Possible specimens to learn!!!
advertisement
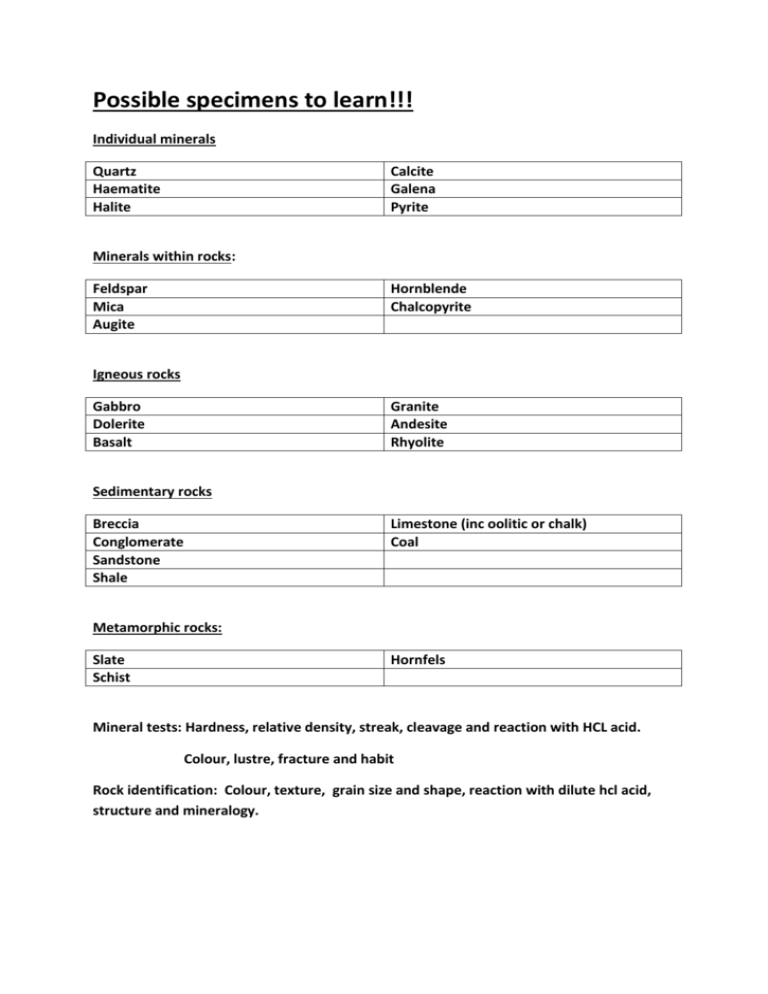
Possible specimens to learn!!! Individual minerals Quartz Haematite Halite Calcite Galena Pyrite Minerals within rocks: Feldspar Mica Augite Hornblende Chalcopyrite Igneous rocks Gabbro Dolerite Basalt Granite Andesite Rhyolite Sedimentary rocks Breccia Conglomerate Sandstone Shale Limestone (inc oolitic or chalk) Coal Metamorphic rocks: Slate Schist Hornfels Mineral tests: Hardness, relative density, streak, cleavage and reaction with HCL acid. Colour, lustre, fracture and habit Rock identification: Colour, texture, grain size and shape, reaction with dilute hcl acid, structure and mineralogy. Fossils: Ammonoids Bivalves Corals Brachiopods Trilobites Dinosaurs Graptolites Plants Formanifera Identification of preservation: Hardly altered hard parts (bones and teeth) Carbonisation of organic material (Graptolites and plants) Replacement of mineral matter (Pyrite) Moulds and casts (bivalves) Trace Fossils (Tracks, trails and burrows) Mapwork: a) Principles of historical geology: The principle of uniformitarianism (the present is the key to the past) The concepts of original horizontality, continuity and superposition of strata. The relative dating of rocks: Fossil content Included fragments Cross-cutting structures Unconformities Folding, faulting and metamorphism. Decay of radioactive materials provides a method for calculating the absolute age of rocks. (parent – daughter ratio, unstable parent, stable daughter) The difference between relative and absolute dating. b) Geological mapwork: A geological map and a cross-section Recognise and describe: Horizontal beds, Dipping beds, strike and dip, Folds (symmetrical, asymmetrical, non-plunging anticlines and synclines, axial plane trace) Faults (normal, reverse, thrust, wrench or tear, throw) Intrusive and extrusive features (dyke, sill, batholiths, lava flow) Metamorphic aureole Mineral veins, Superficial deposits (river, glacial till) Unconformity with angular discordance, formation and significance for dating earth movements. DEPOSITION, (Possible folding and faulting) UPLIFT AND EROSION.











