File 2. kud rocks and minerals1
advertisement
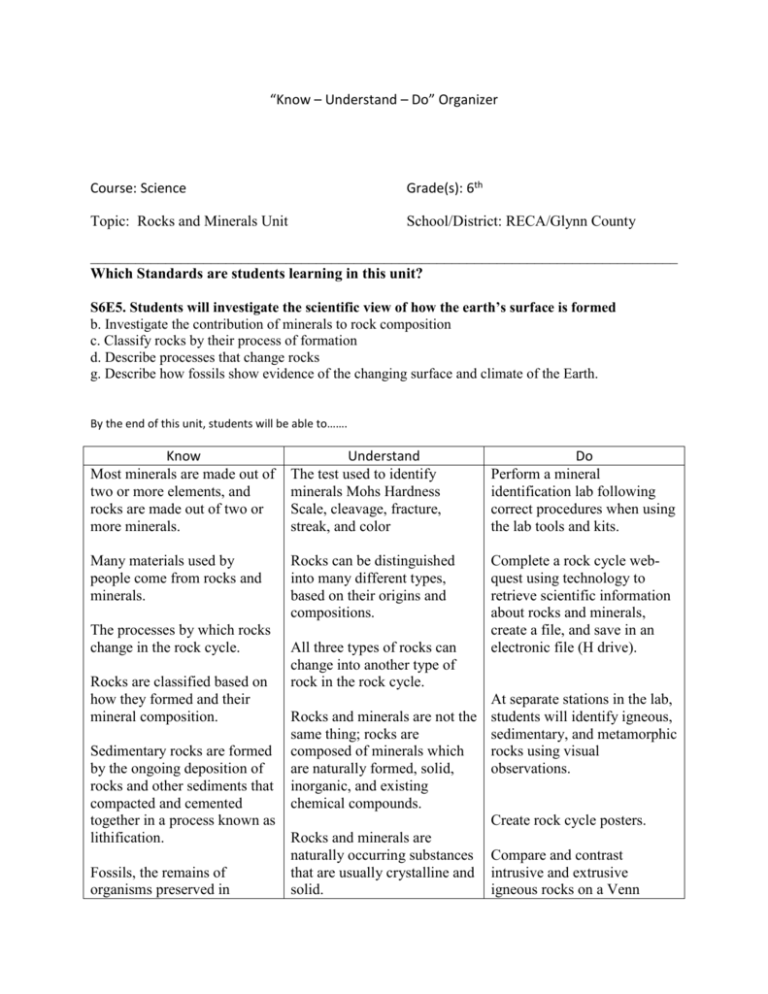
“Know – Understand – Do” Organizer Course: Science Grade(s): 6th Topic: Rocks and Minerals Unit School/District: RECA/Glynn County ______________________________________________________________________________ Which Standards are students learning in this unit? S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition c. Classify rocks by their process of formation d. Describe processes that change rocks g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface and climate of the Earth. By the end of this unit, students will be able to……. Know Most minerals are made out of two or more elements, and rocks are made out of two or more minerals. Understand The test used to identify minerals Mohs Hardness Scale, cleavage, fracture, streak, and color Do Perform a mineral identification lab following correct procedures when using the lab tools and kits. Many materials used by people come from rocks and minerals. Rocks can be distinguished into many different types, based on their origins and compositions. Complete a rock cycle webquest using technology to retrieve scientific information about rocks and minerals, create a file, and save in an electronic file (H drive). The processes by which rocks change in the rock cycle. Rocks are classified based on how they formed and their mineral composition. Sedimentary rocks are formed by the ongoing deposition of rocks and other sediments that compacted and cemented together in a process known as lithification. Fossils, the remains of organisms preserved in All three types of rocks can change into another type of rock in the rock cycle. Rocks and minerals are not the same thing; rocks are composed of minerals which are naturally formed, solid, inorganic, and existing chemical compounds. At separate stations in the lab, students will identify igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks using visual observations. Create rock cycle posters. Rocks and minerals are naturally occurring substances that are usually crystalline and solid. Compare and contrast intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks on a Venn sedimentary rocks, are part of the evidence scientists use to infer changing conditions at the Earth’s surface. Through time, rocks at the Earth’s surface weather, forming sediments that are buried, then compacted, heated, and often recrystallized into new rock. The remains and evidence of plants and animals that once lived on Earth are called fossils. The Law of Superposition Paleontologists are scientists who studies fossils. Fossil evidence is used for the theory of plate tectonics. . Diagram. Almost every product we use in daily life contains minerals that have to be mined. Make direct measurements of mass and volume to determine the density of rocks in the lab. Rocks can be distinguished into many different types, based on their origins and compositions. Draw a visual representation on the types of rocks that contain fossils. Explain why this is so. Fossils are generally most abundant in marine sedimentary rocks. Fossils generally are not found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Fossils are the preserved remains of past life on Earth. Fossils are found in rocks deposited in the environment in which they lived. Fossil preservation depends on properties of organic matter and environment of deposition. Fossils may be used to interpret earth history of plate movement, past environmental conditions, and history of life on earth. Use a visual representation to predict the climate when the fossil organism was alive and the environmental conditions that existed. .








