatic
AD
None
Amyloid
Plaques,
No Tangles
Normal tau
Normal Ab
tau?
Ab?
Mild
Cognitive
Impairment
AD
Amyloid
Amyloid
Plaques
Plaques
Few Tangles Many Tangles
High tau
Low Ab
Disease Progression
High tau
Low Ab
Biomarkers for More Valid
Alzheimer Diagnosis and
Precise Measurement of Severity
Lancet Neurol 2007; 6: 734–46
Potential AD Biomarkers
Blood, urine Aβ40? Aβ42? Neuritic threads?
Most studies suggest not helpful
Protein levels in blood – Proteomics, Leptin.
Lower Leptin predicts MCI progression to dementia
CSF: Aβ40? Aβ42? Others Aβ species?
Possibly highly predictive
CSF: tau, p-tau
Assess active disease progression.
Neuroimaging
Structural (volumetric assessments)
Functional (FDG-PET, SPECT)
Specific protein imaging (PET)
CSF in Alzheimer’s Disease,
both MCI and Dementia patients:
Low Aβ and High Tau
AD Patients
Control Patients
Concentration (pg/mL)
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
Aβ
Sunderland T, et al. JAMA. 2003;289:2094-2103.
Tau
CSF of subjects with
MCI progressing to
AD has elevated tau,
decreased β-amyloid
The relative risk of progression to
AD substantially increased in
patients with MCI who had
pathological concentrations of Ttau and A42 at baseline (hazard
ratio 17·7, p0·0001).
The association between
pathological CSF and progression
to Alzheimer’s disease was much
stronger than, and independent of,
established risk factors including
age, sex, education, APOE
genotype, and plasma
homocysteine.
Hansson et al., Lancet Neurology 2006
ADNI Data – CSF ABeta, total tau
220
Abeta(1-42)
200
180
33
160
34
44
140
120
100
Normal
MCI
Mild AD
140
130
Tau (total)
120
110
33
100
34
90
44
80
70
60
Normal
MCI
Mild AD
Power Calculations for Reduction in Rate of
Decline in AD for an Experimental Treatment
Number needed per arm for 50% effect size
(50% reduction over 1 yr in the rate of cognitive decline )
ADAS-Cog
MMSE
hippocampal volume
temporal horn volume
320 cases
241 cases
21 cases
54 cases
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CSF-tau – if level returns to normal in 12 weeks,
- then only 6 cases (3+3) needed for statistics!!
- plan 15 in each arm due to drop-outs, etc.
Neurology 2003;60:253-260
Numerous Leptin trials have been
performed for several indications
- no safety issues AMGEN: obesity as a monotherapy, congenital obesity
ROCHE: obesity as a monotherapy
Amylin: obesity as a combination therapy with Symlin
(amylin)
Harvard U., Rockefeller U., Columbia U., NIH: obesity,
hypothalamic amenorrhoea, lipodystrophies (i.e.
aggressive anti-HIV therapies)
22
Clinical Trials: Design
1
2
A focused clinical trial, in a group of 45 earlystage AD (MCI range to very mild dementia)
individuals pre-screened for low leptin, elevated
CSF-tau, low CSF-Ab42, with APOE e4 genotype
and MRI enrolled for a 12 week treatment period
(15 on 5mg/d; 15 on 10 mg/d; 15 on placebo)
with decreased CSF-tau as the primary outcome
measure and cognitive function as a secondary
outcome measure.
Leading to a larger, multicenter, double-blind,
placebo controlled trial, for 1 year (number of
patients to be determined by pilot data).
23
Summary Clinical Plan for Trial
for Leptin Treatment in AD
Recruitment
Use of audience screening, genetic testing
Genetics
45 APOE e4 patients
Baseline diagnosis
Baseline measures
Elevated CSF tau, decreased Ab
Drug administration
Amnesic MCI or mild dementia with AD
3 groups - daily injections, placebo, 5, 10 mg SC
Outcome measures
Primary - CSF tau
Secondary – cognitive measures, other CSF/plasma measures
Slides available at:
www.medafile.com/leptin